Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (49): 7411-7417.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.49.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Histopathological features of the rat ileum after Shigella flexneri infection
Luo Su-yi1, Wang Xi-yun2, Li Jin-tao3
- 1Department of Pathogen Biology and Immunology, School of Clinical Medicine, 2Department of Anesthesiology in 2012, 3Institute of Neuroscience, School of Clinical Medicine, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2016-09-02Online:2016-11-30Published:2016-11-30 -
Contact:Li Jin-tao, M.D., Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Institute of Neuroscience, School of Clinical Medicine, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Luo Su-yi, Master, Teaching assistant, Department of Pathogen Biology and Immunology, School of Clinical Medicine, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the General Program of the Joint Research Foundation of Yunnan Provincial Ministry of Science and Technology-Kunming Medical University, No. 2015FB008
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Su-yi, Wang Xi-yun, Li Jin-tao. Histopathological features of the rat ileum after Shigella flexneri infection[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7411-7417.
share this article
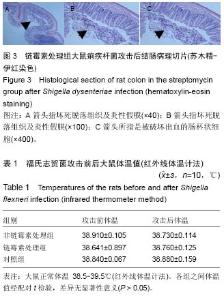
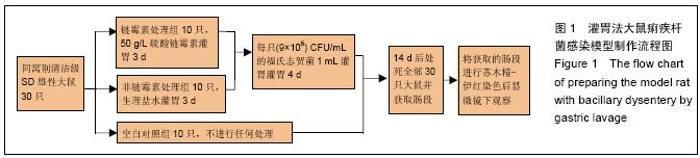
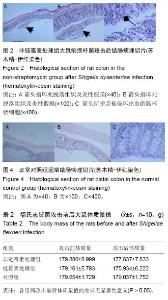
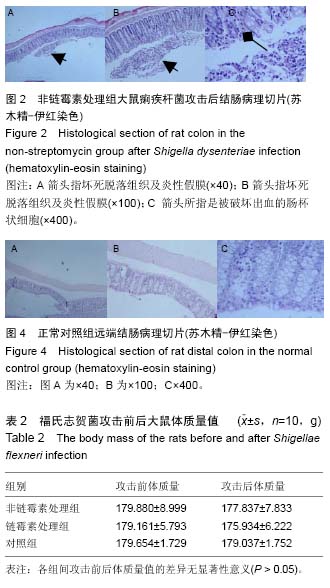
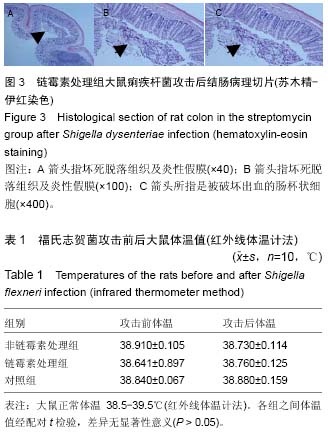
续出现症状,第7天除个别大鼠外几乎所有大鼠都出现症状。表现为粪质较稀,其肛门处较湿润,被稀便覆盖。大鼠精神较往常萎靡,不再活跃,饮食变化不是太大,比对照组饮水量有所增加。 2.5 福氏志贺菌攻击大鼠前后体温、体质量观察 各处理组大鼠在福氏痢疾杆菌攻击前后体温和体质量值经SPSS 17.0配对t 检验,其差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表1,2。 2.6 福氏志贺菌攻击大鼠后各组肠病理切片 链霉素处理组,非链霉素处理组的大鼠远端结肠及直肠都出现典型的痢疾病变黏膜出血、水肿,中性粒细胞浸润,杯状细胞破坏、出血,出现本病特征性的假膜性炎(见图2,3)。脱落后的肠黏膜,形成形状不一的溃疡,溃疡浅表,很少超过黏膜下层。镜下可见,黏膜表层坏死,有大量纤维素渗出,后者与坏死组织、红细胞、白细胞等一起构成假膜。说明SD大鼠的痢疾模型建立成功。而正常对"
| [1] Hathaway LJ, Griffin GE, Sansonetti PJ, et al. Human monocytes kill Shigella flexneri but then die by apoptosis associated with suppression of proinflammatory cytokine production. Infect Immun. 2002;70(7):3833-3842. [2] Zychlinsky A, Thirumalai K, Arondel J, et al. In vivo apoptosis in Shigella flexneri infections. Infect Immun. 1996;64(12):5357-5365. [3] Sansonetti PJ, Tran Van Nhieu G, Egile C.Rupture of the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier and Mucosal Invasion by Shigella flexneri. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28(3):466-475. [4] Ashkenazi S, Levy I, Kazaronovski V, et al. Growing antimicrobial resistance of Shigella isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;51(2):427-429. [5] Sansonetti PJ. Microbes and microbial toxins: paradigms for microbial-mucosal interactions III. Shigellosis: from symptoms to molecular pathogenesis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;280(3):G319-323. [6] Kotloff KL, Winickoff JP, Ivanoff B, et al.Global burden of Shigella infections: implications for vaccine development and implementation of control strategies. Bull World Health Organ. 