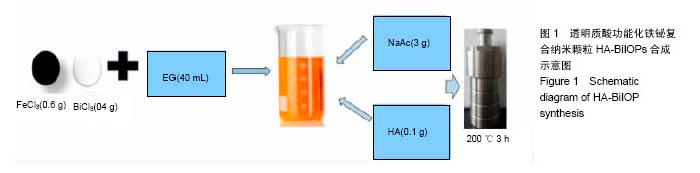
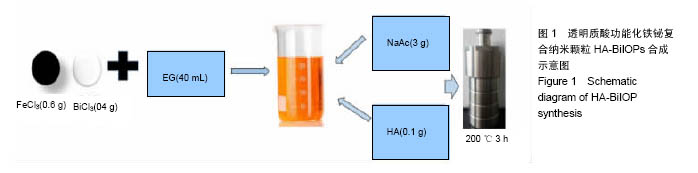
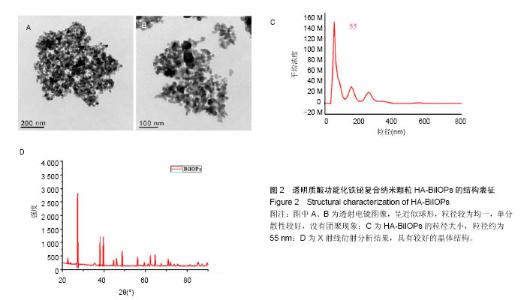
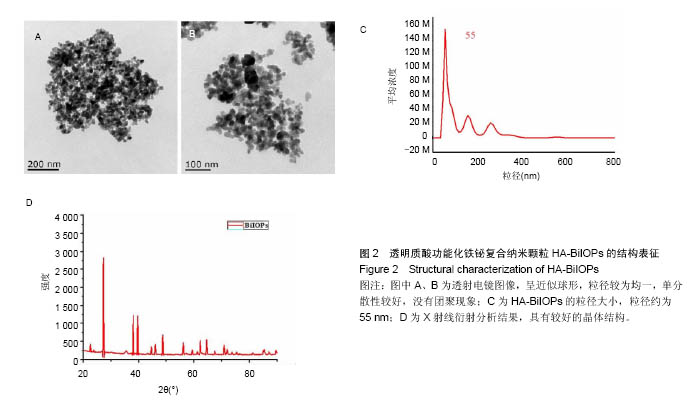
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (18): 2821-2827.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.18.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fabrication of multifunctional bismuth-doped iron nanoparticle and its radiotherapy sensitization in glioblastoma
- 1Department of Neurology, 3Department of Imaging, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212001, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Jiangsu University Medical School, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2017-01-13Online:2017-06-28Published:2017-07-07 -
Contact:Yu Ming, M.D., Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Neurology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212001, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Niu Yuan-yuan, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Neurology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212001, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the “333 Engineering” Scientific Research Project of Jiangsu Province, No. BRA2014173; the “Six Talent Peaks” Scientific Research Project of Jiangsu Province, No. WSN-038
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Niu Yuan-yuan, Yu Ming, Du Feng-yi, Chen Si-yuan, Zhao Tian, Xu Yu-hao, Zhou Qian-wen, Xu Xiu-jian. Fabrication of multifunctional bismuth-doped iron nanoparticle and its radiotherapy sensitization in glioblastoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(18): 2821-2827.
