Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (52): 7821-7828.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.52.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of three-dimensional printed porous titanium scaffolds on bone ingrowth
- the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2016-09-21Online:2016-12-16Published:2016-12-16 -
Contact:Wang Jin-cheng, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Wang Zhong-han, Studying for master’s degree, the Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the International Cooperation Department Foundation of Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 20150414006GH; the Patent Management Department Foundation of Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 20150312028ZG; the High-Tech Department Foundation of Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 20130206060GX; the Talent Training Program for the Doctoral and Postgraduate of Norman Bethune Health Science Center of Jilin University, No. YB201501; the Postgraduate Innovation Foundation of Jilin University, No. 2016108, 2016041
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhong-han, Wang Chen-yu, Liu He, Li Chen, Qin Yan-guo, Cai Xiao-yu, Wang Jin-cheng.
share this article

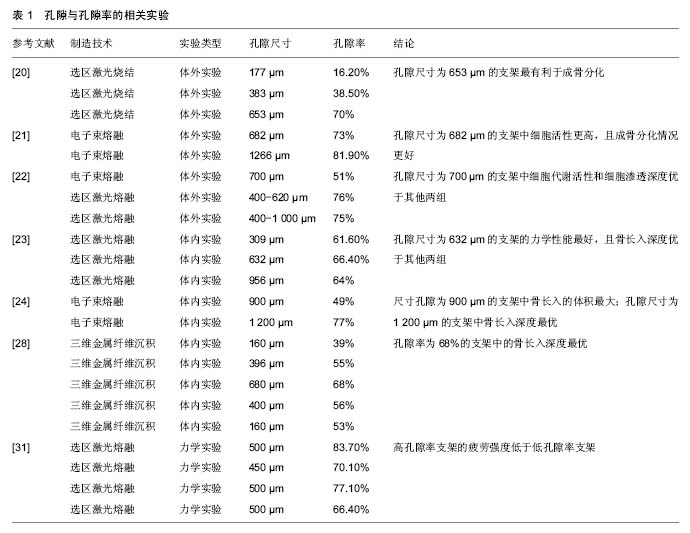
2.1 孔隙尺寸 植入物表面的孔隙结构在成骨诱导和骨长入过程中都起到了重要作用。合适的孔隙尺寸可为成骨细胞的增殖与迁移提供充分的空间,也对间充质干细胞的成血管作用有着促进作用[17]。另外,孔隙的尺寸也应权衡细胞是否易于附着及通过孔隙的供养情况。因此,寻找最适的孔隙尺寸来获得最佳的骨长入效果,对于植入物的制造具有指导意义[18]。 Polo-Corrales等[19]在1970年首次研究并确认允许骨长入的最小孔径为100 μm,这个结论也成为后来研究的一个重要标准。使用3D打印技术的制造的支架孔隙孔径也基本大于100 μm。Cheng等[20]以人体股骨头松质骨为模板并旋转叠加图像,使用激光烧结技术制造出孔隙率为177,383,653 μm的钛合金孔隙支架。在支架内植入MG63细胞并培养24 h后,3种支架中细胞活性均在较高水平且无统计学意义。而骨形态发生蛋白、血管生成因子等成骨标志物随着孔隙尺寸的增加而表达上调,说明细胞在大孔径孔隙中有更好的成骨潜力。碱性磷酸酶水平下降和骨钙素的升高,则说明成骨细胞向成熟方向分化。Lv等[21]则比较了电子束熔融制造孔径为640 μm和1 200 μm钛合金孔隙支架体外细胞植入情况。在支架中植入间充质干细胞并培养至第7天后,640 μm孔径支架中的细胞活性大于85%,显著高于1 200 μm孔径支架中细胞的活性;且小孔径也表现出更高的碱性磷酸酶活性、更好的骨矿化,以及相比于大孔径更高的成骨基因表达。Markhoff等[22]的研究结果有着相似的趋势:使用选区激光束熔融方法制造出孔隙尺寸为500,700, 1 000 μm的3种支架,复合成骨细胞培养8 d后,孔径700 μm支架中的细胞代谢活性显著高于其他两组,且细胞荧光染色后可见这种支架中细胞长入的深度也要高于其他两组。Taniguchi等[23]使用SLM技术制造了孔隙尺寸分别为300,600,900 μm的柱状钛合金支架,在植入兔股骨松质骨2,8周后, 600 μm组支架拔出试验和骨组织长入深度都明显优于另外两组,提示孔隙尺寸为600 μm的支架中骨长入效果最好。 综合以上研究结果,相较于其他孔径支架,孔径为500-700 μm的支架在细胞和动物实验中都有着更好的表现,其他孔隙尺寸越偏离这一区间,细胞活性、骨标志物表达或骨长入的深度与强度越差。而另外一些实验中,Biemond等[24]得出了不同的结论。通过电子束熔融制造的两种不同孔径柱状钛合金支架置入山羊股骨内侧髁,在置入后4周和6周进行动物处置并行组织学检测,发现在第4周和第6周,孔隙为 1 200 μm的支架中骨长入深度高于孔径900 μm的支架,而6周时孔径900 μm支架的骨面积则显著高于孔径1 200 μm的支架。 