1999;77(8):651-666. [7] Von SL, Kim DR, Ali M, et al.A multicentre study of Shigella diarrhoea in six Asian countries: disease burden, clinical manifestations, and microbiology.Plos Medicine.2006;3(9): e353. [8] BingGu, XingKe, ShiyangPan, et al. Prevalence and trends of aminoglycoside resistance in Shigella worldwide, 1999-2010. J Biomed Res. 2013 ;27(2):103-115. [9] Yang SF, Xue WJ, Lu WH, et al. High Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Integrons among Shigella Isolates in Eastern China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(3):1549-1551. [10] Qiu S, Wang Y, Xu X, et al. Multidrug-Resistant Atypical Variants of Shigella flexneri in China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19(7):1147-1150. [11] Barry EM, Pasetti MF, Sztein MB, et al. Progress and pitfalls in Shigella vaccine research. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 ;10(4):245-55 255. [12] Bodhidatta L, Pitisuttithum P, Chamnanchanant S, et al. Establishment of a Shigella sonnei, human challenge model in Thailand ☆. Vaccine.2012; 30(49):7040-7045. [13] Heine SJ,Diaz-Mcnair J,Martinez-Becerra FJ,et al. Evaluation of immunogenicity and protective efficacy of orally delivered Shigella type III secretion system proteins IpaB and IpaD. Vaccine.2013;31(28):2919-2929. [14] Braude R, Newport MJ, Porter JWG. Outer Membrane Protein A (OmpA) of Shigella flexneri 2a Induces B Cell Activation And Protective Immune Response in Mouse Model. Faseb Journal.2015;29(3):827-842. [15] Camacho AI, Irache JM, Souza JD, et al. Nanoparticle- based vaccine for mucosal protection against Shigella flexneri, in mice. Vaccine.2013; 31(32):3288-3294. [16] Fernandez MI, Thuizat A, Pedron T, et al. A newborn mouse model for the study of intestinal pathogenesis of shigellosis. Cellular Microbiology.2003; 5(7):481-491. [17] Shim DH, Chang SY, Park SM, et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy offered by a ribosomal-based vaccine from Shigella flexneri, 2a. Vaccine. 2007; 25(25):4828-4836. [18] Voino-Yasenetsky MV, Voino-Yasenetskaya MK. Experimental pneumonia caused by bacteria of the Shigella group. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung. 1962; 11:439-454. [19] Barman S, Koley H, Ramamurthy T, et al.Protective immunity by oral immunization with heat-killed Shigella strains in a guinea pig colitis model. Microbiol Immunol. 2013;57(11):762-771. [20] Chowdhury FM, Rahman MZ, Khan SI, et al.An Environmental Escherichia albertii, Strain, DM104, Induces Protective Immunity to Shigella dysenteriae, in Guinea Pig Eye Model.Current Microbiology.2014; 68(5):642-647. [21] Shim DH, Suzuki T, Chang SY, et al.New animal model of shigellosis in the Guinea pig: its usefulness for protective efficacy studies. J Immunol. 2007 15;178(4):2476-2482. [22] Rabbani GH,Albert MJ,Rahman H,et al. Development of an improved animal model of shigellosis in the adult rabbit by colonic infection with Shigella flexneri 2a. Infect Immun. 