share this article
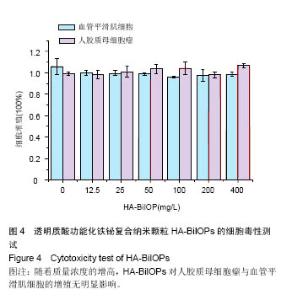
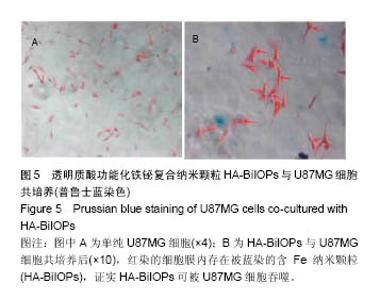
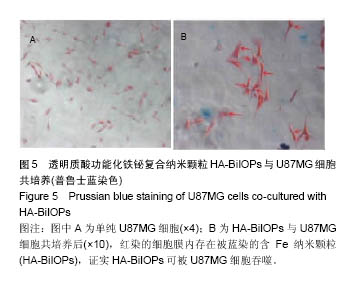
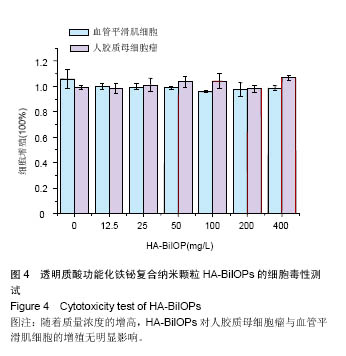
2.3 CCK-8细胞毒性测试结果 实验结果显示,0,12.5,25,50,100,200,400mg/L HA-BiIOPs组血管平滑肌细胞的增殖率分别为(105±7.5)%、(99.7±2.3)%、(99.4±2.4)%,(98.7±1.2)%、(95.7±0.7)%、(97.5±5.2)%、(98.6±1.6)%;0,12.5,25,50,100,200,400 mg/L HA- BiIOPs组U87MG细胞的增殖率分别为(99.0±1.8)%、(98.0±4)%、(100.0±5.2)%,(103.0±4.2)%、(103.0±5.8)%、(98.0±2.7)%、(106.0±2.0)%。随着材料质量浓度的增高,两种细胞的增殖率无降低趋势,各组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。结果表明HA-BiIOPs对细胞无明显毒性,见图4。"
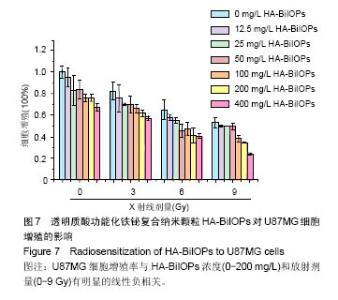
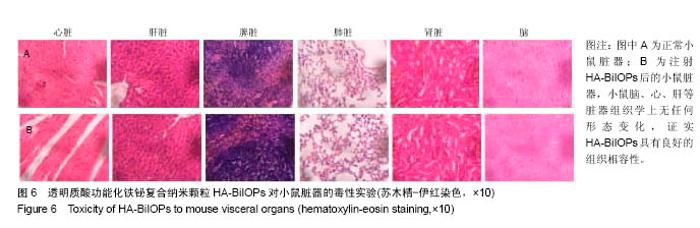
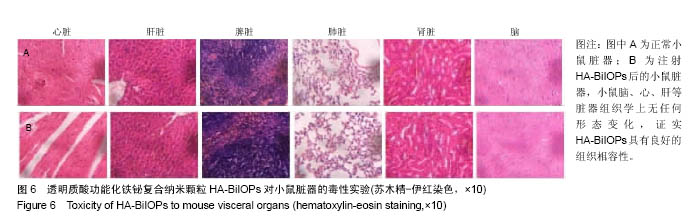
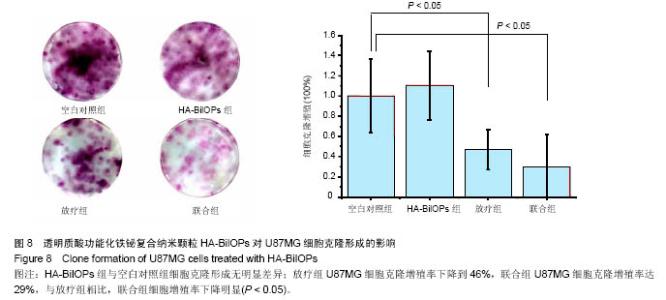
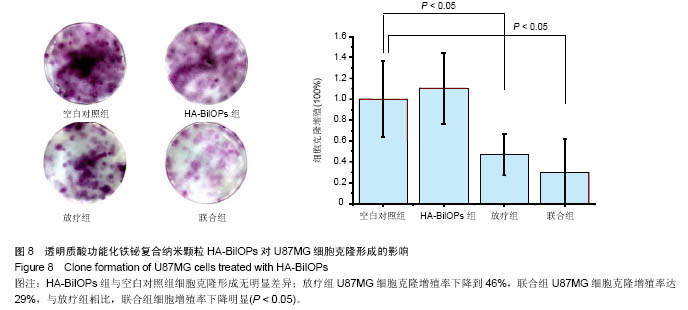
2.6 放疗增敏实验结果 U87MG细胞增殖率与HA-BiIOPs质量浓度(0-200 mg/L)和放射剂量(0-9 Gy)有明显的线性负相关,尤其是在6 Gy X线照射下,200 mg/L的HA-BiIOPs使细胞增殖率下降至(41±7)%,结果充分表明了HA-BiIOPs的放疗增敏能力,见图7;但当HA-BiIOPs质量浓度达到400 mg/L时,细胞增殖率为(40±2)%。考虑细胞吞噬纳米颗粒存在着浓度饱和性,同时为了减少过剩的HA-BiIOPs影响U87MG细胞的生存环境,根据细胞活性CCK-8的结果,选用100 mg/L的HA-BiIOPs在6 Gy X线照射下进行克隆形成实验。结果表明,HA-BiIOPs组与空白对照组的U87MG细胞克隆形成无明显差异;放疗组U87MG细胞克隆增殖率下降到46%,联合组U87MG细胞克隆增殖率达29%,与放疗组相比,联合组细胞增殖率下降明显(P < 0.05),因此说明HA-BiIOPs具有放疗增敏能力,见图8。 "

| [1]Sun L,Joh DY,Al-Zaki A.Theranostic application of mixed gold and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle micelles in Glioblastoma multiforme.J Biomed Nanotechnol.2016;2(2): 347-356.[2]Dolecek TA,Propp JM,Stroup NE,et al.CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005-2009. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14 (suppl 5):v1-49.[3]Dhermain F.Radiotherapy of high-grade gliomas: current standards and new concepts, innovations in imaging and radiotherapy, and new therapeutic approaches.Chin J Cancer. 2014;33(1):16-24.[4]Harrison L,Blackwell K.Hypoxia and anemia: factors in decreased sensitivity to radiation therapy and chemotherapy.Oncologist.2004;9(suppl 5):31-40. [5]Klaus M,Frank U,Dirk N,et al.Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme.Neurooncol. 2011;103(2):317-324.[6]Kakuta T,Takashima Y,Nakahata M,et al.Preorganized hydrogel: self-healing properties of supramolecular hydrogels formed by polymerization of host-guest-monomers that contain cyclodextrins and hydrophobic guest groups.Adv Mater.2013;25(20): 2849-2853.[7]Gu JH,Zhang QY,Zhang W,et al.Preparation of amphiphilic superparamagneticcomposite particles with tumor targeted MRIcontrast agent.Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 2014;18(30): 4823-4830.[8]Huang Y,LuoY,Zheng W.Rational design of cancer-targeted BSA protein nanoparticles as radiosensitizer to overcome cancer radioresistance.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2014; 6(21):19217-19228.