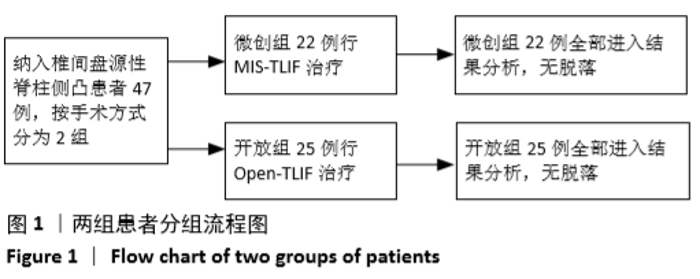
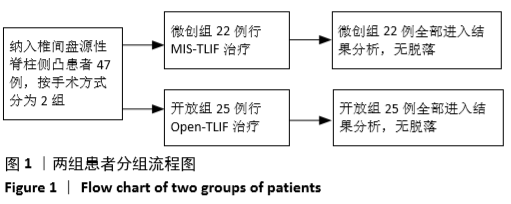
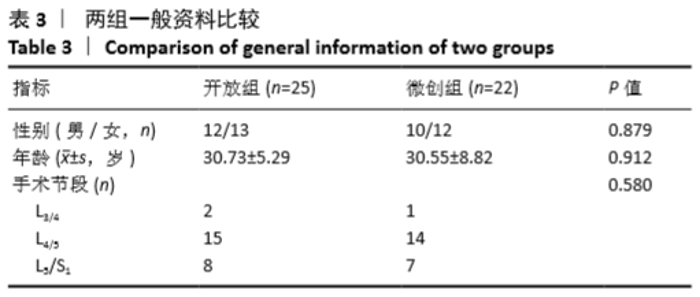
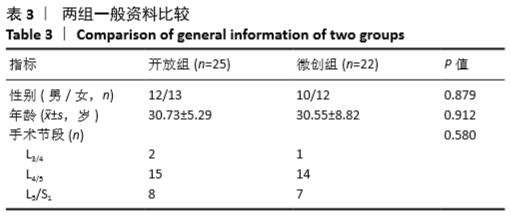
[1] MATSUI H, OHMORI K, KANAMORI M, et al. Significance of sciatic scoliotic list in operated patients with lumbar disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(3):338-342.
[2] SUK KS, LEE HM, MOON SH, et al. Lumbosacral scoliotic list by lumbar disc herniation. Spine. 2001;26(6):667-671.
[3] ZHAO J, ZHANG S, LI X, et al. Comparison of minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective cohort study. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:8693-8698.
[4] HAGIWARA Y, YABE Y, YAMADA H, et al. Effects of a wearable type lumbosacral support for low back pain among hospital workers: A randomized controlled trial. J Occup Health. 2017;59(2):201-209.
[5] WANG H, CHENG J, XIAO H, et al. Adolescent lumbar disc herniation: Experience from a large minimally invasive treatment centre for lumbar degenerative disease in Chongqing, China. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:1415-1419.
[6] CAHILL KS, DUNN I, GUNNARSSON T, et al. Lumbar microdiscectomy in pediatric patients: A large single-institution series. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010; 12:165-170.
[7] TU Z, WANG B, LI L, et al. Early experience of full endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for adolescent lumbar disc herniation with sciatic scoliosis. Pain Physician. 2018; 21:E63-E70.
[8] CHEN RQ, WATANABE K, HOSOGANE N, et al. Spinal coronal profiles and proximal femur bone mineral density in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:2433-2437.
[9] FINNESON BE, COOPER VR. A lumbar disc surgery predictive score card. A retrospective evaluation. Spine. 1979;4(2):141-144.
[10] ZHANG Y, LI W, XU L, et al. Sciatic scoliosis evolution after lumbar discectomy: a comparison between adolescents and young adults. Pain Physician. 2019; 22:E457-E465.
[11] SENCER A, YORUKOGLU AG, AKCAKAYA MO, et al. Fully endoscopic interlaminar and transforaminal lumbar discectomy: Short-term clinical results of 163 surgically treated patients. World Neurosurg. 2014; 82:884-890.
[12] WANG B, LÜ GH, LI J, et al. Contrast study of full-endoscopic interlaminar approach for the surgical treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011; 49:74-78.
[13] ZHU Z, ZHAO Q, WANG B, et al. Scoliotic posture as the initial symptom in adolescents with lumbar disc herniation: its curve pattern and natural history after lumbar discectomy. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2011; 12:216.
[14] WU W, CHEN Y, YU L, et al. Coronal and sagittal spinal alignment in lumbar disc herniation with scoliosis and trunk shift. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):264.
[15] TU Z, LI YW, WANG B, et al. Clinical outcome of full-endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for single-level lumbar disc herniation: A minimum of 5-year follow-up. Pain Physician. 2017; 20:E425-E430.
[16] WANG X, ZENG J, NIE H, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for pediatric lumbar disc herniation. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014; 30:897-902.
[17] KIM R, KIM RH, KIM CH, et al. The incidence and risk factors for lumbar or sciatic scoliosis in lumbar disc herniation and the outcomes after percutaneous endoscopic discectomy. Pain Physician.2015; 18:555-564.
[18] CHANG HK, CHANG HC, WU JC, et al. Scoliosis may increase the risk of recurrence of lumbar disc herniation after microdiscectomy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24:586-591.
[19] KAMBIN P, FOLEY KT, HOLLY LT, et al. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine. 2004;29(5):598-599
[20] SHUNWU F, XING Z, FENGDONG Z, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of degenerative lumbar diseases. Spine. 2010;35(17):1615-1620.
[21] LEE KH, YUE WM, YEO W, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of open versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(11):2265-2270.
[22] KIM R, KIM RH, KIM CH, et al. The incidence and risk factors for lumbar or sciatic scoliosis in lumbar disc herniation and the outcomes after percutaneous endoscopic discectomy. Pain Physician. 2015; 18 (6):555-564.
[23] SPANOS GP. Sciatic scoliosis, its natural history and the ability of the Mckenzie management to influence it. Studies in health technology and informatics. 2002;91:332-335.
[24] LI M, YANG H, YANG Q. Full-endoscopic technique discectomy versus microendoscopic discectomy for the surgical treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Pain Physician. 2015;18:359-363.
[25] BIRKENMAIER C, KOMP M, LEU HF, et al. The current state of endoscopic disc surgery: Review of controlled studies comparing full-endoscopic procedures for disc herniations to standard procedures. Pain Physician. 2013;16:335-344.
[26] CHOI KC, LEE JH, KIM JS, et al. Unsuccessful percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: A single-center experience of 10,228 cases. Neurosurgery. 2015; 76:372-380; discussion 380-381.
[27] KIM HS, PARK JY. Comparative assessment of different percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar lumbar discectomy (PEID) techniques. Pain Physician. 2013;16:359-367.
[28] RUETTEN S, KOMP M, MERK H, et al. Use of newly developed instruments and endoscopes: Full-endoscopic resection of lumbar disc herniations via the interlaminar and lateral transforaminal approach. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6:521-530.
[29] CHUMNANVEJ S, KESORNSAK W, SARNVIVAD P, et al. Full endoscopic lumbar discectomy via interlaminar approach: 2-year results in ramathibodi hospital. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011; 94:1465-1470. |