仅追求绝对骨长入深度或高细胞活性是片面的,较小的孔径会阻碍养供的运输,使其无法运输至支架中心滋养其间的组织细胞,使成骨细胞的增殖与成熟受限,导致成骨不良;较大孔径中的骨生长率则较低,在成骨量相等的前提下,大孔径支架中的新生骨组织在支架孔隙中所占体积相对较小,在初期成骨阶段不能保证骨-植入物界面的链接稳定性[25]。因此,寻找最适成骨的孔隙尺寸仍是一个有待研究解决的问题。 2.2 孔隙率 孔隙率是指材料中孔隙体积与材料在自然状态下总体积之比,这一参数与假体中孔隙的尺寸、梁的粗细和孔隙形状都相关。传统的表面涂层制造工艺,如等离子喷涂、颗粒烧结、酸蚀等可获得的孔隙率范围通常为35%-60%,且在对于这些不同孔隙率支架对于骨长入能力的研究中发现,孔隙率越高骨长入的效果越明显[26]。仅有少量的文献报道孔隙率与骨长入的效果无明显关联,而无文献有关于孔隙率越小骨长入效果越佳结论的报道。随着孔隙率增加,假体的表面积也会随之增大,较大的表面积为细胞的附着和组织形成提供了足够的空间,凹凸的表面形态也会提高组织在表面的附着强度。通过摩擦实验可以发现,高孔隙率假体表面有着更高的粗糙度,高粗糙度可起到稳定骨-植入物接触面的效果,在置入假体的初始阶段可防止假体松动下沉,维持假体的稳定性[27]。 人体松质骨孔隙率为70%-90%,孔隙率在这一区间内层被认为最有利于骨生长。Cheng等[20]以人股骨头松质骨为模板旋转叠加后,制造出孔隙率分别为15%、37.9%、70%的3种钛合金孔隙支架,植入成骨细胞后发现高孔隙率组中的细胞分化情况相比于低孔隙率组更好。Li等[28]的研究也显示出类似的规律,他们比较了孔隙率分别为68%和39%的3D打印孔隙金属假体在体骨长入的情况,植入3周后发现孔隙率为68%的孔隙假体骨长入深度显著高于孔隙率39%假体的骨长入深度。综合文献结果可以发现这一趋势,当金属假体孔隙率在68%以下时,体外细胞实验或体内动物实验中高孔隙率假体的表现均优于低孔隙率假体。而在比较孔隙率区间为68%-88%的孔隙金属假体时则发现了不统一的规律。Lv等[21]发现,孔隙率为73%金属假体中植入间充质干细胞的细胞活性比孔隙率为81%假体中的高,且细胞分化情况更好。Nover等[29]的研究则得出相反的结论,他们将圆柱状(φ为5 mm,L为10 mm)置入犬股骨干,在置入后的第4,16周均发现高孔隙率植入物(80%)中的骨组织占孔隙比例要高于低孔隙率植入物(75%)。Van der Stok等[30]在体内实验中验证了孔隙率为68%和88%的钛合金孔隙支架在置入大鼠股骨12周时,两种支架中的新生骨骨量和支架-骨接合的强度没有明显差异。在对于植入物孔隙率的设计时,也应考虑到孔隙率改变对于植入物力学性能的影响。随着孔隙率的增加,植入物的抗压强度呈指数递减,当孔隙率从50%增加到75%时,植入物的抗压强度从120 MPa下降至仅35 MPa。同时孔隙率的增加也会缩短孔隙植入物的疲劳寿命,在长期反复微小应力的刺激下造成植入物的断裂。而低孔隙率植入物的弹性模量则较大,因应力遮挡效应会造成植入物周围骨质的疏松溶解而导致植入物下沉松动,增加翻修手术的概率[31]。关于孔隙与孔隙率的相关实验见表1。 另一个与孔隙率相关的概念是孔隙互通性。孔隙在植入物中具有2种状态:一种为相互连通的孔隙,这种孔隙间具有通路使得各个孔隙得以连通;另一种孔隙则为盲道,仅有通入假体的单一通道且不与其他孔隙相连通。在Otsuki等[32]的研究中,引入“ADI”(平均迂回指数)这一参数,用以评价盲道孔隙在总孔隙中所占比率,并得出了这样的结论:盲道率高的植入物中骨长入情况较差,而在互通孔隙较高的植入物中骨长入情况则好。组织在长入植入物过程的方向为外周向中心生长,盲道孔隙会阻碍组织向中心生长的过程,也不利于植入物中心区域的养供和生血管的过程。 2.3 孔隙形状 在孔隙材料制造和材料性能评估过程中,孔隙形状是一个项不可忽略的因素。孔隙形状影响着孔隙在材料内的空间分布情况,细胞的黏附、转移等行为也会在不同孔隙形状的材料中有着不同的表现。在评估不同孔隙形状对于骨长入效果时,应注意的一点是控制变量法在实验过程中难以达到,因为孔隙形状的改变必然会引起孔隙尺寸和孔隙率的变化,而无法单一改变孔隙形状这一变量。 使用传统技术,材料内部精细的孔隙形状难以控制制造,而评估孔隙形状的生物学性能更是天方夜谭。3D打印技术的出现则彻底改变了状况,通过CAD构造出材料内部规律排列的孔隙形状模板,融化的材料粉末固化后可塑造成预先设计好的结构,材料内部的微观构造也得以精确控制。 在大多数研究中,研究者仅选取一种单一形状的孔隙测评这种孔隙材料的其他性能,选择构造最多的两种形状为蜂巢形和立方形。蜂巢形也称为菱状结构,是由数个开口方向一致、背对背对称排列的六边形单房所构成,这种形状结构的密合度很高,可使用最少材料构建的强度最高、空间最大[33-34]。立方形结构则是中空的正六面体连续排列所组成的立体空间结构[35]。仅有少数的研究对于不同孔隙形状中骨长入能力进行了横向对比。Van Bael等[36]使用选区激光束熔融技术成功制出平面孔隙形状为三角形、蜂巢形和立方形,且孔隙大小分别为1 000 μm和500 μm的6组钛合金孔隙支架,并将人骨膜源性细胞植入支架中,培养14 d后观察3种形状支架中细胞存活情况及成骨标志物表达情况。结果发现,孔隙形状为三角形且孔隙大小为500 μm的支架中细胞存活情况最好且成骨标志物表达最高。笔者对这种结果的解释为:细胞在小孔隙尺寸支架中的渗透速度较大孔隙尺寸要低,而低的渗透速度易于细胞在支架中的黏附过程。在孔隙尺寸相同的条件下,三角形的孔隙中节点两条梁的夹角为锐角,比正六边形和立方形孔隙的梁间夹角小,细胞在这种支架中易于接触更多的粱,因此受到更多的物理刺激促进了分化。Markhoff等[22]比较了成骨细胞在立方结构、对角结构和金字塔结构孔隙钛合金支架中的细胞代谢活性和分化情况,在比较成骨细胞在3种结构中的分化状态中没有发现明显差异,而金字塔结构支架中的细胞代谢活性则高于其他两组。笔者认为金字塔结构中细胞活性的增高是因为其有着最高的孔隙率和最小的孔隙尺寸,而缺少这种孔隙结构对其中成骨细胞所产生作用影响的分析。