Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (45): 6814-6820.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.45.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of miR-2135 on the P19 cell proliferation and differentiation into cardiomyocytes
Li Hui
- Second Ward, Department of Cardiology, First People’s Hospital of Shangqiu, Shangqiu 476000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2016-10-09Online:2016-11-04Published:2016-11-04 -
About author:Li Hui, Attending physician, Second Ward, Department of Cardiology, First People’s Hospital of Shangqiu, Shangqiu 476000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Hui. Effect of miR-2135 on the P19 cell proliferation and differentiation into cardiomyocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(45): 6814-6820.
share this article
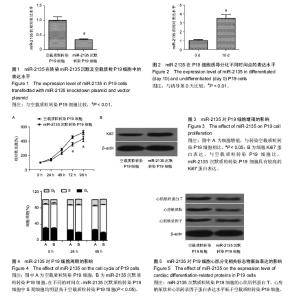
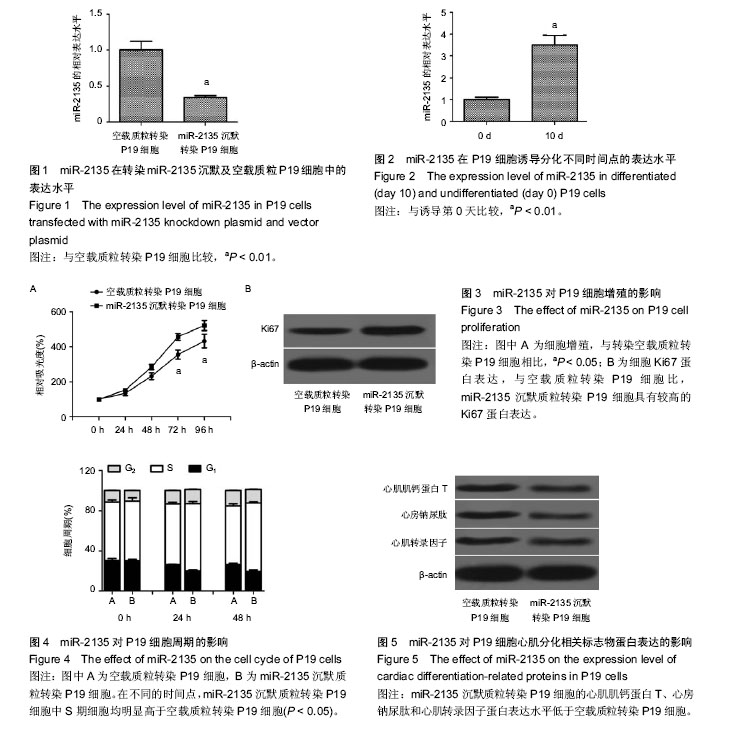
2.1 miR-2135低表达稳定株的成功建立 miR-2135在转染miR-2135沉默质粒的P19细胞中的表达水平明显低于其在转染空载质粒的P19细胞中的表达水平,证实miR-2135低表达稳定株成功建立,见图1。 2.2 miR-2135在分化的P19细胞中高表达 采用qRT-PCR检测miR-2135在P19细胞诱导分化第0,10天中的表达水平,发现miR-2135在P19细胞分化第10天的表达水平明显高于其在第0天中的表达水平,见图2。 2.3 miR-2135抑制P19细胞增殖 MTT检测结果发现,miR-2135沉默质粒转染P19细胞的增殖速度明显高于空载质粒转染 P19细胞(图3A)。此外,还采用蛋白免疫印迹检测增殖相关蛋白Ki67在两组细胞中的表达水平,发现与空载质粒转染P19细胞比,miR-2135沉默质粒转染P19细胞具有较高的Ki67蛋白表达(图3B)。这些结果表明,miR-2135抑制P19细胞增殖。 2.4 miR-2135使P19细胞阻滞于G1/S期 流式细胞仪检测结果发现,自恢复胎牛血清后,在不同的时间点,miR-2135沉默质粒转染P19细胞中S期细胞均明显高于空载质粒转染P19细胞(P < 0.05),表明miR-2135低表达能够促进P19细胞进入S期(图4)。由于S期为细胞染色质的合成期,miR-2135低表达促进更多细胞进入S期的现象表明,miR-2135具有抑制P19细胞增殖的作用。 2.5 miR-2135促进P19细胞向心肌细胞的分化 miR-2135沉默质粒转染P19细胞的心肌肌钙蛋白T、心房钠尿肽和心肌转录因子蛋白表达水平低于空载质粒转染P19细胞(图5);miR-2135低表达抑制P19细胞分化的现象表明,miR-2135能够促进P19细胞向心肌细胞的分化进程。"
| [1] Zaffran S,Frasch M.Early signals in cardiac development.Circ Res.2002; 91(6):457-469. [2] 王春梅,姜涛,周春燕.诱导心脏发生的早期信号通路[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2004,20(5):572-577. [3] Miyazono K,Kamiya Y,Morikawa M.Bone morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J Biochem.2010;147(1):35-51. [4] Bajolle F,Zaffran S,Bonnet D.Genetics and embryological mechanisms of congenital heart diseases.Arch Cardiovasc Dis.2009;102(1):59-63. [5] Kajstura J,Rota M,Cappetta D,et al.Cardiomyogenesis in the aging and failing human heart. Circulation. 2012; 126(15):1869-1881. [6] Aguilar JS,Begum AN,Alvarez J,et al.Directed cardiomyogenesis of human pluripotent stem cells by modulating Wnt/β-catenin and BMP signalling with small molecules. Biochem J.2015;469(2):235-241. [7] Müller M,Stockmann M,Malan D,et al.Ca2+ activated K channels-new tools to induce cardiac commitment from pluripotent stem cells in mice and men.Stem Cell Rev.2012;8(3):720-740. [8] Zhao Y,Ransom JF,Li A,et al.Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2.Cell.2007;129(2):303-317. [9] Morton SU,Scherz PJ,Cordes KR,et al.microRNA-138 modulates cardiac patterning during embryonic development.PNAS.2008;105(46):17830-17835. [10] Qin DN,Qian L,Hu DL,et al.Effects of miR-19b overexpression on proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in P19 cell model of cardiac differentiation in vitro. Cell Biochem Biophys.2013;66(3):709-722. [11] Hoffman JI,Kaplan S.The incidence of congenital heart disease.J Am Coll Cardiol.2002;39(12):1890-1900. [12] Yutzey KE,Colbert M,Robbins J.Ras-related signaling pathways in valve development: ebb and flow. Physiology. 