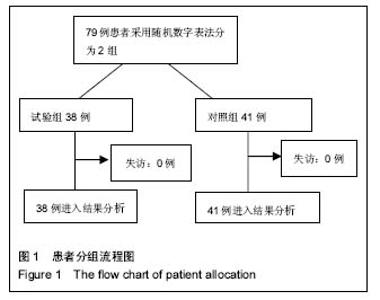
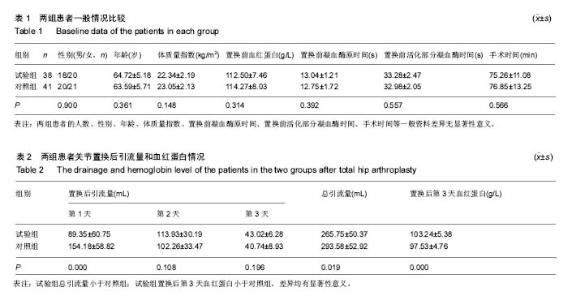
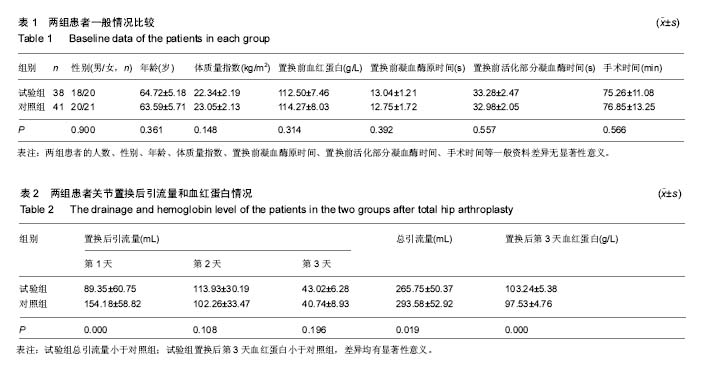
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Drainage at different time points after tranexamic acid administration in total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective study
Hao Shen-shen, Liu Yan-xiong, Liu Zhi-bin
- Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Online:2017-08-18Published:2017-09-01 -
Contact:Liu Yan-xiong, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Hao Shen-shen, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Technologies Research & Development Program of Shaanxi Province, No. 2015SF115; the Technology Huimin Program of Yan’an, Shaanxi Province, No. 2016HM-10-03
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hao Shen-shen, Liu Yan-xiong, Liu Zhi-bin. Drainage at different time points after tranexamic acid administration in total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective study[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.23.004.
share this article
| [1] Lanting B A, Macdonald S J. The painful total hip replacement: diagnosis and deliverance.Bone Joint J.2013; 95-B(11 Suppl A):70-73.[2] Schräder P, Boy O, Schleiz W, et al. Determining the indication for primary total hip and knee replacement. Results of external quality assurance of over 270,000 primary total hip and knee replacements. Orthopade. 2008; 37(10):1016-1026.[3] ClavÉ A, Fazilleau F, Dumser D, et al. Efficacy of tranexamic acid on blood loss after primary cementless total hip replacement with rivaroxaban thromboprophylaxis: A case-control study in 70 patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012, 98(5):484-490.[4] 王慧东,郭明,刘福达. 初次全髋关节置换术后关节腔注射氨甲环酸对出血量及安全性的评估[J]. 临床医药实践, 2016, (12): 902-905.[5] Mednick RE, Alvi HM,Krishnan V,et al. Factors Affecting Readmission Rates Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2014;96(14):1201-1209. [6] Alshryda S,Mason J,Sarda P,et al.Topical (Intra-Articular) Tranexamic Acid Reduces Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates Following Total Hip Replacement A Randomized Controlled Trial (TRANX-H). J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95:1969. [7] Moskal JT, Capps SG. Meta-analysis of Intravenous Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. Orthopedics.2016;39:e883-892. [8] Bierbaum B E, Callaghan J J, Galante J O, et al. An analysis of blood management in patients having a total hip or knee arthroplasty[J]. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery American Volume.1999; 81(1):2-10.[9] Hiippala ST, Strid LJ, Wennerstrand MI, et al. Tranexamic acid radically decreases blood loss and transfusions associated with total knee arthroplasty. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 1997; 84(4):839-844.[10] 袁刚, 陈波涛. 氨甲环酸在脊柱手术中的应用进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015, 25(7):653-655.[11] Dowd NP, Karski JM, Cheng DC, et al. Pharmacokinetics of tranexamic acid during cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesthesiology. 2002;97(2): 390-399.[12] 马金辉,孙伟,高福强,等. 氨甲环酸在人工关节外科领域的应用[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2014,29(11):847-851.[13] 高景,杨永斌,马宏伟,等.氨甲环酸对脊柱结核手术出血量和炎症反应的影响[J].现代医学,2014,42( 8):847-849.[14] Chen S, Wu K, Kong G, et al. The efficacy of topical tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders.2016;17(1):1-7.[15] Li J,Zhang Z,Chen J.Comparison of efficacy and safety of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis.Medicine. 2016;95(36): e4689.[16] Murphy M,Stanworth S,Yazer M.Transfusion practice and safety: current status and possibilities for improvement. Vox Sang.2011;100:46-59. [17] Hemlata SS,Verma A.Adverse events related to blood transfusion. Indian J Anaesth.2014;58(5):543-551.[18] Kotze A, Carter L, Scally A. Effect of a patient blood management programme on preoperative anaemia , transfusion rate, and outcome after primary hip or knee arthroplasty: a quality improvement cycle. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108:943–952. [19] Marulanda GA, Ulrich SD, Seyler TM, et al. Reductions in blood loss with a bipolar sealer in total hip arthroplasty. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2008;5(2):125-131. [20] Atay EF, Güven M, Alt?nta? F, et al. Allogeneic blood transfusion decreases with postoperative autotransfusion in hip and knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010; 44(4):306-312. [21] MoonenAF, Thomassen BJ, KnoorsNT, et al. Pre-operative injections of epoetin-alpha versus post operative retransfusion of autologousshed blood in total hip and knee replacement: a prospective randomised clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(8):1079-1083. [22] Chen LL, Wang WC, Mao XZ, et al. Evaluation and treatment of hemorrhage after hip and knee arthroplasty in the aged. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007;32(2): 316-319. [23] Blanié A, Bellamy L, Rhayem Y, et al. Duration of postoperative fibrinolysis after total hip or knee replacement: a laboratory follow-up study.Thromb Res. 2013;131(1):e6-e11.[24] 赵艳丽. 全髋置换术后引流患者100例的临床观察及护理体会[J]. 临床合理用药杂志, 2016, 9(7):128-129.[25] Ekbäck G,Axelsson K,Ryttberg L, et al.Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in total hip replacement surgery. Anesth Analg. 2000;91(5):1124-1130.[26] Lemaire R. Strategies for blood management in orthopaedicand trauma surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2008;90(9): 1128-1136.[27] Hanna SA, Prasad A, Lee J,et al.Topical Versus Intravenous Administration of Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2016; 8(3):6792. [28] Yamasaki S, Masuhara K, Fuji T.Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss after cementless total hip arthroplasty-prospective randomized study in 40 cases.Int Orthop.2004;28(2):69-73.[29] Rajesparan K, Biant L C, Ahmad M, et al. The effect of an intravenous bolus of tranexamic acid on blood loss in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(6):776-783.[30] Lozano M,Basora M,Peidro L,et al.Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid administration during total knee arthroplasty. Vox Sang.2008;95(1):39-44. [31] 王本海,林松庆,陈金水. 单侧全髋关节置换术术后局部应用氨甲环酸与引流管夹闭2h的止血效果分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(5):554-555.[32] Wei Z,Liu M.The effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in to-tal hip or knee arthroplasty:a meta -analysis of 2720 cases.Transfus Med.2015;25(3):151-162.[33] Ishida K, Tsumura N, Kitagawa A, et al. Intra -articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2011;35(11):1639-1645. [34] Poeran J, Rasul R, Suzuki S, et al.Tranexamic acid useand postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing totalhip or knee arthroplasty in the United States: retrospec-tive analysis of effectiveness and safety. BMJ.2014;12( 349) : g4829.[35] 朱灿,储小兵,章建华. 氨甲环酸3种不同应用方法对全髋关节置换术失血量的影响[J]. 江西中医药大学学报, 2016, 28(1): 47-49+92.[36] REDONH,JOST,TROQUES. [Closure under reduced atmospheric pressure of extensive wounds].Mém Acad Chir(Paris).1954;80(12-14):394-396.[37] Kim YH, Cho SH, Kim RS. Drainage versus nondrainage in simultaneous bilateral total hip arthroplasties.J Anhroplaty.1998;13(2):156-161. [38] Ridgeway S, Wilson J, Charlet A, et al. Infection of the surgical site after arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol.2005; 87(6):844-850.[39] March GM, Elfatori S, Beaulé PE. Clinical experience with tranexamic acid during primary total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2013;23(1):72-79.[40] Wei W, Wei BF. Comparison of topical and intravenous tranexamic acid on blood loss and transfusion rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthrop. 2014;29(11):2113-2116. [41] 谢锦伟,蔡迎春,马俊,等. 抗纤溶序贯抗凝平衡预防初次THA术后VTE的单中心大样本连续病例观察性研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(3):230-235.[42] 尹勇,马广文,黄斐,等. 氨甲环酸减少全髋关节置换失血量的 Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(17):2752 -2757.