Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (34): 5142-5148.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.34.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of different materials for skull defect repair
Zhang Hai-fang
- Department of Neurosurgery, Feicheng Mining Center Hospital, Feicheng 271608, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2016-05-29Online:2016-08-19Published:2016-08-19 -
About author:Zhang Hai-fang, Physician, Department of Neurosurgery, Feicheng Mining Center Hospital, Feicheng 271608, Shandong province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Hai-fang. Comparison of different materials for skull defect repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(34): 5142-5148.
share this article
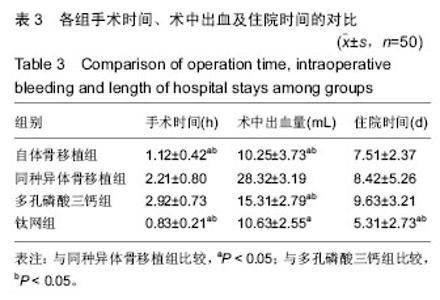
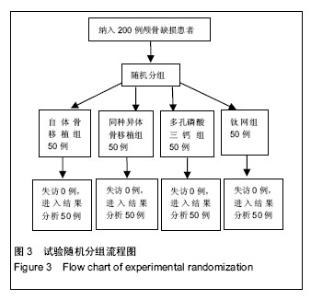
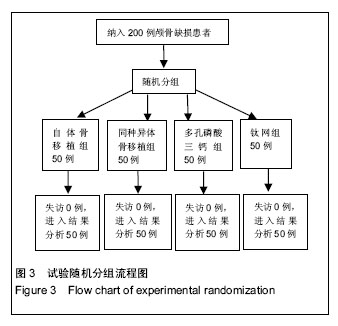
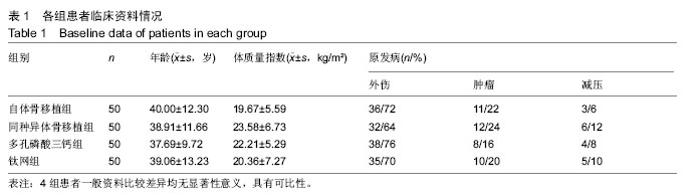
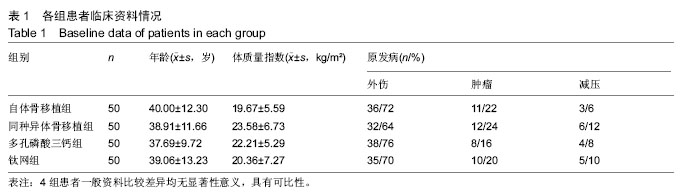
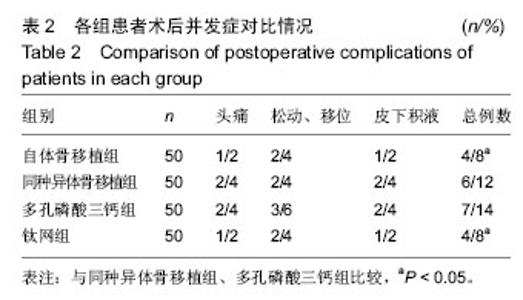
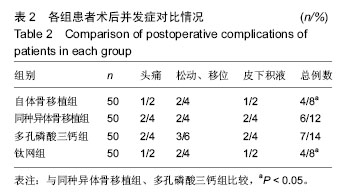
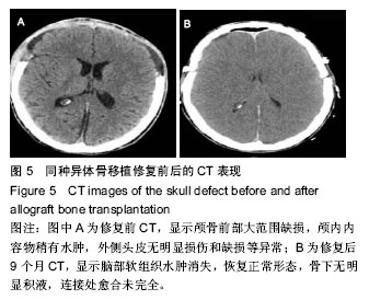
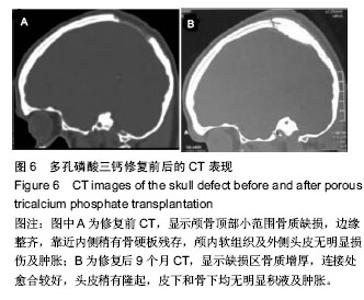
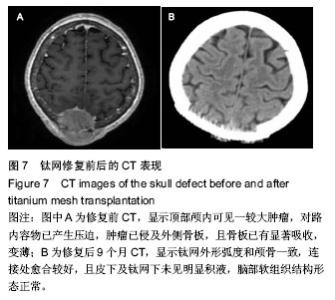
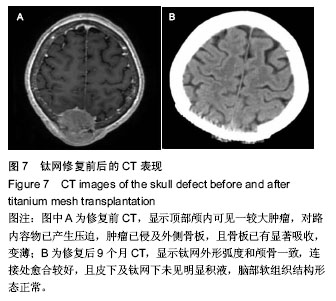
2.5 各组手术时间、术中出血及住院时间的比较 钛网组、自体骨移植组手术时间显著少于同种异体骨移植组、多孔磷酸三钙组(P < 0.05),钛网组与自体骨移植组手术时间比较差异无显著性意义,多孔磷酸三钙组与同种异体骨移植组手术时间比较差异无显著性意义;钛网组、自体骨移植组术中出血量显著少于同种异体骨移植组、多孔磷酸三钙组(P < 0.05),钛网组与自体骨移植组术中出血量比较差异无显著性意义,多孔磷酸三钙组术中出血量显著少于同种异体骨移植组(P < 0.05);钛网组住院时间最少,显著少于同种异体骨移植组、多孔磷酸三钙组(P < 0.05),其余组间住院时间两两比较差异均无显著性意义,见表3。 "
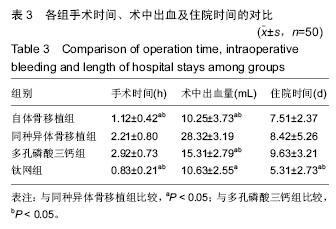
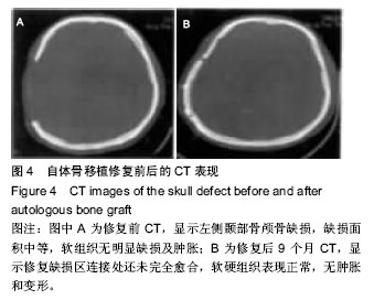
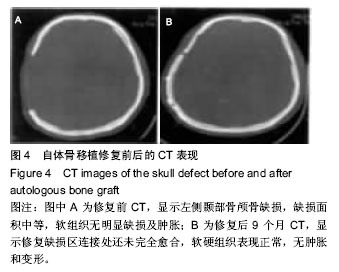
