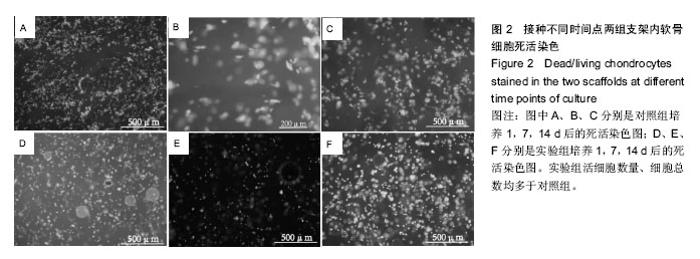
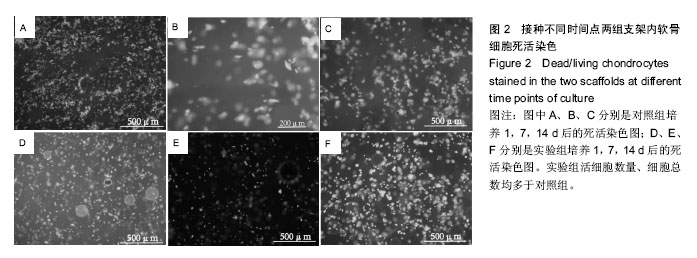
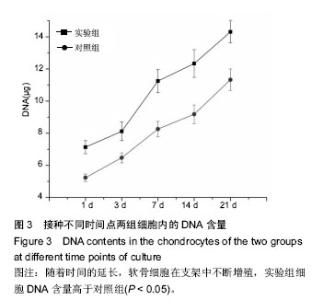
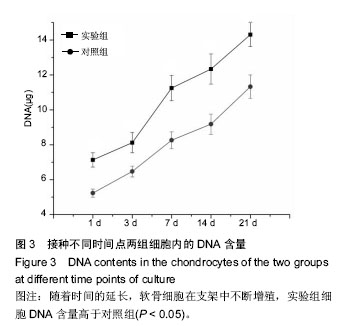
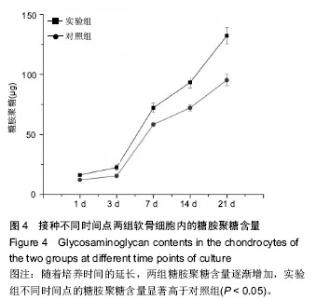
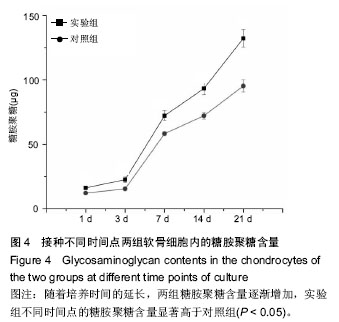
| [1] Johnstone B,Alini M,Cucchiarini M,et al.Tissue engineering for articular cartilage repair the state of the art. Eur Cells Mater.2013;25:248-267.
[2] Matsunaga D,Akizuki S,Takizawa T,et al.Repair of articular cartilage and clinical outcome after osteotomy with microfracture or abrasion arthroplasty for medial gonarthrosis.Knee.2007;14(6):465-471.
[3] 刘奕,谢林.组织工程技术修复损伤关节软骨的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(41):7310-7316.
[4] Eyrich D,Brandl F,Appel B,et al.Long-term stable fibrin gels for cartilage engineering.Biomaterials. 2007; 28(1):55-65.
[5] Balakrishnan B,Jayakrishnan A.Self-cross-linking biopolymers as injectable in situ forming biodegradable scaffolds.Biomaterials.2005;26:3941-3951.
[6] 徐虎,胡蕴玉,刘松波,等.可注射性藻酸钙凝胶载体组织工程性软骨的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2000,20(9): 19-22.
[7] 李卫平,韩运,黄建荣,等.可注射性材料藻酸钠体外培养幼猪关节软骨细胞及形成组织工程化软骨的能力[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(14):2705-2707.
[8] 周建林,方洪松,彭昊,等.自体、异体骨软骨移植及组织工程材料修复的关节软骨损伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(34):5530-5535.
[9] 朱琳,刘海霞,公衍道,等.利用细胞装配系统直接形成组织工程三维复合支架[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(48):9650-9654.
[10] 康红军,卢世璧,许文静,等.人脂肪干细胞结合微载体在生物反应器中向软骨细胞分化[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2007, 15(10):773-775,803.
[11] 宁斌,田周斌,贾堂宏.微载体培养技术在骨与软骨组织工程研究中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(8): 1459-1462.
[12] Shao X,Goh JC,Hutmacher DW,et al.Repair of large articular osteochondral defects using hybrid scaffolds and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model. Tissue Eng. 2006;12: 1539-1551.
[13] Yang Q,Peng J,Guo Q,et al.A cartilage ECM-derived 3-D porous acellular matrix scaffold for in vivo cartilage tissue engineering with PKH26-labeled chondrogenic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials.2008;29:2378-2387.
[14] Hong Y,Gao C,Xie Y,et al.Collagen-coated polylactide microspheres as chondrocyte microcarriers. Biomaterials.2005;26:6305-6313.
[15] Bouwmeester PS,Kuijer R,Homminga GN,et al.A retrospective analysis of two independent prospective cartilagerepair studies: autogenous perichondrial grafting versus subchondraldrilling 10 years post-surgery. J Orthop Res.2002;20(2):267-273.
[16] Harris JD,Siston RA,Pan X,et al. Flanigan, Autologous chondrocyte implantation: a systematic review.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(12):2220-2233.
[17] Chung HJ,Go DH,Bae JW,et al.Synthesis and characterization of Pluronic grafted chitosan copolymer as a novel injectable biomaterial.Curr Appl Phys. 2005; 5:485-488.
[18] Choi YS,Park S,Suh H.Adipose tissue engineering usingmesenchymal stem cells attached to injectable PLGA spheres.Biomaterials.2005;26:5855-5863.
[19] Matricali GA,Dereymaeker GPE,Luyten FP.Donor site morbidity after articular cartilage repair procedures : a review.Acta Orthop Belg.2010;76:669-674.
[20] Schrobback K, Klein TJ,Crawford R,et al.Effects of oxygen and culture system on in vitro propagation and redifferentiation of osteoarthritic human articular chondrocytes.Cell Tissue Res.2012;347:649-663.
[21] Cummings LJ,Waters SK, Tissue growth in a rotating bioreactor. Part II: ?uid ?ow and nutrient transport problems. Math Med Biol.2007;24:169-208.
[22] Li YY,Cheng HW,Cheung KMet al.Mesenchymal stem cell-collagen microspheres for articular cartilage repair: cell density and differentiation status.Acta Biomater. 2014;10:1919-1929.
[23] Malda J,van Blitterswijk CA,Grojec M,et al.Expansion of bovine chondrocytes on microcarriers enhances redifferentiation.Tissue Eng. 2003;9:939-948.
[24] Schrobback K,Klein TJ,Schuetz M,et el.Adult human articular chon-drocytes in a microcarrier-based culture system: expansion and redifferentiation.J Orthop Res 2011;29:539-546.
[25] Mathieu M,Vigier S,Labour MN,et al.Induction of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and cartilage formation by cross-linker-free collagen microspheres. Eur Cell Mater.2014;28:82-96.
[26] Hong Y,Gao C,Xie Y,et al.Collagen-coated polylactide microspheres as chondrocyte microcarriers. Biomaterials.2005;26:6305-6313. |