2005;20(6):390-397. [13] Bruneau BG.The developmental genetics of congenital heart disease.Nature.2008; 451(7181):943-948. [14] Olson EN.Gene regulatory networks in the evolution and development of the heart. Science. 2006; 313 (5795):1922-1927. [15] van der Heyden MA,Defize LH.Twenty one years of P19 cells: what an embryonal carcinoma cell line taught us about cardiomyocyte differentiation. Cardiovasc Res.2003;58(2):292-302. [16] van der Heyden MA,van Kempen MJ,Tsuji Y,et al. P19 embryonal carcinoma cells: a suitable model system for cardiac electrophysiological differentiation at the molecular and functional level.Cardiovasc Res. 2003; 58(2):410-422. [17] 万楠,刘培燕,邱广蓉,等.miR-324-5p 在先天性心脏病患者血浆中的表达[C].第十二次全国医学遗传学学术会议论文汇编,2014. [18] 夏曦.儿童先天性心脏病心力衰竭与血清 miR-30a水平的关系[J].临床儿科杂志,2014, 32(7):607. [19] Sluijter JP,van Mil A,van Vliet P,et al.MicroRNA-1 and-499 regulate differentiation and proliferation in human-derived cardiomyocyte progenitor cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2010;30(4):859- 868. [20] Cheng Y,Ji R,Yue J,et al.MicroRNAs are aberrantly expressed in hypertrophic heart: do they play a role in cardiac hypertrophy? Am J Pathol.2007;170(6): 1831-1840. [21] Ventura A,Young AG,Winslow MM,et al.Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17∼ 92 family of miRNA clusters.Cell.2008; 132(5):875-886. [22] Li Q,Song XW,Zou J,et al.Attenuation of microRNA-1 derepresses the cytoskeleton regulatory protein twinfilin-1 to provoke cardiac hypertrophy.J Cell Sci. 2010;123(14):2444-2452. [23] Wong S,Ritner C,Ramachandran S,et al.miR-125b promotes early germ layer specification through Lin28/let-7d and preferential differentiation of mesoderm in human embryonic stem cells.PLoS One.2012;7(4):e36121. [24] Li X,Wang J,Jia Z,et al.MiR-499 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis during late-stage cardiac differentiation via Sox6 and cyclin D1.PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74504. [25] Rajala K,Pekkanen-Mattila M,Aalto-Setälä K.Cardiac differentiation of pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cells Int. 2011;2011:383709. [26] Yao CX,Wei QX,Zhang YY,et al.miR-200b targets GATA-4 during cell growth and differentiation.RNA Biol.2013;10(4):465-480. [27] Knezevic I,Patel A,Sundaresan NR,et al.A novel cardiomyocyte-enriched MicroRNA, miR-378, targets insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor implications in postnatal cardiac remodeling and cell survival.J Biol Chem.2012;287(16):12913-12926. [28] Clément T,Salone V,Rederstorff M.Dual Luciferase Gene Reporter Assays to Study miRNA Function.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1296:187-198. [29] Meng J,Shi GL,Luan YS.Plant miRNA function prediction based on functional similarity network and transductive multi-label classification algorithm. Neurocomputing.2015;179:283-289. [30] Enlund E,Fischer S,Handrick R,et al.Establishment of Lipofection for Studying miRNA Function in Human Adipocytes.PLoS One.2014;9(5):e98023. [31] Schöniger C,Arenz C.Perspectives in targeting miRNA function.