另外,Cheng等[20]制造的仿人体骨小梁结构孔隙支架也可认为是一种孔隙结构,且已证明成骨细胞细胞在这种孔隙结构中培养能获得较高的细胞活性。 孔隙形状对其中细胞起作用的方式是通过支架当中梁与梁的空间位置构成对细胞形成生物机械性刺激,梁与梁间相对密集的排列可以增加细胞附着的面积而接受更多的机械刺激。在孔隙尺寸相同的前提下,每个单元结构节点处汇集梁的数量越多,两条梁间的相对距离也越小,细胞也越易于在多梁上附着。也可以理解为相对两条梁夹角越小,细胞越易于在多梁上附着而获得更多的机械刺激。支架中孔隙形状为正三角形、立方形和正六边形的单元格中,梁夹角依次为60°、90°、120°,故而可以认为孔隙形状为正三角形的孔隙支架更易于增加细胞的接触和分化[37]。但关于不同支架间孔隙形状对于骨长入的影响仍缺乏在体实验,需进一步完善。 2.4 表面处理 非骨水泥型假体植入后,其依靠自体骨与假体间的压力保持固定。为了得到长期稳定性而避免假体松动、下沉等的产生,假体表面的骨长入成为至关重要因素。假体孔隙中长入的骨组织可以有效给予两个界面牢固地锁定,以维持足够的力学强度。 钛及其合金因其有着良好的生物相容性、无毒性、高强度和耐腐蚀性,已被广泛应用于骨科植入物的制造。但钛及钛合金材料有着一定的生物惰性,不能有效激发骨生长过程,故在钛及钛合金植入物的制造过程中,通常应用表面改性技术改变表面的物理特性或使用涂层技术使得植入物有着更好的骨长入能力[38-39]。着些表面改性技术通常需要达到几种标准:表面改性后植入物需仍具有良好的生物相容性,不引发感染或免疫排斥等反应;表面改性后假体应具有更好的促进骨诱导的能力,成骨细胞能够在表面上良好的黏附、分化,并形成植入物与自体骨间牢固的结合;植入物表面的涂层或修饰结构应与植入物体紧密贴附,在生理应力下也应维持稳定性而不宜分离脱落[12]。 现已有多种表面处理技术包括物理、化学等方法来得到生物活性表面,且这些表面处理技术已成为植入物制造中的常规程序步骤。表面处理技术根据处理的方法不同可以大体分为3类:表面生物涂层技术;砂喷、打磨、热处理等物理处理技术;以及酸蚀、碱蚀、氧化等化学处理技术。第一项技术是在植入物表面贴附一层生物涂层,来达到更好的生物亲和性的作用[40]。Biemond等[24]通过电沉积方法分别在EBM支架上获得2种不同涂层:磷酸钙涂层和磷酸氢钙涂层。将2种表面涂层处理的支架和未进行表面处理的支架同时置入成年羊髂嵴处,于置入后第5,15周取支架进行组织学分析,可见进行生物涂层处理的支架中骨长入的深度在2个时间点都高于未进行表面涂层处理的支架,证明生物磷酸钙涂层可具有加速骨形成的作用,可显著提高支架中骨长入的深度。Matena等[17]在支架表面复合上聚己内酯涂层,由于聚己内酯生物活性高于钛合金,体外实验中细胞在聚己内酯涂层支架中的接触、增殖情况更好。 后两项技术通过增加支架表面的微观结构和表面粗糙度来影响细胞在支架表面的细胞的黏附、分化等行为。成骨细胞在粗糙表面钛合金中培养后,可观察到碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素等成骨分化指标的明显上调[12,41]。酸、碱处理属于一种化学处理技术,是组织工程支架制造后进行表面处理的常用手段。酸处理后,金属表面受到腐蚀后形成微米级、边缘锋利的坑状结构。再经碱处理后,坑状结构仍得以保留,但边缘经侵蚀后变圆钝。Cheng等[20]依次使用羟基磷灰石喷涂、酸洗和酸蚀技术对选区激光烧结钛合金样品进行处理。处理后,使用扫描电镜可在宏观尺度可见细微颗粒结构,而在微观尺度上观察则可见支架表面近乎光滑。这是由于喷涂和酸蚀在宏观上改变了支架的表面特征而对微观尺度表面形态影响不大。酸洗处理后出现均匀的纳米颗粒覆盖在支架表面。Amin Yavari等[42]比较了3种不同表面处理技术支架中的骨再生性能表现。对选区激光束熔融制造的支架分别进行酸-碱-热、酸-碱、阳极氧化3种表面处理,在体内外实验中,3种支架表现出不同的生物学表现,酸-碱-热、酸-碱处理后支架表面形成尺度为100- 200 nm的不规则纳米结构;阳极氧化处理的表面则出现规律排列的纳米坑和纳米管结构,每个纳米管直径为25-30 nm。细胞植入体外实验中,阳极氧化支架中细胞增殖、分化和磷灰石形成能力优于酸-碱-热和酸-碱处理的支架。体内实验中,酸-碱-热处理支架中新骨形成体积高于阳极氧化处理支架。而生物力学实验中,阳极氧化处理的支架与骨间有着最高强度的力学连接。对于这种组织学分析和生物力学结果不对等的现象,笔者解释为在阳极氧化处理的支架中新生骨的成熟度和互通性更好,可保持更好的力学强度。 "
| [1]Pauly S,Back DA,Kaeppler K,et al.Influence of statins locally applied from orthopedic implants on osseous integration.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;26(13): 208. [2]Rentsch C,Schneiders W,Manthey S,et al. Comprehensive histological evaluation of bone implants. Biomatter.2014;4pii:e27993[3]Amer MA,Rodríguez PA,Renou SJ,et al.Use of Human Fascia Lata in Rat Calvarial Bone Defects.Acta Odontol Latinoam.2015;28(3):231-235.[4]Balla VK,Martinez S,Rogoza BT,et al.Quasi-static Torsional Deformation Behavior of Porous Ti6Al4V alloy.