2.6 各组骨性愈合评分比较 植入后3个月时,自体骨移植组骨愈合性显著高于同种异体骨移植组、多孔磷酸三钙组(P < 0.05),钛网组骨愈合性高于多孔磷酸三钙组(P < 0.05),自体骨移植组与钛网组骨愈合性比较差异无显著性意义,同种异体骨移植组与多孔磷酸三钙组、钛网组骨愈合性比较差异无显著性意义;植入6个月时,自体骨移植组骨愈合性显著高于其他3组(P < 0.05),钛网组骨愈合性高于多孔磷酸三钙组(P < 0.05),其余组间骨愈合性两两比较差异均无显著性意义;植入9个月后,自体骨移植组和钛网组愈合性相差不多(P > 0.05),都显著高于多孔磷酸三钙组(P < 0.05),同种异体骨移植组骨愈合性高于多孔磷酸三钙组(P > 0.05),同种异体骨移植组与自体骨移植组、钛网组骨愈合性比较差异无显著性意义,见表4。"
| [1] 任维维,周志武.神经干细胞移植治疗颜脑损伤的研究进展[J].中外医学研究,2012,10(1):163-164.
[2] 张延平.颅内出血的外科治疗[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2010:7-9.
[3] Hu YE,Mao JH,Zhu Y,et al.Nerve growth factor pretreatment against glutaxnate-induced hippocampal neuronal injury: action mechanism of phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome.Neural Regen Res.2010;5(1):5-9.
[4] 张杰,施庆余,罗爱林.麻醉期间目标导向液体治疗对胶质瘤开颅切除术患者预后的影响[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2012,41(1):2299-2300.
[5] Brouwers HB,Golddstein JN.Therapeutic strateies in acute intracerebral hemorrhage.Neurotherapeuties. 2012;11(9):87-88.
[6] 曾春生,荆国杰,姚晓腾,等.小骨窗与传统大骨瓣开颅血肿清除术治疗高血压脑出血的疗效比较[J].河南外科学杂志,2014,20(4):1-2.
[7] Abu-Abeeleh M,Bani Ismail ZA,Alzaben KR,et al. A preliminary study of the use of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells for the treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in a rat model.Comp Clin Pathol.2010;19(1):1-4.
[8] 张艳军,孙海波,薛维华,等.高血压基底节区脑出血量最佳微创手术时机研究[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2013,30(1):68-69
[9] 陈兰,孙敏,张皑峰,等.生物活性材料支架诱导成年大鼠神经再生脑损伤的研究[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2014, 19(4):209-210.
[10] 张天祥,杨波,关方霞,等.静脉移植人脂肪间质干细胞治疗大鼠卢贞脑损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(14):2551-2556.
[11] Aguirre A,Rubio ME,Gallo V.Notch and EGFR pathway interaction regulates neural stem cell number and self-renewal.Nature. 2010;467(7313):323-327.
[12] Lavado A,Lagutin OV,Chow LM,et al.Prox1 is required for granule cell maturation and intermediate progenitor maintenance during brain neurogenesis.PLoS Biol. 2010;8(8):456-457.
