Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (49): 7418-7424.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.49.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cloning of rat C-sis gene and construction of its eukaryotic expression vector
Sun Guo-fang1, Ding Hao2
- 1Diagnosis Room of ECG, 2Department of Gastroenterology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2016-10-13Online:2016-11-30Published:2016-11-30 -
Contact:Ding Hao, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Gastroenterology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Sun Guo-fang, Master, Attending physician, Diagnosis Room of ECG, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81300348; the Science Foundation for the Youth of Jiangxi Province, No. 20151BAB215006, 20132BAB215015
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Guo-fang, Ding Hao. Cloning of rat C-sis gene and construction of its eukaryotic expression vector[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7418-7424.
share this article
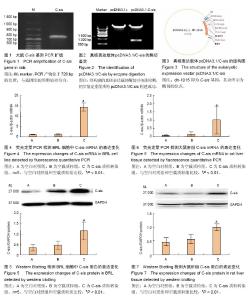
2.1 造模方法的改进 首先克隆了大鼠C-sis基因,并构建pcDNA3.1/C-sis真核表达载体,通过酶切测序以证实C-sis基因克隆成功与否。然后将pcDNA3.1/C-sis转染进入大鼠肝脏细胞,并通过RT-PCR和Western Blot检测C-sis基因在大鼠正常肝细胞株BRL细胞和在体大鼠肝脏细胞中的表达。 2.2 模型稳定性 结果显示,pcDNA3.1/C-sis真核表达载体构建成功,且将其转染入BRL细胞及导入在体大鼠肝脏,RT-PCR和Western Blot均显示C-sis的表达增加。C-sis能在肝脏稳定高表达,这为后续研究C-sis对暴发性肝衰竭的治疗作用提供了稳定模型。 2.3 大鼠C-sis基因的RT-PCR扩增 大鼠C-sis基因通过特异性引物扩展的PCR产物只有一条亮带,位于726 bp的位置。根据数据库GenBank所收录的C-sis的基因序列(NM_24628),所得产物大小与预期值相符合,见图1。 2.4 真核表达载体pcDNA3.1/C-sis的鉴定 限制性内切酶EcoRⅠ、XbaⅠ酶切重组质粒pcDNA3.1/C-sis,用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,初步鉴定重组质粒pcDNA3.1/ C-sis构建成功,见图2。经南京金斯瑞公司测序,与Pubmed数据库中GenBank所给序列(No:NM24628)对比同源性达到100%,进一步证实重组质粒pcDNA3.1/C-sis构建成功。 2.5 真核表达载体pcDNA3.1/C-sis的结构图 如图3所示,dh-1015即为C-sis基因,其余所示为酶切的位点。 2.6 pcDNA3.1/C-sis转染BRL细胞后C-sis mRNA的表达 与空白对照组和空载质粒组比较,C-sis质粒组的C-sis mRNA表达量有明显增加,见图4。 2.7 pcDNA3.1/C-sis转染BRL细胞后C-sis蛋白的表达 与空白对照组、空载质粒组比较,C-sis质粒组的C-sis蛋白表达量有明显增加,见图5。 2.8 pcDNA3.1/C-sis导入大鼠肝脏后C-sis mRNA的表达 实验结果由荧光定量PCR分析软件BIO-RAD CFX Manager自动进行统计和计算。与空白对照组和空载质粒组比较,C-sis质粒组的C-sis mRNA表达量有明显增加,见图6。 2.9 pcDNA3.1/C-sis导入大鼠肝脏后C-sis蛋白的表达 与空白对照组、空载质粒组比较,C-sis质粒组的C-sis蛋白表达量有明显增加,见图7。"
| [1] Hellström M, Kalén M, Lindahl P, et al. Role of PDGF-B and PDGFR-beta in recruitment of vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes during embryonic blood vessel formation in the mouse. Development. 1999; 126(14):3047-3055. [2] Hoofnagke JH, Carithers RL, Shaprio C, et al. Fulminant hepatic failure: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 1995;21(1): 240-252. [3] Zanet J, Pibre S, Jacquet C, et al. Endogenous Myc controls mammalian epidermal cell size, hyperproliferation, endoreplication and stem cell amplication. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 8): 1693-1704. [4] Landau E, Tirosh R, Pinson A, et al. Protection of thrombin receptor expression under hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(4): 2281-2287. [5] Liu W, Kong H, Zeng X, et al. Iptakalim inhibits PDGF-BB-induced human airway smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration. Exp Cell Res. 2015;336(2): 204-210. [6] Virakul S, Dalm VA, Paridaens D, et al. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Enhances Adipogenesis in Orbital Fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(9):5457-5464. [7] Saito Y, Hojo Y, Tanimoto T, et al. Protein kinase C-alpha and protein kinase C-epsilon are required for Grb2-associated binder-1 tyrosine phosphorylation in response to platelet-derived growth factor.J Biol Chem. 2002;277(26):23216-23222. [8] Lindqvist A, Nilsson BO, Ekblad E, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors expressed in response to injury of differentiated vascular smooth muscle in vitro: effects on Ca2+ and growth signals. Acta Physiol Scand. 