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2011;31(5): 945-949.[5]Lewallen EA,Riester SM,Bonin CA,et al.Biological strategies for improved osseointegration and osteoinduction of porous metal orthopedic implants. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2015;21(2):218-230.[6]Frydman A,Simonian K.Review of models for titanium as a foreign body.J Calif Dent Assoc. 2014;42(12):829-833.[7]Jemat A,Ghazali MJ,Razali M,et al.Surface Modifications and Their Effects on Titanium Dental Implants.Biomed Res Int.2015;2015:791725. [8]García-Rey E,García-Cimbrelo E.Clinical and radiographic results and wear performance in different generations of a cementless porous-coated acetabular cup.Int Orthop.2008;32(2):181-187.[9]Hirota M,Shima T,Sato I,et al.Development of a biointegrated mandibular reconstruction device consisting of bone compatible titanium fiber mesh scaffold.Biomaterials.2016;75:223-236. [10]Ratnayake JT,Mucalo M,Dias GJ.Substituted hydroxyapatites for bone regeneration: A review of current trends.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016.doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33651. [Epub ahead of print][11]Yamako G,Chosa E,Totoribe K,et al.Trade-offbetween stress shielding and initial stability on an anatomical cementless stem shortening: in-vitro biomechanical study.ed Eng Phys.2015;37(8):820-825.[12]Zhang BG,Myers DE,Wallace GG,et al.Bioactive Coatings for Orthopaedic Implants—Recent Trendsin Development of Implant Coatings.Int J Mol Sci.2014; 15(7):11878-11921.[13]Eltorai AE,Nguyen E,Daniels AH.Three-Dimensional Printing in Orthopedic Surgery. Orthopedics. 2015; 38(11):684-687.[14]Cronskar M,Backstrom M,Rannar LE.Production of customized hip stem prostheses –a comparison between conventional machiningand electron beam melting (EBM). Rapid Prototyping J. 2013;19(5):365-372.[15]Xu J,Weng XJ,Wang X,et al.Potential use of porous titanium-niobium alloy in orthopedic implants: preparation and experimental study of its biocompatibility in vitro.PLoS One.2013;8(11):e79289.[16]Balla VK,Banerjee S,Bose S,et al.Direct laser processing of a tantalum coating on titanium for bone replacement structures.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(6):2329-2334. [17]Matena J,Petersen S,Gieseke M,et al.SLM produced porous titanium implant improvements for enhanced vascularization and osteoblast seeding.Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(4):7478-7492.