[9]Borchiellini D,Etienne-Grimaldi MC,Thariat J,et al.The impact of pharmacogenetics on radiation therapy outcome in cancer patients. A focus on DNA damage response genes .Cancer Treat Rev.2012;38(6):737-759. [10]Corso CD,Ali AN,Diaz R.Radiation-induced tumor neoantigens: imaging and therapeutic implications.Am J Cancer Res.2011;1(3):390-412. [11]Kleinauskas A,Rocha S,Sahu S.Carbon-core silver-shell nanodots as sensitizers for phototherapy and radiotherapy.Nanotechnology.2013;24(32):325103.[12]Subiel A,Ashmore R,Schettino G.Standards and methodologies for characterizing radiobiological impact of high-Z nanoparticles.Theranostics.2016;6(10):1651-1671. [13]Li M,Zhao Q,Yi X,et al.Au@MnS@ZnS core/shell/shell nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging and enhanced cancer radiation therapy.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016; 8(15):9557-9564.[14]Xing H,Zheng X,Ren Q,et al.Computed tomography imaging-guided radiotherapy by targeting upconversion nanocubes with significant imaging and radiosensitization enhancements.Sci Rep.2013;3:1751-1759.[15]李慧,王大新,顾健.超顺磁性纳米颗粒治疗肿瘤的应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(51):10133-10136.[16]Bogart LK,Pourroy G,Murphy CJ,et al.Nanoparticles for imaging, sensing, and therapeutic intervention.ACS Nano. 2014;8(4):3107-3122.[17]Dev KC,Parmeswaran D,Sunil K.Nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia in cancer therapy .NIH Public Access Author Manuscript.2011;2(8):1001-1014. [18]Bazak R,Houri M,EI Achy S,et al.Cancer active targeting by nanoparticles: a comprehensive review of literature.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.2015;141(5):769-784.[19]Xing H,Zheng X,Ren Q,et al.Computed tomography imaging-guided radiotherapy by targeting upconversion nanocubes with significant imaging and radiosensitization enhancements.Sci Rep.2013;3:1751.[20]Yao MH,Ma M,Chen Y,et al.Multifunctional Bi2S3/PLGA nanocapsule for combined HIFU/radiation therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(28):8197-8205.[21]Huang HH,Chen J,Meng YZ,et al.Synthesis and characterization of Bi2S3 composite nanoparticles with high X-ray absorption.Mater Res Bull.2013;48:3800-3804.[22]Ai K,Liu Y,Liu J,et al.Large-scale synthesis of Bi2S3 nanodots as a contrast agent for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging.Adv Mater.2011;23(42):4886-4891.[23]Mesbahi A.A review on gold nanoparticles radiosensitization effect in radiation therapy of cancer. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2010;15(6):176-180.[24]Lee CT,Boss MK,Dewhirst MW.Imaging tumor hypoxia to advance radiation oncology.Antioxid Redox Signal.2014; 21(2):313-337. [25]Lammers T,Aime S,Hennink WE,et al.Theranostic nanomedicine.Acc Chem Res.2011;44(10):1029-1038.