1995;63(11):4350-4357. [23] Schnupf P, Sansonetti PJ. Quantitative RT-PCR profiling of the rabbit immune response: assessment of acute Shigella flexneri infection. Plos One. 2012;7(6): e36446-e36446. [24] Shipley ST, Panda A, Khan AQ, et al.A challenge model for Shigella dysenteriae 1 in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis).Comparative Medicine. 2010;60(1):54-61. [25] Islam D, Ruamsap N, Khantapura P, et al. Evaluation of an intragastric challenge model for Shigella dysenteriae, 1 in rhesus monkeys ( Macaca mulatta ) for the pre-clinical assessment of Shigella, vaccine formulations. Apmis Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Et Immunologica Scandinavica, 2014;122(6):463-475. [26] Mostowy S, Boucontet L, Mazon Moya M J, et al. The zebrafish as a new model for the in vivo study of Shigella flexneri interaction with phagocytes and bacterial autophagy.Plos Pathogens.2013;9(9):191-197. [27] 邓超,曹均强,梁鸿寅,等.早期腹腔置管引流对大鼠重症急性胰腺炎相关肠黏膜损伤的作用[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2016,41(2):119-122. [28] 刘松,金梅香,谭兴文.西洋参茎叶皂苷保护大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的作用[J].中成药, 2016,38(2):418-421. [29] 郭敏,李延青,于秀娟,等.大鼠急性肠道感染后肠功能紊乱动物模型的建立[J].山东大学学报:医学版, 2006, 44(6): 586-589. [30] Savchenko ZI, Iushchuk ND, Tsyb AF, et al. [Immunostimulating activity of eubiotic bioflor in intestinal dysbacteriosis of various origin]. Klin Med (Mosk). 2000;78(3):50-53. [31] 吴利先,王国富,高峰.两歧双歧杆菌抗福氏痢疾杆菌感染的机制研究[J]. 大理学院学报:综合版, 2010, 9(6):16-18. [32] Mitra S, Barman S, Nag D, et al.Outer membrane vesicles of Shigella boydii, type 4 induce passive immunity in neonatal mice. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012;66(2):240-250. [33] Lawson JD, Mainwaring SJ. Detection of pseudodiarrhoea by simple clinical assessment of intestinal transit rate. BMJ. 1990;300(6722):439-440. [34] Bai J, Hao J, Zhang X,et al. Netrin-1 attenuates the progression of renal dysfunction by blocking endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the 5/6 nephrectomy rat model. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17(1):47. [35] Chang SY, Lee SN, Yang JY, et al.Autophagy Controls an Intrinsic Host Defense to Bacteria by Promoting Epithelial Cell Survival: A Murine Model. Plos One. 2013;8(11):e81095. [36] Islam D,Ruamsap N,Khantapura P,et al.Evaluation of an intragastric challenge model for Shigella dysenteriae, 1 in rhesus monkeys ( Macaca mulatta ) for the pre-clinical assessment of Shigella, vaccine formulations. APMIS. 2014;122(6):463-475. [37] Kim YJ, Yeo SG, Park JH, et al.Shigella vaccine development: prospective animal models and current status.Curr Pharm Biotechnol.2013;14(10):903-912. [38] 孙艳玲, 张炳华. 两歧双歧杆菌对鼠伤寒感染小鼠模型的生物治疗作用[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2006, 29(6): 483-484. [39] Pimentel M,Chatterjee S,Chang C,et al.A New Rat Model Links Two Contemporary Theories in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(4):982-989. [40] Ross S, Controni G, Khan W. Resistance of shigellae to ampicillin and other antibiotics. Its clinical and epidemiological implications. JAMA. 1972;221(1):45-47. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||