[18]Asa'ad F,Pagni G,Pilipchuk SP,et al.3D-Printed Scaffolds and Biomaterials: Review of Alveolar Bone Augmentation and Periodontal Regeneration Applications.Int J Dent. 2016;2016:1239842. [19]Polo-Corrales L,Latorre-Esteves M,Ramirez-Vick JE.Scaffold design for bone regeneration.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2014;14(1):15-56.[20]Cheng A,Humayun A,Cohen DJ,et al. Additively Manufactured 3D Porous Ti-6Al-4V Constructs Mimic Trabecular BoneStructure and Regulate Osteoblast Proliferation, Differentiation and LocalFactor Production in a Porosity and Surface Roughness Dependent Manner.Biofabrication.2014;6(4):045007.[21]Lv J,Jia Z,Li J,et al.Electron Beam Melting Fabrication of Porous Ti6Al4VScaffolds: Cytocompatibility and Osteogenesis.Adv Eng Mater.2015;17(9):1391-1398.[22]Markhoff J,Wieding J,Weissmann V,et al.Influence of Different Three-Dimensional Open Porous TitaniumScaffold Designs on Human Osteoblasts Behavior in Static andDynamic Cell Investigations. Materials.2015;8(8):5490-5507.[23]Taniguchi N,Fujibayashi S,Takemoto M,et al.Effect of pore size on bone ingrowth into porous titanium implantsfabricated by additive manufacturing: An in vivo experiment.Mater Sci EngC.2016;59:690-701.[24]Biemond JE,Aquarius R,Verdonschot N,et al.Frictional and bone ingrowth properties of engineered surfacetopographies produced by electron beam technology.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(5): 711-718.[25]Prananingrum W,Naito Y,Galli S,et al.Bone ingrowth of various porous titanium scaffolds produced by a moldless and space holder technique: an in vivo study in rabbits.Biomed Mater.2016;11(1):015012.[26]Loh QL,Choong C.Three-Dimensional Scaffoldsfor Tissue Engineering Applications:Role of Porosity and Pore Size. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2013;19(6):485-502.[27]Jeon H,Lee H,Kim G.A surface-modified poly(?-caprolactone) scaffold comprising variable nanosized surface-roughnessusing a plasma treatment.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2014;20(12):951-963.[28]Li JP,Habibovic P,van den Doel M,et al.van Blitterswijk, Klaas de Groot. Bone ingrowth in poroustitanium implants producedby 3D fiber deposition. Biomaterials. 2007;28(18):2810-2820.[29]Nover AB,Lee SL,Georgescu MS,et al.Porous titanium bases for osteochondral tissue engineering.Acta Biomater.2015;27:286-293. [30]Van der Stok J,Van der Jagt OP,Amin Yavari S,et al.Selective laser melting-produced porous titanium scaffolds regenerate bone in critical size cortical bone defects.J Orthop Res.2013;31(5):792-799.