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013;21(20):6115-6118. [32] DeCastro AJ,DiRenzo J.miRNA function and modulation in stem cells and cancer stem cells. Microrna Diagn Ther.2014;1(1):222-227. [33] Chen X,Liu MX,Yan GY. RWRMDA: predicting novel human microRNA–disease associations. Mol Biosyst. 2012;8(10):2792-2798. [34] Lau P,Bossers K,Salta E,et al.Alteration of the microRNA network during the progression of Alzheimer's disease.EMBO Mol Med.2013; 5(10): 1613-1634. [35] Hudson RS,Yi M,Esposito D,et al.MicroRNA-106b-25 cluster expression is associated with early disease recurrence and targets caspase-7 and focal adhesion in human prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2013;32(35): 4139-4147. [36] van Rooij E,Olson EN.MicroRNA therapeutics for cardiovascular disease: opportunities and obstacles.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2012;11(11):860-872. [37] Li A,Yu J,Kim H,et al.MicroRNA array analysis finds elevated serum miR-1290 accurately distinguishes patients with low-stage pancreatic cancer from healthy and disease controls.Clin Cancer Res.2013; 19(13): 3600-3610. [38] Patel V,Williams D,Hajarnis S,et al.miR-17~92 miRNA cluster promotes kidney cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease. PNAS. 2013;110(26): 10765-10770. [39] Pirola CJ,Gianotti TF,Castaño GO,et al.Circulating microRNA signature in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: from serum non-coding RNAs to liver histology and disease pathogenesis.Gut.2015;64(5):800-812. [40] Dangwal S,Thum T.microRNA therapeutics in cardiovascular disease models.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.2014;54:185-203. [41] Alvarez-Erviti L,Seow Y,Schapira AH,et al.Influence of microRNA deregulation on chaperone-mediated autophagy and α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Dis.2013;4(3):e545. [42] Gong Y,Lu J,Yu X,et al.Expression of Sp7 in Satb2-induced osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow stromal cells is regulated by microRNA-27a. Mol Cell Biochem.2016;417(1-2):7-16. [43] Qiu J,Zhou XG,Zhou XY,et al.Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in 3T3-L1 adipocytes overexpressing C10orf116.Mol Biol Rep.2013; 40(11): 6469-6476. [44] Hu DL,Liu YQ,Chen FK,et al.Differential expression of microRNAs in cardiac myocytes compared to undifferentiated P19 cells.Int J Mol Med.2011;28(1): 59-64. [45] Mishaly D,Ghosh P,Preisman S.Minimally invasive congenital cardiac surgery through right anterior minithoracotomy approach.Ann Thorac Surg.2008; 85(3):831-835. [46] Iribarne A,Easterwood R,Chan EY,et al.The golden age of minimally invasive cardiothoracic surgery: current and future perspectives.Future Cardiol.2011; 7(3):333-346. [47] Omran A,Elimam D,Webster KA,et al.MicroRNAs: a new piece in the paediatric cardiovascular disease puzzle.Cardiol Young.2013;23(5):642-655. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||