[43] O'Brien JG, Battistini B, Zaharia F, et al. Effects of tranexamic acid and aprotinin, two antifibrinolytic drugs, on PAF-induced plasma extravasation in unanesthetized rats. Inflammation. 2000;24(5):411-429.[44] 李大坤,高忠,邢刚,等. 局部应用与静脉注射氨甲环酸减少全髋关节置换术术后失血量有效性与安全性的研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016,31(8):843-844. [45] 刘丙根,庞清江. 氨甲环酸用于全髋关节置换有效性与安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(35):5699-5706.[46] 谢锦伟,姚欢,岳辰,等. 初次髋、膝关节置换术后纤溶变化[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016, 24(10):931-936.[47] 赵清斌,任姜栋,张晓岗,等. 氨甲环酸静脉或局部及联合应用初次单侧全髋关节置换:围置换期出血及输血率的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(4):459-464.[48] Li J,Li H, Zhao H, et al. Combined use of intravenous and topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12:22. [49] Wong J, Abrishami A, El B H, et al.Topical application of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(15):2503-2513.[50] Kazemi SM, Mosaffa F, Eajazi A, et al.The effect of tranexamic acid on reducing blood loss in cementless total hip arthroplasty under epidural anesthesia. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(1):17.[51] Stulberg BN, Zadzilka JD.Blood management issues using blood management strategies. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22 (4 Suppl 1):95-98.[52] Yue C, Kang P, Yang P, et al. Topical application of tranexamic Acid in primary total hip arthroplasty: a randomized double-blind controlled trial.J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(12): 2452-2456.[53] Martin JG, Cassatt KB, Kincaid-Cinnamon KA,et al.Topical administration of tranexamic acid in primary total hip and total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(5):889-894. [54] 殷晗,王大伟,马文谱,等. 经引流管逆行注入氨甲环酸降低初次全髋置换术后失血量的有效性及近期安全性评估[J].中华关节外科杂志电子版,2014,8(5):84-87.[55] 袁晓伟,李林. 局部注入氨甲环酸对40例首次单侧全髋关节置换术后失血量的影响[J]. 延边大学医学学报, 2015, 38(2): 135-138.[56] 谢美兆,练伟东,张浩,等. 全髋置换局部应用氨甲环酸后输血及成本效益分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2016,(05):399-402.[57] Yamasaki S, Masuhara K, Fuji T. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss after cementless total hip arthroplasty- prospective randomized study in 40 cases. Int Orthop.2004; 28(2):69-73.[58] 刘志刚,张上上,陈如见,等. 全髋关节置换后的隐性失血[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(13):2305-2312.[59] 李少斐,郭亭,赵建宁,等. 围髋关节置换期隐性失血相关危险因素及预后[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(13):2006-2011. |
| [1] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [2] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [5] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [6] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [7] | Xu Kuishuai, Zhang Liang, Chen Jinli, Ren Zhongkai, Zhao Xia, Li Tianyu, Yu Tengbo. Effect of force line changes on lower limb joints after medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 821-826. |
| [8] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [9] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [10] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [11] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [12] | Wang Shaoling, Wang Yanxue, Zheng Yaochao, Yu Shaojun, Ma Chao, Wu Shaoling. Feasibility of ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection in rabbit hip joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 657-662. |
| [13] | Lu Qinxue, Xu Ning, Yang Yinglan, Han Qianqian, Duanmu Xianyu, Guo Yuwei, Han Qing. Femoroacetabular impingement: strength trainings for nerve-muscle, peripheral muscle and core muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 786-791. |
| [14] | Tang Jiping, Zhang Yeting. Exercise regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanism and role [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 798-803. |
| [15] | Huang Shibo, Xie Hui, Wang Zongpu, Wang Weidan, Qin Kairong, Zhao Dewei. Application of degradable high-purity magnesium screw in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 493-498. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||