2001;173(2):175-184. [9] Li L, Xu M, Li X, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B) induced by hypoxia promotes the survival of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells through the PI3K/Akt/Stat3 pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35(2):441-451. [10] Sun L, Zhao R, Lan X, et al.Goniolactone C, a styryl lactone derivative, inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation via PDGFR/ERK signaling. Molecules. 2014;19(12): 19501-19515. [11] Gressot LV, Doucette TA, Yang Y, et al.Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b drives malignant progression in aPDGFB-dependent proneural glioma model by suppressing apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(9):2047-2054. [12] Lynes J, Wibowo M, Koschmann C, et al. Lentiviral-induced high-grade gliomas in rats: the effects of PDGFB, HRAS-G12V, AKT, and IDH1-R132H. Neurotherapeutics. 2014;11(3):623-635. [13] Doucette TA, Kong LY, Yang Y,et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes angiogenesis and drives malignant progression in glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14(9):1136-1145. [14] Hu G, Yao H, Chaudhuri AD, et al. Exosome-mediated shuttling of microRNA-29 regulates HIV Tat and morphine-mediated neuronal dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e381. [15] Yao H, Duan M, Yang L, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB restores human immunodeficiency virus Tat-cocaine-mediated impairment of neurogenesis: role of TRPC1 channels. J Neurosci. 2012;32(29): 9835-9847. [16] Geng H, Lan R, Singha PK, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid increases proximal tubule cell secretion of profibrotic cytokines PDGF-B and CTGF through LPA2- and Gαq-mediated Rho and αvβ6 integrin-dependent activation of TGF-β. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(4):1236-1249. [17] Phipps MC, Xu Y, Bellis SL. Delivery of platelet-derived growth factor as a chemotactic factor for mesenchymal stem cells by bone-mimetic electrospun scaffolds. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40831. [18] Zhang Y, Cheng N, Miron R, et al. Delivery of PDGF-B and BMP-7 by mesoporous bioglass/silk fibrin scaffolds for the repair of osteoporotic defects. Biomaterials. 2012;33(28):6698-6708. [19] Yoshida S, Iwasaki R, Kawana H,et al. PDGFBB promotes PDGFRα-positive cell migration into artificial bone in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 421(4):785-789. [20] Fukuda K, Ogawa M, Taniguchi H, et al. Molecular Approaches to Studying Microbial Communities: Targeting the 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene. J UOEH. 2016;38(3):223-232. [21] Li B, Zhang Y, Li J, et al. Fine Mapping of Two Additive Effect Genes for Awn Development in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) . PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e0160792. [22] Hackmann K, Kuhlee F, Betcheva-Krajcir E, et al. Ready to clone: CNV detection and breakpoint fine-mapping in breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility genes by high-resolution array CGH. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;159(3):585-590. [23] Mukae H, Noguchi S, Naito K, et al. The Importance of Obligate Anaerobes and the Streptococcus anginosus Group in Pulmonary Abscess: A Clone Library Analysis Using Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid. Respiration. 2016; 92(2):80-89. [24] Tuo D, Shen W, Yan P, et al. Rapid Construction of Stable Infectious Full-Length cDNA Clone of Papaya Leaf Distortion Mosaic Virus Using In-Fusion Cloning. Viruses. 