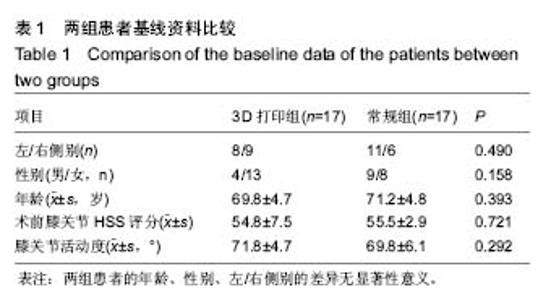
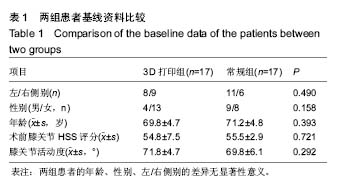
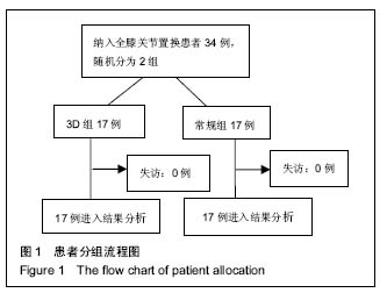
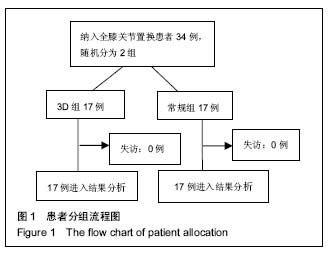
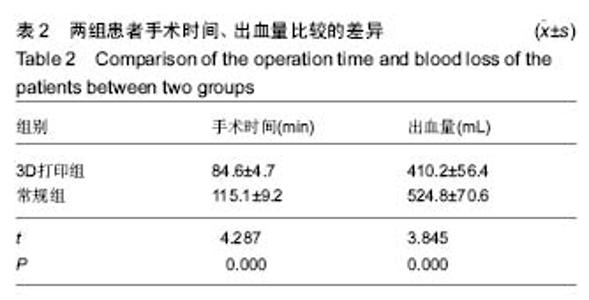
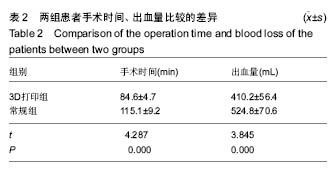
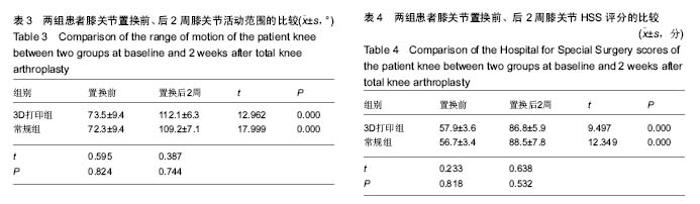
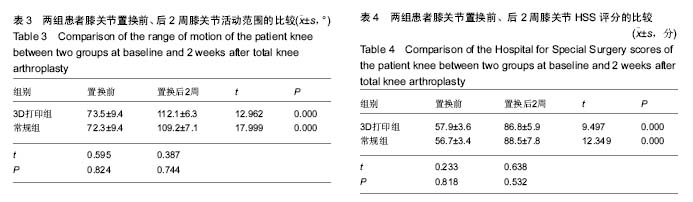
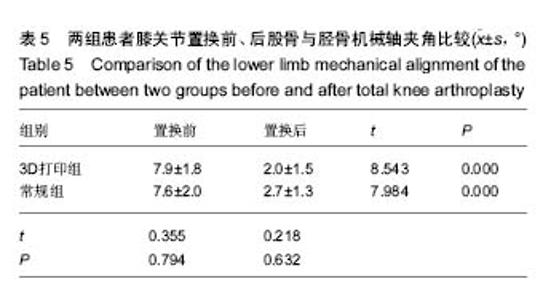
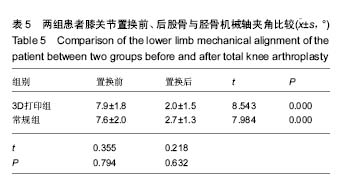
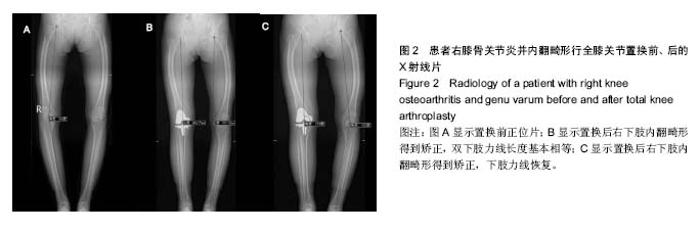
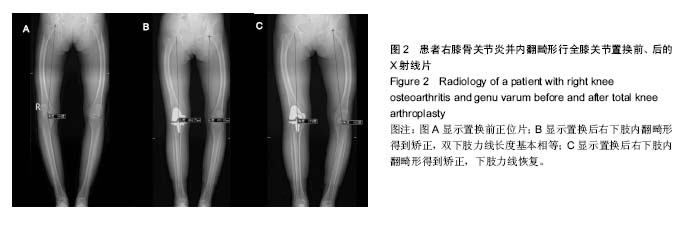
| [1] 张长杰肌肉骨骼康复学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2008: 175-176.[2] Olszewski R.Three-dimensional rapid prototyping models incraniomaxillofacial surgery:systematic review and new clinical applications.P Belg Roy Acad Med.2013;11(2):43-77.[3] 潘伟,郝永强,严孟宁,等.个体化数字导板结合3D打印技术在旋转铰链型人工膝关节置换术中的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2015, 36(3): 231-234.[4] Stindel E, Briard JL, Merloz P,et al.Bone morphing: 3D morpho-logical data for total knee arthroplasty. Comput Aided Surg.2002; 7(3): 156-168.[5] 康鹏德,杨静,沈彬,等. Crowe IV型髋关节发育不良全髋关节置换术前计算机辅助设计[J].中华骨科杂志, 2012, 32(5): 442-446.[6] Zhang S,Liu X, Xu Y, et al. Application of rapid prototyping fortemporomandibular joint reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2011;69(2): 432-438.[7] Lin SJ, Lee CY, Huang KC, et al. Improved femoral component rotation in advanced genu valgum deformity using computerassisted measured resection total knee arthroplasty. J OrthopSurgRes.2015;10: 135.