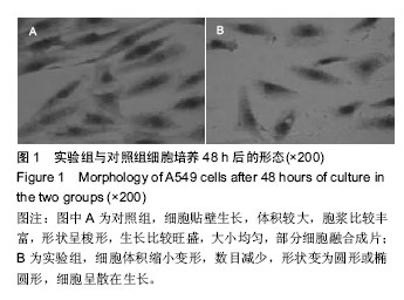
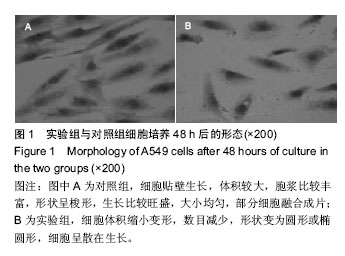
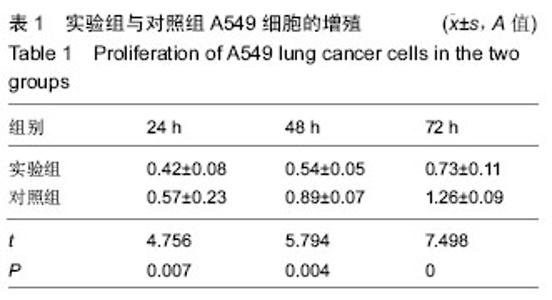
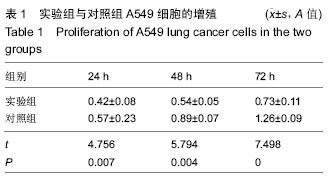
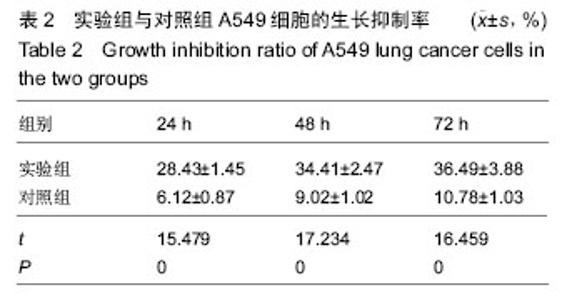
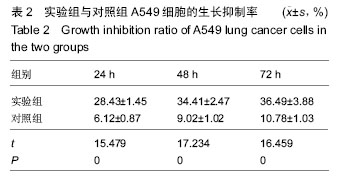
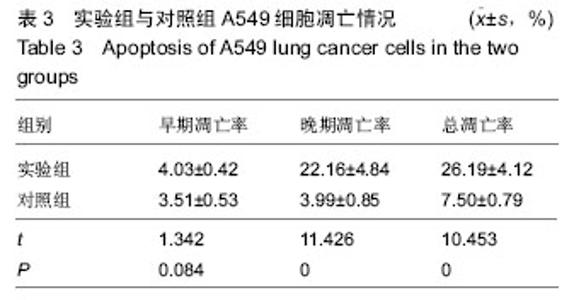
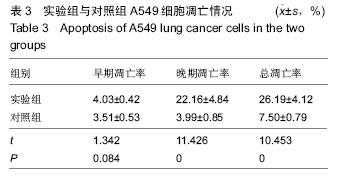
| [1] 肺癌筛查白皮书[J].中国肿瘤临床与康复, 2015,22(12): 1511.
[2] 聂立功.肺癌的筛查——机遇与挑战[J].中国肺癌杂志, 2015,18(12):721-724.
[3] 侯晶晶,王慧娟,张国伟,等.多原发肺癌的诊断与治疗[J].中国肺癌杂志,2015,18(12):764-769.
[4] Kilburn JM,Soike MH,Lucas JT,et al.Image guided radiation therapy may result in improved local control in locally advanced lung cancer patients.Pract Radiat Oncol.2016;6(3):e73-80.
[5] Ganti AK,Shostrom V,Alorabi M,et al.Early Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Octogenarian and Older Patients: A SEER Database Analysis.Clin Lung Cancer.2016;17(4):285-291.
[6] Yang JC, Srimuninnimit V, Ahn MJ,et al.First-Line Pemetrexed plus Cisplatin followed by Gefitinib Maintenance Therapy versus Gefitinib Monotherapy in East Asian Never-Smoker Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Final Overall Survival Results from a Randomized Phase 3 Study.J Thorac Oncol. 2016; 11(3): 370-379.
[7] 李超.中医综合方案维持治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌对疾病进展时间和生活质量的影响[J].实用中西医结合临床, 2015,15(4):36-37.
[8] 郑东京,许鑫,郑伟达.名老中医郑伟达治疗原发性支气管肺癌经验探析[J].中医临床研究,2015,7(18):1-4.
[9] 王富文.中医防护治疗对非小细胞肺癌化疗患者临床症状干预作用的随机对照研究[D].北京中医药大学, 2015.
[10] Jiang HW,Hu Q,He DF,et al.Clinical Application of Immune-related Response Criteria in Evaluating Chinese Medical Treatme for Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2015 ;35(9):1074-1077.
