Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (13): 2029-2035.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.13.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neural stem cell transplantation effects on neuronal apoptosis, differentiation and neurobehavior changes in rats with cerebral ischemia
Liu Yi-min1, Zhao Yan-yan2, Chen Hong-bing1
- 1Department of Neurology, 2Department of Endocrinology, Yidu Central Hospital Affiliated to Weifang Medical University, Qingzhou 262500, Shandong Province, China
-
Revised:2017-03-21Online:2017-05-08Published:2017-06-09 -
Contact:Chen Hong-bing, M.D., Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, Yidu Central Hospital Affiliated to Weifang Medical University, Qingzhou 262500, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Yi-min, Attending physician, Department of Neurology, Yidu Central Hospital Affiliated to Weifang Medical University, Qingzhou 262500, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yi-min, Zhao Yan-yan, Chen Hong-bing. Neural stem cell transplantation effects on neuronal apoptosis, differentiation and neurobehavior changes in rats with cerebral ischemia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(13): 2029-2035.
share this article
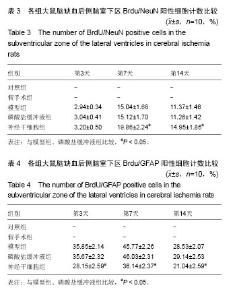
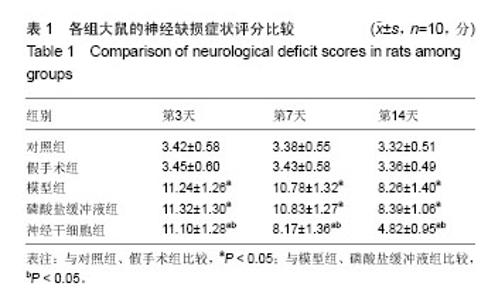
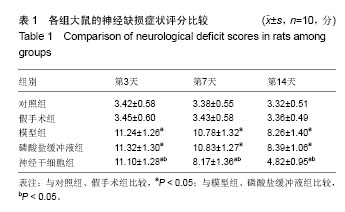
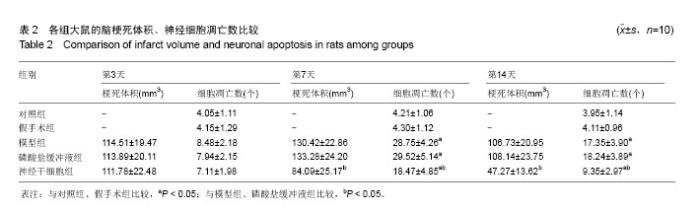
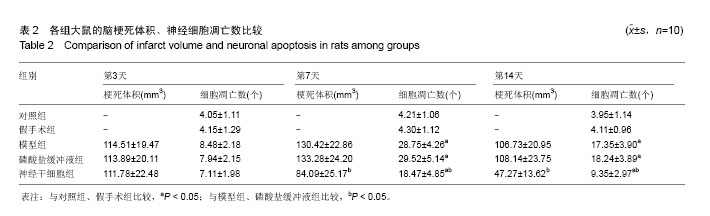
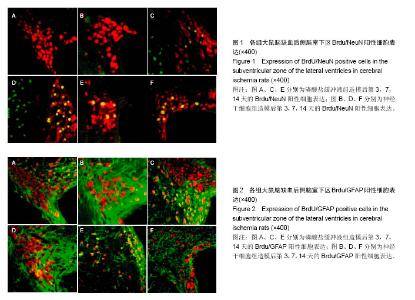
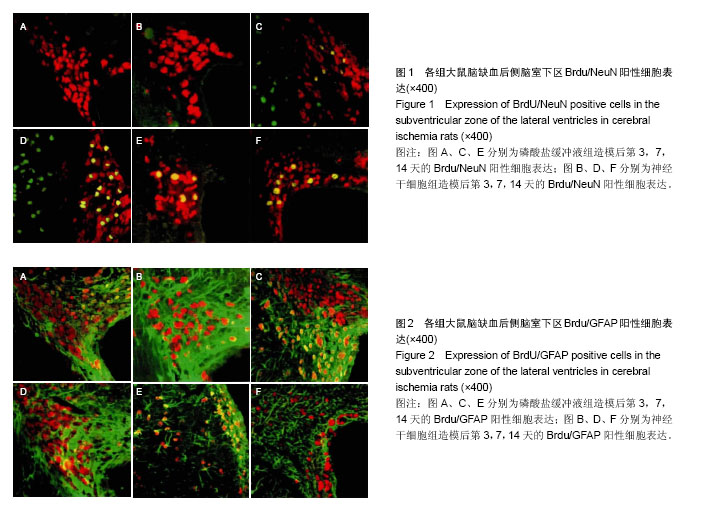
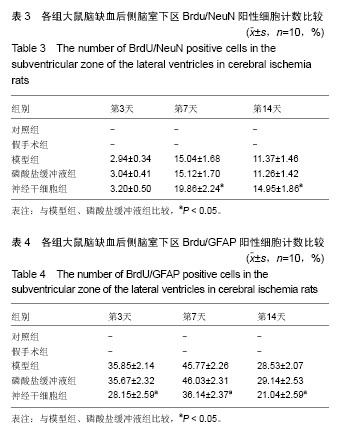
2.4 各组大鼠脑缺血后侧脑室下区Brdu/NeuN阳性细胞计数 对照组、假手术组未见Brdu/NeuN阳性细胞表达。造模后第3天,模型组、磷酸盐缓冲液组和神经干细胞组的Brdu/NeuN阳性细胞计数差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);造模后第7,14天,神经干细胞组的Brdu/NeuN计数均显著高于模型组和磷酸盐缓冲液组(P < 0.05),模型组和磷酸盐缓冲液组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表3。Brdu阳性免疫荧光双标法着色为红色,NeuN阳性免疫荧光双标法着色为绿色,见图1。 2.5 各组大鼠脑缺血后侧脑室下区Brdu/GFAP阳性细胞计数 对照组、假手术组未见Brdu/GFAP阳性细胞表达。造模后第3,7,14天神经干细胞组的Brdu/GFAP计数均显著低于模型组、磷酸盐缓冲液组(P < 0.05),模型组、磷酸盐缓冲液组在造模后第3,7,14天的Brdu/GFAP计数差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表4。Brdu阳性免疫荧光双标法着色为红色,GFAP阳性免疫荧光双标法着色为绿色,见图2。"
| [1] Deng X, Wang XM, Yang HY. Advantages of Mongolian Gerbils in Cerebral Ischemia Model. J Med Pharm Chin Minorit. 2014;13(9):4-10.[2] 朱道湘. 缺血性脑血管病患者颈部血管超声特点分析[J].现代仪器与医疗, 2014,8(3):11-16.[3] Ma J, Shui S, Han X, et al. microRNA-200a silencing protects neural stem cells against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0172178. [4] Li Y, Suo L, Liu Y, et al. Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 against oxygen-glucose-deprivation-induced apoptosis in neural stem cells. J Neurol Sci. 2017;373:107-112.[5] Felling RJ, Covey MV, Wolujewicz P, et al. Astrocyte-produced leukemia inhibitory factor expands the neural stem/progenitor pool following perinatal hypoxia-ischemia. J Neurosci Res. 2016;94(12):1531-1545.[6] Okuda A, Kurokawa S, Takehashi M,et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors activate the p53 signaling pathway in neural stem/progenitor cells. BMC Neurosci. 2017;18(1): 14. [7] Braccioli L, Heijnen CJ, Coffer PJ,et al. Delayed administration of neural stem cells after hypoxia-ischemia reduces sensorimotor deficits, cerebral lesion size, and neuroinflammation in neonatal mice. Pediatr Res. 2017;81 (1-1):127-135.[8] Shin YJ, Riew TR, Jin X,et al. Increased expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 in the subventricular zone after transient focal cerebral ischemia in adult rats. Brain Res. 2016;1648(Pt A):163-171.[9] Li YB,Wang Y,Tang JP,et al.Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1-induced neural stem cell transplantation on hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(5): 753-759.[10] 董静,刘斌.