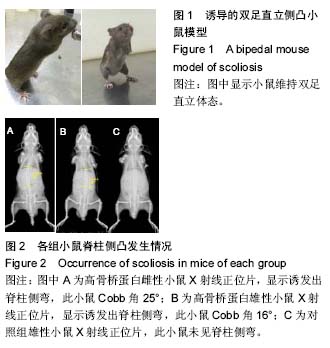
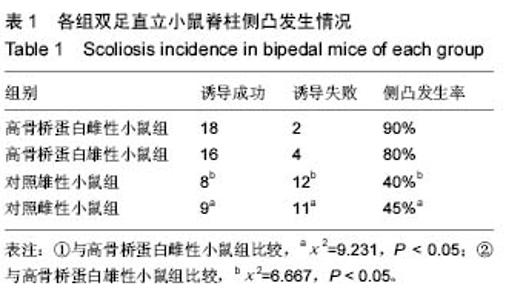
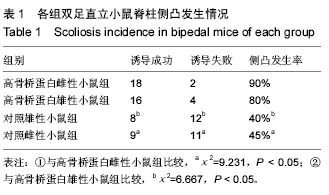
| [1] Hefti F. Pathogenesis and biomechanics of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). J Child Orthop. 2013;7(1): 17-24.
[2] Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet. 2008;371(9623):1527-1537.
[3] Machida M, Saito M, Dubousset J, et al. Pathological mechanism of idiopathic scoliosis: experimental scoliosis in pinealectomized rats. Eur Spine J. 2005; 14(9):843-848.
[4] Oyama J, Murai I, Kanazawa K, et al. Bipedal ambulation induces experimental scoliosis in C57BL/6J mice with reduced plasma and pineal melatonin levels. J Pineal Res. 2006;40(3):219-224.
[5] de Sèze M, Cugy E. Pathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis: a review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2012; 55(2):128-138.
[6] Asou Y, Rittling SR, Yoshitake H, et al. Osteopontin facilitates angiogenesis, accumulation of osteoclasts, and resorption in ectopic bone. Endocrinology. 2001; 142(3):1325-1332.
[7] Kojima H, Uede T, Uemura T. In vitro and in vivo effects of the overexpression of osteopontin on osteoblast differentiation using a recombinant adenoviral vector. J Biochem. 2004;136(3):377-386.
[8] Narisawa S, Yadav MC, Millán JL. In vivo overexpression of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase increases skeletal mineralization and affects the phosphorylation status of osteopontin. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(7):1587-1598.
[9] Yadav MC, Huesa C, Narisawa S, et al. Ablation of osteopontin improves the skeletal phenotype of phospho1(-/-) mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(11): 2369-2381.
[10] Moreau A, Franco A, Azeddine B, et al. High circulating levels of osteopontin are associated with idiopathic scoliosis onset and spinal deformity progression: Paper# 79. Spine Journal Meeting Abstracts: LWW, 2009:109.
[11] Sun GQ, Lam TP, Bobby NG, et al. High osteopontin plasma level associated with abnormal cortical bone mineral density in girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Studies in Health Technology & Informatics. 2012; 176(1):457.
[12] Xie N, Li M, Wu T, et al. Does elevated osteopontin level play an important role in the development of scoliosis in bipedal mice. Spine J. 2015;15(7): 1660-1664.
[13] Machida M, Dubousset J, Imamura Y, et al. An experimental study in chickens for the pathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(12): 1609-1615.
[14] Dubousset J, Queneau P, Thillard MJ. Experimental scoliosis induced by pineal and diencephalic lesions in young chickens: Its relation with clinical findings. Orthop Trans. 1983;7(7):4.
[15] Kanemura T, Kawakami N, Deguchi M, et al. Natural course of experimental scoliosis in pinealectomized chickens. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(14):1563-1567.
[16] Nette F, Dolynchuk K, Wang X, et al. The effects of exposure to intense, 24 h light on the development of scoliosis in young chickens. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2002;91:1-6.
[17] 肖军,吴志宏,邱贵兴,等. 直立姿势对脊柱侧凸易感性及侧凸曲线进展规律的影响[J].中华医学杂志, 2007,87(1): 48-52.
[18] Cheung KM, Wang T, Poon AM, et al. The effect of pinealectomy on scoliosis development in young nonhuman primates. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(18):2009-2013.
[19] 邱贵兴,肖军,吴志宏,等. 双足鼠直立姿势相关因素及促直立的措施[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2006,23(6):734-736.
[20] Leboeuf D, Letellier K, Alos N, et al. Do estrogens impact adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009;20(4):147-152.
[21] Warren MP, Brooks-Gunn J, Hamilton LH, et al. Scoliosis and fractures in young ballet dancers. Relation to delayed menarche and secondary amenorrhea. N Engl J Med. 1986;314(21):1348-1353.
[22] Janusz P, Kotwicka M, Andrusiewicz M,et al. Estrogen receptors genes polymorphisms and age at menarche in idiopathic scoliosis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:383.
[23] Fendri K, Patten S, Zaouter C,et al. Recent advances in the study of candidate genes for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2010;158:3-7.
[24] Inoue M, Minami S, Nakata Y, et al. Association between estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms and curve severity of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(21):2357-2362.
[25] Rusin B, Kotwicki T, G?odek A,et al. Estrogen receptor 2 expression in back muscles of girls with idiopathic scoliosis - relation to radiological parameters. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2012;176:59-62. |