[11] Wu M,Lu P,Shi L,et al.Traditional Chinese patent medicines for cancer treatment in China: a nationwide medical insurance data analysis.Oncotarget. 2015; 6(35):38283-38295.
[12] Cui S,Zhao Y,Gu A,et al.Efficacy and tolerability of crizotinib in the treatment of ALK-positive, advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Chinese patients.Med Oncol. 2015;32(6):626.
[13] 齐元富,李慧杰,于连洋.纳米雄黄干预肺癌A549细胞对血管内皮生长因子及缺氧诱导因子-1表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(3):720-722.
[14] 齐元富,李慧杰,刘寨东.纳米雄黄对肺癌A549细胞增殖影响及其机制的探讨[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2013,20(1): 27-30.
[15] 刘寨东,齐元富,李秀荣.纳米雄黄协同顺铂对人肺癌A_(549)细胞b-FGF、MMP-9表达的影响[J].中国中医药科技,2013,20(3):252-253.
[16] Shi ZT.Report of a lung cancer survey in Hunan realgar miners.Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 1989;12(4):230-231,255-256.
[17] Ding W,Zhang L,Kim S,et al.Arsenic sulfide as a potential anti cancer drug.Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(2): 968-974.
[18] Tian Y,Wang X,Xi R,et al.Enhanced antitumor activity of realgar mediated by milling it to nanosize.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:745-757.
[19] 阎丽珠,周洁.半夏泻心汤治疗非小细胞肺癌化疗所致恶心呕吐40例[J].福建中医药,2012,43(2):4-5.
[20] 刘黎,周强,旷云祥.百合固金汤对肺癌患者生活质量的干预的观察[J].四川医学,2012,33(6):959-960.
[21] 张翔,朱斌,周建伟,等.补阳还五汤联合化疗治疗中晚期非小细胞肺癌的疗效[J].求医问药(下半月刊), 2012,10(11): 606-607.
[22] 钱钧,林胜友.龟鹿二仙汤对非小细胞肺癌患者化疗后外周血白细胞与细胞免疫功能的影响研究[J].江苏中医药, 2014,46(4):35-37.
[23] 胡传杏子.参苓白术加味汤对非小细胞肺癌化疗患者血清血管内皮生长因子、基质金属蛋白酶-9表达的影响[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(29):72-75.
[24] 张毓升.桃红四物汤加减联合化疗治疗气滞血瘀型肺癌[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(7):310-314.
[25] 王海波,陈鹊汀,赵丽,等.加味当归补血汤对非小细胞肺癌的辅助治疗疗效分析[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2014, 20(10):1428-1430.
[26] 周斌,单泽松,方媚媚,等.六君子汤加减辅助化疗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌31例临床观察[J].中医杂志, 2015,56(3): 219-222.
[27] 刘明,薛芳芳.化疗联合补中益气汤加减治疗中晚期非小细胞肺癌30例[J].湖南中医杂志,2013,29(5):42-44.
[28] 桂海涛,韦劲松,黄智芬,等.参芪泻白散联合化疗对晚期非小细胞肺癌生存质量的影响[J].中医学报, 2013,28(5): 629-631.
[29] 熊良庚,柏茂树,刘继明,等.沙参麦冬汤与桑菊饮联合同步放化疗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌临床观察[J].临床合理用药,2014,7(7A):46-47.
[30] 蔡江河,項昌盛,李静,等.自拟肺癌方治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌疗效观察[J].中医药临床杂志,2013,25(10):847-848.
[31] 蒋泽华,周梅娟,周红芬,等.固本解毒汤联合TP 方案治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌疗效研究[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2013,40 (10):2067-2069.
[32] 冯家昌,吴国水,王建芳,等.健脾润肺解毒汤联合化疗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌近期疗效观察[J].中华中医药学刊, 2013, 31(11):2567-2569.
[33] 吴继,徐振晔,王中奇,等.健脾化湿法对晚期非小细胞肺癌患者血清CEA、CYFRA21-1及免疫功能的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2014,32(4):874-876.
[34] 高海利,郭少芬,陈高峰.自拟下气散结汤治疗中晚期非小细胞肺癌35例临床观察[J].中国民族民间医药, 2014, 23(11): 73-74.
[35] 黄誉.注射用薏苡油联合泰素帝+顺铂治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌90例[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2012,21(33): 3695-3696.
[36] 于海英,高绍英,郝云霞.TP 方案联合华蟾素治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌的临床观察[J].实用癌症杂志, 2012,27(1): 55-57.
[37] 张海英.康莱特注射液对非小细胞肺癌的辅助治疗效果分析[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2014,23(9):997-999.
[38] 李东华.中西医结合治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌的临床研究[J].中医学报,2012,27(8):931-933.
[39] 夏艳阳,李艳.中药苦参抗肿瘤作用研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志,2014,26(1):91-92.
[40] 董菊,吴娟,王明艳,等.雄黄及其复方的毒理学研究进展[J].中国药理学和毒理学杂志,2011,25(6):601-603. |