脂肪组织来源的基质细胞向神经细胞分化及其在脑缺血疾病治疗中的应用进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2007, 22(11): 1050-1053.[11] Wang J, Wen CY, Cui CC,et al. Effect of activation of the Ca(2+)-permeable acid-sensing ion channel 1a on focal cerebral ischemia in diabetic rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8(10):13255-13260.[12] Song C, Song C, Chen K,et al. Inhibition of long non-coding RNA IGF2AS protects apoptosis and neuronal loss in anesthetic-damaged mouse neural stem cell derived neurons. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;85:218-224. [13] Wakai T, Narasimhan P, Sakata H,et al. Hypoxic preconditioning enhances neural stem cell transplantation therapy after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016; 36(12):2134-2145. [14] Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang Z,et al. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats.Stroke. 2001;32(4):1005-1011. [15] 晏正辉, 王兴元.老年人急性脑血管疾病的脑电图特征[J].医学研究生学报, 2013, 26(6): 615-617.[16] Moeller S, Lücke C, Struffert T,et al. Ischemic stroke associated with the use of a synthetic cannabinoid (spice). Asian J Psychiatr. 2017;25:127-130.[17] Abboud H, Sissani L, Labreuche J,et al. Specificities of Ischemic Stroke Risk Factors in Arab-Speaking Countries. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;43(3-4):169-177.[18] Hu X, De Silva TM, Chen J,et al. Cerebral Vascular Disease and Neurovascular Injury in Ischemic Stroke. Circ Res. 2017; 120(3):449-471. [19] 马志波. CTA与DSA在脑血管疾病诊断中的价值研究[J].中国医学创新, 2013,6(5): 110-111.[20] 鲍爽,吴晓丹,林卫红. TPA的综合治疗[J].中国老年学杂志, 2013, 33(15): 3819-3822.[21] 短暂性脑缺血发作中国专家共识组.短暂性脑缺血发作的中国专家共识[J]. 中国实用乡村医生杂志, 2013, 20(2): 24-27.[22] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system.Science.1992;255(5052):1707-1710.[23] 田兆华,刘柏炎. 神经干细胞与脑缺血损伤[J].亚洲心脑血管病例研究, 2014, 3(4):18-21.[24] Miao MS, Guo L, Li RQ,et al. Radix Ilicis Pubescentis total flavonoids combined with mobilization of bone marrow stem cells to protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(2):278-284.[25] Qin M, Chen R, Li H,et al.Direct Reprogramming of Human Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells by OCT4 and Application in Repairing of Cerebral Ischemia Damage. Int J Biol Sci. 2016; 12(5):558-568.[26] He X, Deng FJ, Ge JW. Effects of total saponins of Panax notoginseng on immature neuroblasts in the adult olfactory bulb following global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(9):1450-1456.[27] Vay SU, Blaschke S, Klein R,et al. Minocycline mitigates the gliogenic effects of proinflammatory cytokines on neural stem cells. J Neurosci Res. 2016;94(2):149-160. [28] 周菊花, 方素珍,周细中. 神经干细胞移植治疗重度脑瘫患儿的研究进展[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2014, 32(1): 85-87.[29] Song M, Kim YJ, Kim YH, et al. Long-term effects of magnetically targeted ferumoxide-labeled human neural stem cells in focal cerebral ischemia. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(2): 183-190. [30] Chen L, Qiu R, Li L,et al. The role of exogenous neural stem cells transplantation in cerebral ischemic stroke. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(11):3219-3230.[31] Wang J, Xia J, Zhang F,et al.Galectin-1-secreting neural stem cells elicit long-term neuroprotection against ischemic brain injury. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:9621.[32] 赵强,金华,李艳华.神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的现状及移植途径[J].生命科学, 2013,14(3): 320-323.[33] Tavares I. Human neural stem cell transplantation in spinal cord injury models: how far from clinical application? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(22): 1093-1099. [34] Tonchev AB, Yamashima T, Sawamoto K, et al. Enhanced proliferation of progenitor cells in the subventricular zone and limited neuronal production in the striatum and neocortex of adult macaque monkeys after global cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res. 2005;81(2):776-788.