[31]Yavari SA,Wauthle R,van der Stok J,et al.Fatigue behavior of porous biomaterials manufactured using selectivelaser melting.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(8):4849-4858.[32]Otsuki B,Takemoto M,Fujibayashi S,et al.Pore throat size and connectivity determine bone and tissue ingrowthinto porous implants: Three-dimensional micro-CT based structuralanalyses of porous bioactive titanium implants. Biomaterials. 2006;27(35):5892-5900.[33]Gómez S,Vlad MD,López J,et al.Design and properties of 3D scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomater. 2016.pii: S1742-7061(16)30309-9.[34]Marin E,Fusi S,Pressacco M,et al.Characterization of cellular solids in Ti6Al4V for orthopaedicimplant applications: Trabeculartitanium.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010;3(5):373-381. [35]Parthasarathy J,Starly B,Raman S,et al.Mechanical evaluation of porous titanium (Ti6Al4V)structures with electron beam melting (EBM).J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2010;3(3):249-259.[36]Van Bael S,Chai YC,Truscello S,et al.The effect of pore geometry on the in vitro biological behavior of humanperiosteum-derived cells seeded on selective laser-melted Ti6Al4V bone scaffolds.Acta Biomater. 2012;8(7):2824-2834.[37]Di Luca A,Lorenzo-Moldero I,Mota C,et al. Osteochondral Regeneration: Tuning Cell Differentiation into a 3D Scaffold Presenting a Pore Shape Gradient for Osteochondral Regeneration.Adv Healthc Mater.2016;5(14):1832. [38]Liang Y,Li H,Xu J,et al.Morphology, Composition, and Bioactivity of Strontium-Doped Brushite Coatings Deposited on Titanium Implants via Electrochemical Deposition. Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(6):9952-9962.[39]Medvedev AE,Ng HP,Lapovok R,et al.Effect of bulk microstructure of commercially pure titanium on surface characteristics and fatigue properties after surface modification by sand blasting and acid-etching. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2015;57:55-68. [40]Heinl P,Müller L,Körner C,et al.Cellular Ti–6Al–4V structures with interconnected macro porosity for bone implants fabricated by selective electron beam melting. Acta Biomaterialia.2008;4(5):1536-1544.[41]Le VQ,Pourroy G,Cochis A,et al.Alternative technique for calcium phosphate coating on titanium alloy implants. Biomatter.2014;4:e28534.[42]Amin Yavari S,van der Stok J,Chai YC,et al.Bone regeneration performance of surface-treated porous titanium.Biomaterials.2014;35(24):6172-6181. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||