2015;7(12):6241-6250. [25] Zheng X, Tong W, Liu F, et al. Genetic instability of Japanese encephalitis virus cDNA clones propagated in Escherichia coli. Virus Genes. 2016;52(2):195-203. [26] O'Halloran DM. STITCHER: A web resource for high-throughput design of primers for overlapping PCR applications. Biotechniques. 2015;58(6):325-328. [27] Camilo CM, Lima GM, Maluf FV, et al. HTP-OligoDesigner: An Online Primer Design Tool for High-Throughput Gene Cloning and Site-Directed Mutagenesis. J Comput Biol. 2016;23(1):27-29. [28] Sun J, Wang L, Dong MM, et al. Construction and identification of multiple genes Co silence of plasmid shRNA. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(12):22053-22062. [29] Cheng A, Zhang Y, Mei H, et al. Construction of recombinant pEGFP-N1-hPer2 plasmid and its expression in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(4):2768-2772. [30] Shyma KP, Gupta SK, Gupta JP, et al. Restriction site detection in repetitive nuclear DNA sequences of Trypanosoma evansi for strain differentiation among different isolates. J Parasit Dis. 2016;40(3):1087-1090. [31] Zarrin M, Erfaninejad M. Molecular variation analysis of <i>Aspergillus flavus</i> using polymerase chain reaction-restrictionfragment length polymorphism of the internal transcribed spacer rDNA region. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(3):1628-1632. [32] Thomsen MC, Ahrenfeldt J, Cisneros JL, et al. A Bacterial Analysis Platform: An Integrated System for Analysing Bacterial Whole GenomeSequencing Data for Clinical Diagnostics and Surveillance. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0157718. [33] Garrigue I, Moulinas R, Recordon-Pinson P, et al. Contribution of next generation sequencing to early detection of cytomegalovirus UL97 emerging mutants and viral subpopulations analysis in kidney transplant recipients. J Clin Virol. 2016;80:74-81. [34] Zhang R, Duan G, Shi Q, et al. Construction of a recombinant Lactococcus lactis strain expressing a fusion protein of Omp22 and HpaA from Helicobacter pylori for oral vaccine development. Biotechnol Lett. 2016;38(11):1911-1916. [35] Liu X, Fu G, Ji Z, et al. A Recombinant DNA Plasmid Encoding the sIL-4R-NAP Fusion Protein Suppress Airway Inflammation in an OVA-Induced Mouse Model of Asthma. Inflammation. 2016;39(4):1434-1440. [36] Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D, Stasinopoulos M, et al. Polyol accumulation in muscle and liver in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2016; 30(6): 999-1007. [37] Cairns RA, Mak TW. Lung Cancer Resets the Liver's Metabolic Clock. Cell Metab. 2016;23(5):767-769. [38] Liu F, Song Y, Liu D.Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999;6(7):1258-1266. [39] Wang CH, Jawan B, Lee TH, et al. Single injection of naked plasmid encoding alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone protects against thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;322(1):153-161. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [6] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [7] | Ma Zhijie, Li Jingyu, Cao Fang, Liu Rong, Zhao Dewei. Influencing factors and biological property of novel biomedical materials: porous silicon carbide coated with bioactive tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 558-563. |
| [8] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [9] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [10] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [11] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [12] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [13] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [14] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [15] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||