[35] Rhl C, Lucius R, Sievers J. The effect of activated m icroglia on astrogliosis param eters in astrocyte cultures. Brain Res. 2007;1129(1):43-52.[36] 楮纯,赵元立.脂肪干细胞及其在脑缺血性疾病治疗中的研究进展[J].中国卒中杂志,2009,4(11):916-919.[37] Yao Y,Zheng XR,Zhang SS,et al.Transplantation of vascular endothelial growth factor-modifed neural stem/progenitor cells promotes the recovery of neurological function following hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Neural Regen Res.2016; 11(9): 1456-1463.[38] 刘斌,董静,李建民,等.人脂肪组织来源的神经干细胞移植对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注后细胞凋亡及 Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达的影响[J].临床神经病学杂志,2010,23(1):42-45.[39] Okazaki T,Magaki T,Takeda M,et al. Intravenous administration of bone marorow stromal cells increases survivin and Bcl-2 protain expression and improves sensorimotor function following ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2008;430:109-114.[40] Komatsu K,Honmou O,Suzuki J,et al.Therapeutic time window of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2010;1334:84-92.[41] Augestad IL, Nyman AK, Costa AI, et al. Effects of Neural Stem Cell and Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Co-transplants on Tissue Remodelling After Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in the Adult Rat. Neurochem Res. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2098-3. [Epub ahead of print][42] Nih LR, Moshayedi P, Llorente IL, et al. Engineered HA hydrogel for stem cell transplantation in the brain: Biocompatibility data using a design of experiment approach. Data Brief. 2016;10:202-209.[43] Bacigaluppi M, Russo GL, Peruzzotti-Jametti L, et al. Neural Stem Cell Transplantation Induces Stroke Recovery by Upregulating Glutamate Transporter GLT-1 in Astrocytes. J Neurosci. 2016;36(41):10529-10544.[44] hen L, Zhang G, Gu Y, et al. Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Neural Stem Cells therapy for experimental ischemiastroke in preclinical studies. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32291. doi: 10.1038/srep32291.[45] Ryu S, Lee SH, Kim SU, et al. Human neural stem cells promote proliferation of endogenous neural stem cells and enhance angiogenesis in ischemic rat brain.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(2):298-304. [46] Hou B, Ma J, Guo X, et al. Exogenous Neural Stem Cells Transplantation as a Potential Therapy for PhotothromboticIschemia Stroke in Kunming Mice Model. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(2):1254-1262. [47] Watanabe T, Nagai A, Sheikh AM, et al. A human neural stem cell line provides neuroprotection and improves neurological performance by early intervention of neuroinflammatory system. Brain Res. 2016;1631:194-203. [48] Abeysinghe HC, Bokhari L, Quigley A, et al. Pre-differentiation of human neural stem cells into GABAergic neurons prior to transplant results in greater repopulation of the damaged brain and accelerates functional recovery after transient ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:186. [49] Yao H, Gao M, Ma J, et al. Transdifferentiation-Induced Neural Stem Cells Promote Recovery of Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke Rats. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0137211. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [5] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [6] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [7] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [11] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [12] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [13] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [15] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||