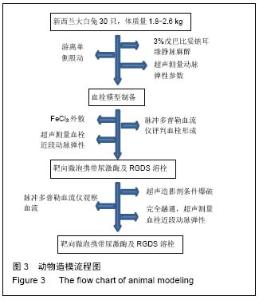
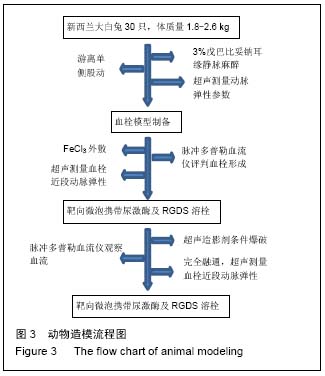
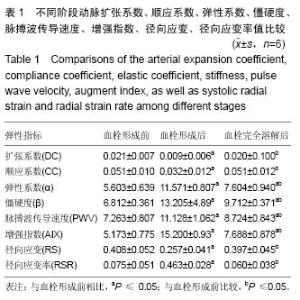
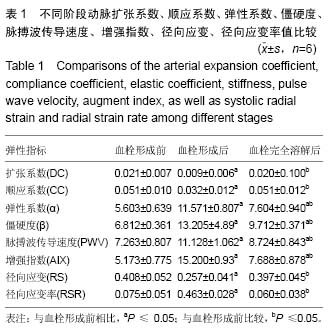
| [1] Dzeko M, Peters CD, Kjaergaard KD,et al.Aortic pulse wave velocity results depend on which carotid artery is used for the measurements.J Hypertens.2013;31(1): 117-122.[2] 万琳媛,谢明星,吕清,等.超声评价下肢动脉粥样硬化性疾病患者股动脉僵硬度与心功能关系的初步研究[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2012,21(8):675-678.[3] Turiel M, Gianturco L, Ricci C,et al. Silent cardiovascular involvement in patients with diffuse systemic sclerosis: a controlled cross-sectional study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken).2013;65(2): 274-280.[4] 王晓燕,贾永平,吕吉元,等.动脉僵硬度指数与冠脉狭窄程度的相关性研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2010, 08(6):671-673.[5] 严子君,张瑞岩,左君丽等.多种大动脉僵硬度指标的联合应用对冠心病预测价值的研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2010,12(1):23-26.[6] Ichino N, Osakabe K, Sugimoto K,et al.The stiffness parameter β assessed by an ultrasonic phase-locked echo-tracking system is associated with plaque formation in the common carotid artery.J Med Ultrason. 2012;39(1):3-9. [7] 吴长君,雷博,张璐,等.QAS技术对2型糖尿病患者颈动脉弹性的评价[J].中国超声医学杂志,2011,27(11): 997-1001. [8] Demaria RG, Vernhet H, Aya G, et al .Experimental model for comparative evaluation of pharmacologically induced vasodilation of arterial wall mechanical properties.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2003;42(3):389-394.[9] 王文娟,白梅,蔡江涛,等.超声技术对睡眠呼吸暂停患者左室几何构型的评价及其与颈动脉结构和功能的相关性研究[J].海南医学院报,2015,21(10):1437-1439,1442.[10] Pokrovski? AV, Kuntsevich GI, Zotikov EA, et al. Structural-and-functional alterations in the arterial wall and clinical manifestations of nonspecific aortoarteritis. Angiol Sosud Khir,2009;15(1):7-16.[11] Aminuddin A, Chellappan K, Maskon O, et al. Augmentation index is a better marker for cardiovascular risk in young Malaysian males. A comparison of involvement of pulse wave velocity, augmentation index,and C-reactive protein.Saudi Med J.2014;35(2):138-146.[12] Barnes JN, Nualnim N, Sugawara J,et al.Arterial stiffening, wave reflection, and inflammation in habitually exercising systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Am J Hypertens.2011;24(11):1194-200.[13] Aminuddin A, Chellappan K, Maskon O,et al.Augmentation index is a better marker for cardiovascular risk in young Malaysian males. A comparison of involvement of pulse wave velocity, augmentation index,and C-reactive protein.SSaudi Med J.2014;35(2):138-146.[14] Hayashi S,Yamada H,Bando M,et al.Augmentation index does not reflect risk of coronary artery disease in elderly patients.Circ J.2014;78(5):1176-1182.[15] Dzeko M, Peters CD, Kjaergaard KD,et al.Aortic pulse wave velocity results depend on which carotid artery is used for the measurements.J Hypertens.2013;31(1): 117-122.[16] Sae Young Jae,Kevin Heffernan,Jeffrey Woods,et al.Abstract 4854: Acute Systemic Inflammation Increases Central Blood Pressure and Pulse Wave Velocity in Healthy Subjects.Circulation. 2009;120(18): S1006[17] Sie MP, Mattace-Raso FU, Uitterlinden AG,et al.The interleukin-6-174 G/C promoter polymorphism and arterial stiffness; the Rotterdam Study. Vasc Health Risk Manag.2008;4(4):863-869. [18] Nikitina NM, Rebrov AP.Cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ter Arkh.2009;81(6):29-34.[19] hirai K, Utino J, Otsuka K, et al.A novel blood pressure-independent arterial wall stiffness parameter; cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI). J Atheroscler Thromb.2006;13(2):101-107.[20] Celik T, Yuksel UC, Fici F,et al.Vascular inflammation and aortic stiffness relate to early left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in prehypertension. Blood Press. 2013;22(2):94-100.[21] Rosfors S, Persson LM, Blomgren L.Computerized venous strain-gauge plethysmography is a reliable method for measuring venous function. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2014;47(1):81-86. [22] 罗玉群,全学模,王荞等.速度向量成像技术评价挫伤股动脉管壁短轴方向应变及应变率[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(26):5067-5070. [23] Kawasaki T, Fukuda S, Shimada K, et al. Direct measurement of wall stiffness for carotid arteries by ultrasound strain imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009;22(12):1389-1395. [24] 许磊,曹铁生,刘禧,等.血管环向应变在评价高血压患者颈动脉弹性中的价值[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2010,19(10): 842-845.[25] 郭朝锋,穆玉明,关丽娜等.超声在兔股动脉血栓模型评价中的价值[J].中华超声影像学志,2010,19(10):901-904.[26] 唐映红,梁燕,杨静,等.FeCl3诱导的大鼠颈总动脉血栓模型血浆TXA2、PGI2、抗凝和纤溶活性的变化[J].中国药理学通报,2006,22(11):1353-1356. [27] 董丽丽.超声检查冠心病患者心外膜脂肪层厚度与颈部血管弹性及其两者的相关性研究[J].中国实用医药,2015, (27):69-69,70.[28] 刘涛.超声测量冠心病患者心外膜脂肪层厚度与颈部血管弹性的相关性[J].临床医学,2015,35(5):63-64.[29] van Bussel BC, Schouten F, Henry RM,et al. Endothelial dysfunction and low-grade inflammation are associated with greater arterial stiffness over a 6-year period.Hypertension. 2011;58(4):588-95.[30] Catalano M,Lamberti-Castronuovo A,Catalano A,et al.Two-dimensional speckle-tracking strain imaging in the assessment of mechanical properties of carotid arteries: feasibility and comparison with conventional markers of subclinical atherosclerosis.Eur J Echocardiogr. 2011;12(7):528-535. [31] 黄晓春.超声二维应变成像评价高血压病患者颈总动脉弹性的研究[J].实用医技杂志,2012,19(9):903-905. |