[8] Heyse TJ,Tibesku CO.Improved tibial component rotation in TKA using patient-specifi c instrumentation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015;135(5):697-701.[9] Heyse TJ, Tibesku CO. Improved femoral component rotation in TKA using patient-specific instrumentation.Knee.2014; 21(1):268-271.[10] Innocenti B, Bellemans J, Catani F. Deviations from optimal alignment in TKA: Is there a biomechanical difference between femoral or tibial component alignment? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(1):295-301. [11] Daniilidis K,Tibesku CO.Frontal plane alignment after total knee arthroplasty using patient-specific instruments.Int Orthop. 2013;37(1):45-50.[12] 李伟,方学伟,周游,等.基于MRI 技术全膝关节置换术中个 体化导航模板的基础研究[J/CD].中华关节外科杂志: 电子版, 2015, 9(1) :71-77.[13] Shen C,Tang ZH,Hu JZ,et al.Patient-specific instrumentation does not improve accuracy in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics.2015;38(3):e178-188.[14] Bae DK, Song SJ, Heo DB, et al. Does the severity of preoperativevarus deformity influence postoperative alignment in bothconventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty? KneeSurg Sports TraumatolArthrosc. 2013;21(10): 2248-2254.[15] 汪锡龙,尚希福,贺瑞,等.关节内注射氨甲环酸联合引流管夹闭3 小时方案减少初次单膝关节置换术患者围术期失血的有效性及安全性研究[J].中国全科医学,2015, 18(6): 657-660, 664. |