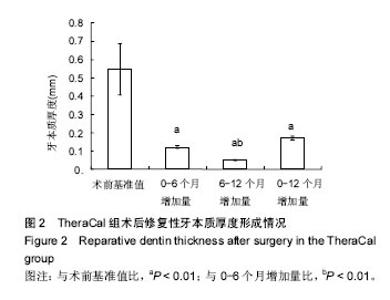
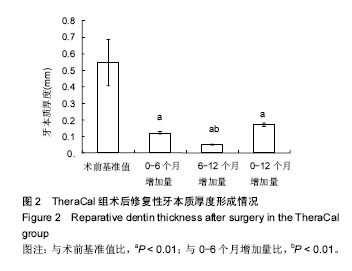
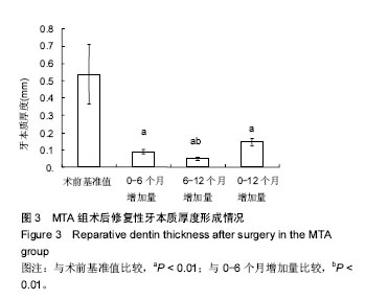
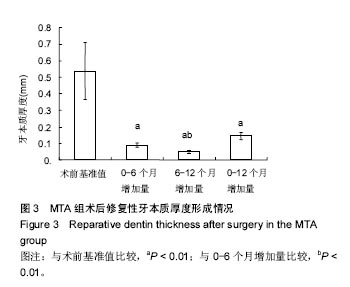
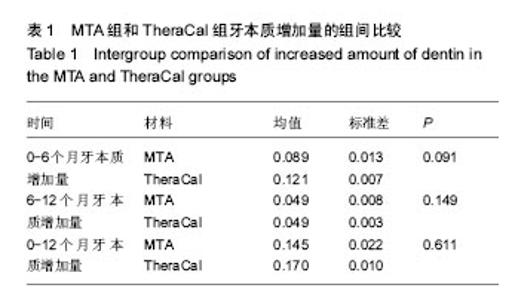
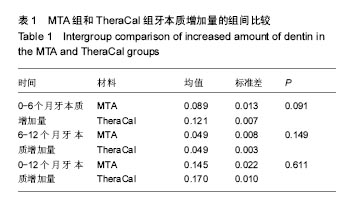
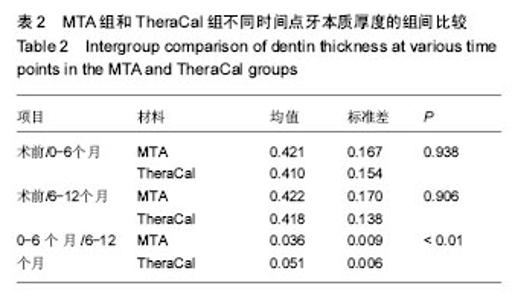
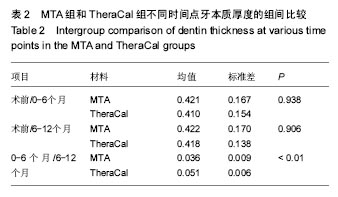
| [1]赵玮,高硕.乳牙牙髓病及根尖周病的临床治疗原则及注意事项[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2011,4(1):4-7.[2]陈娥.儿童牙髓病和根尖周病治疗的原则及方法[J].现代临床医学,2007,33 (suppl,2):260-262.[3]Parisay I, Ghoddusi J, Forghani M.A review on vital pulp therapy in primary teeth.Iran Endod J. 2015 Winter;10(1): 6-15.[4]Akhlaghi N, Khademi A.Outcomes of vital pulp therapy in permanent teeth with different medicaments based on review of the literature.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2015; 12(5):406-417.[5]Fuks AB.Pulp therapy for the primary and young permanent dentitions.Dent Clin North Am. 2000;44(3):571-96, vii.[6]Donmez SB, Turgut MD, Uysal S,et al.Randomized Clinical Trial of Composite Restorations in Primary Teeth: Effect of Adhesive System after Three Years.Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:5409392.[7]Conti TR, Sakai VT, Fornetti AP, et al.Pulpotomies with Portland cement in human primary molars.J Appl Oral Sci. 2009;17(1):66-69.[8]Smaïl-Faugeron V, Courson F, Durieux P, et al.Pulp treatment for extensive decay in primary teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; (8):CD003220.[9]Kindelan SA, Day P, Nichol R,et al.UK National Clinical Guidelines in Paediatric Dentistry: stainless steel preformed crowns for primary molars.Int J Paediatr Dent. 2008;18 Suppl 1:20-28. [10]Smallridge J.UK National Clinical Guidelines in Paediatric Dentistry: Use of fissure sealants including management of the stained fissure in first permanent molars.Int J Paediatr Dent. 2010 Jun 2. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-263X.2009.01035.x.[11]No authors listed.American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry reference manual 2009-2010.Pediatr Dent. 2009;31 (6 Reference Manual):1-302.[12]Samprasit W, Rojanarata T, Akkaramongkolporn P, et al.Fabrication and In Vitro/In Vivo Performance of Mucoadhesive Electrospun Nanofiber Mats Containing α-Mangostin.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015; 16(5):1140-1152.[13]Shayegan A,Jurysta C,Atash R,et al. Biodentine used as a pulp-capping agent in primary pig teeth. Pediatr Dent.2012; 34(7):e202-e208.[14]Ree MH, Schwartz RS.Long-term Success of Nonvital, Immature Permanent Incisors Treated With a Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Plug and Adhesive Restorations: A Case Series from a Private Endodontic Practice.J Endod. 2017. pii: S0099-2399(17)30262-5. |