[26]Hu F,Jia Q,Li Y,et al.Facile synthesis of ultrasmall PEGylated iron oxide nanoparticles for dual-contrast T1-and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Nanotechnology.2011;22(24): 245604-245611.[27]Phillipsa WT,Bao A,Brenner AJ,et al.Image-guided interventional therapy for cancer with radiotherapeutic nanoparticles.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2014;76:39-59.[28]Yu M,Jambhrunkar S,Thorn P,et al.Hyaluronic acid modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery to CD44-overexpressing cancer cells. Nanoscale. 2013;5: 178-183.[29]Ma M,Huang Y,Chen H,et al.Bi2S3-embedded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient drug delivery and interstitial radiotherapy sensitization.Biomaterials.2015;37:447-455.[30]Babaei M,Ganjalikhani M.The potential effectiveness of nanoparticles as radio sensitizers for radiotherapy.Bioimpacts. 2014;4(1):15-20. [31]Yang Y,Zhang L,Cai J,et al.Tumor angiogenesis targeted radiosensitization therapy using gold nanoprobes guided by MRI/SPECT imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016; 8(3): 1718-1732.[32]Gao B,Shen L,He KW.GNRs@SiO2-FA in combination with radiotherapy induces the apoptosis of HepG2 cells by modulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins.Int J Mol Med.2015;36(5):1282-1290. [33]Miladi I,Aloy MT,Armandy E,et al.Combining ultrasmall gadolinium-based nanoparticles with photon irradiation overcomes radioresistance of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Nanomedicine.2015;11(1):247-257.[34]Retif P,Pinel S,Toussaint M,et al.Nanoparticles for radiation therapy enhancement: the key parameters.Theranostics. 2015;5(9):1030-1044.[35]Runowski M,Grzyb T,Lis S.Magnetic and luminescent hybrid nanomaterial based on Fe3O4 nanocrystals and GdPO4: Eu(3+) nanoneedles.Nanopart Res.2012;14(10):1188. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| [5] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [6] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [7] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [8] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [9] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [10] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [11] | Le Guoping, Zhang Ming, Xi Licheng, Luo Hanwen. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of vancomycin hydrochloride@polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer-chitosan-hyaluronic acid composite sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 528-534. |
| [12] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [13] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [14] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [15] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||