[13] Ohira1 K,Furuta T,Hioki H,et al.Ischemia-induced neurogenesis of neocortical layer 1 progenitor cells. Nat Neurosci.2010;13(2):173-179.
[14] 王其平,那汉荣,高恒,等.帽状腱膜下计算机三维塑形钛网修补颅骨缺损25例分析[J].泰山医学院学报,2010, 31(12): 963-964.
[15] 金铃江,张月清,林达,等.数字化三维成形钛网修补颅骨缺损33例临床分析[J].浙江创伤外科,2010,15(4):528-529.
[16] 罗桂云,吕梁,季云海.颅内动脉狭窄支架置入与植入材料的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(25):110-111.
[17] Zhang XQ.Cerebrovascular stent types and hyperperfusion syndrome following stenting.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010; 14(22):4119-4122.
[18] 韦鹏翔,李丹青,周玉嘉,等.人工硬脑膜在神经外科手术中的应用:附100例分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(29):10-11.
[19] 穆霄静,侯芳,徐敏宁,等.脱细胞生物膜修复硬膜缺损的多中心临床试验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2011,36(1): 73-74.
[20] 陈汇浩.壳聚糖硬膜补片和羟丁基壳聚糖修复硬脑膜的实验研究[D].上海:第二军医大学, 2011:1-4.
[21] 周玉峰,黄梅,邓聪颖,等.人工硬脑膜材料的生物相容性[J].中古组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(16):234-235.
[22] 张念平,付振,王元飞,等.硬脑膜修补材料在神经外科手术中的应用[J].中国医学创新,2010,7(2):129-131.
[23] 凌成明,刘业,石强,等.灭活自体颅骨复位治疗颅骨缺损44例[J].甘肃医药,2011,30(1):46-47.
[24] 郎福新,牟静.钛网边角料治疗粉碎凹陷骨折25例临床体会[J].基层医学论坛,2011,15(10):377-378.
[25] 倪万成,董玉萍,张侃玺,等.钛网边角料在颅骨凹陷粉碎性骨折中的应用[J].宁夏医学杂志, 2011, 33(5):446-447.
[26] Hansen DV,Lui JH,Parker PR,et al.Neurogenic radial glia in the outer subventricular zone of human neocortex.Nature.2010;464(7288):554-561.
[27] 李邦安,刘鹏鹏.数字化多点成型技术塑形钛网修补颅骨缺损16例[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2010,35(7):707-709.
[28] 李先松,陈治标.CT颅骨三维成像塑形钛网修补颅骨68例临床分析[J].实用医院临床杂志,2011,8(1):94-95.
[29] 熊杰,姜岩.不同颅内植入材料对脑损伤修复的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,42(15):123-124.
[30] Blaiss CA,Yu TS,Zhang G,et al.Temporally specified genetic ablation of neurogenesis impairs cognitive recovery after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci.2011; 31(13):4906-4916.
[31] Yan RZ,Luo DM,Qin XY,et al.Digital modeling for the individual mandibular 3D mesh scaffold based on 3D printing technology.Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016;51(5):280-285.
[32] Parshikov VV,Mironov AA,Kazantsev AA,et al. Intraperitoneal and retromuscular abdominal wall repair using ultra-light and titanium-containing polypropylene mesh (experimental research).Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2016;(4):40-44.
[33] Xu L,Kong Peng,Xu ZW.Anterior corpectomy decompression and titanium mesh bone iraft fusion combined with titanium nate fixation for the treatment of the multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016;29(3):211-215.
[34] Li H,Dong Q.Comment on Wang et al.One-stage posterior focus debridement, interbody graft using titanium mesh cages, posterior instrumentation and fusion in the surgical treatment of lumbo-sacral spinal tuberculosis in the aged.Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1125.
[35] Levine RA,McAllister BS.Implant Site Development Using Ti-Mesh and Cellular Allograft in the Esthetic Zone for Restorative-Driven Implant Placement: A Case Report.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2016;36(3):373-381.
[36] Yamada H,Nakaoka K,Sonoyama T,et al.Clinical Usefulness of Mandibular Reconstruction Using Custom-Made Titanium Mesh Tray and Autogenous Particulate Cancellous Bone and Marrow Harvested From Tibia and/or Ilia.J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(3): 586-92.
[37] Ozaki H,Sakurai H,Yusa K,et al.Mandibular reconstruction with fibula bone graft followed by PCBM graft with titanium mesh tray.J Oral Implantol.2016. [Epub ahead of print]
[38] Gordon CR,Tamargo RJ,Brem H,et al.Discussion of Effect of Reflection of Temporalis Muscle During Cranioplasty With Titanium Mesh After Standard Trauma Craniectomy.J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(3): 654-655. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [14] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [15] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||