Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (21): 3110-3116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.21.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of the small intestinal submucosa sponge
Sun Hui-zhe, Tian Wei, Zeng Liang, Wang Xiao-jie, Wang Zheng-dong, Ren Yue, Kuang Bao-ping
- Department of Anatomy, Shenyang Medical University, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2016-03-28Online:2016-05-20Published:2016-05-20 -
About author:Sun Hui-zhe, Master, Associate professor, Department of Anatomy, Shenyang Medical University, Shenyang 110034,Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Science Research General Project of Provincial Education Department in 2014, No. L2014416
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Hui-zhe, Tian Wei, Zeng Liang, Wang Xiao-jie, Wang Zheng-dong, Ren Yue, Kuang Bao-ping . Preparation of the small intestinal submucosa sponge[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(21): 3110-3116.
share this article
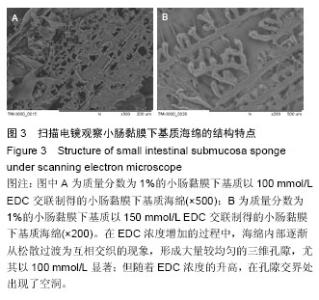
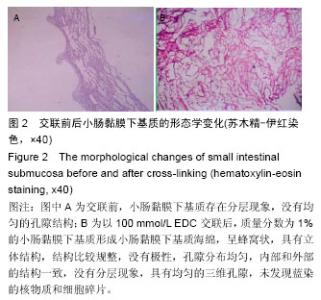
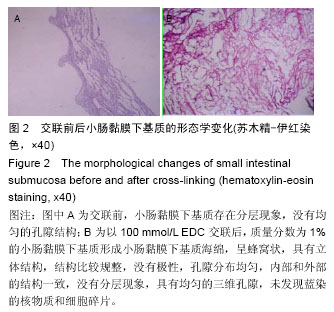
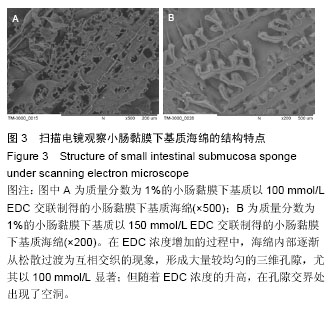
2.2 电镜观察结果 交联后,扫描电镜下小肠黏膜下基质海绵材料呈三维网孔状结构,孔间相通,随着小肠黏膜下基质质量分数的升高,出现了小肠黏膜下基质海绵孔径大小和密度的变化。在EDC浓度增加的过程中,海绵内部逐渐从松散过渡为互相交织的现象,形成大量较均匀的三维孔隙,尤其以100 mmol/L显著;但随着EDC浓度的升高,在孔隙交界处出现了空洞,见图3。在小肠黏膜下基质质量分数1%组孔径为100-150 µm,小肠黏膜下基质质量分数2%组孔径大小为150-200 µm,但随着小肠黏膜下基质质量分数的增加,孔径值逐渐下降,而且结构出现松散现象,因此质量分数1%的小肠黏膜 下基质以100 mmol/L EDC交联效果较好。"
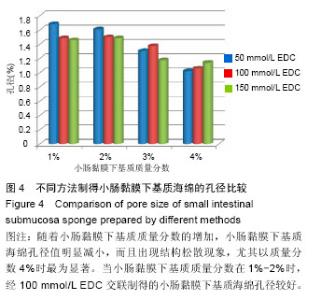
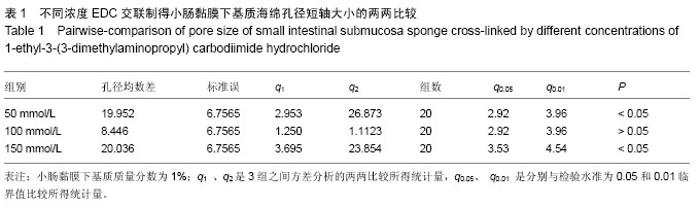
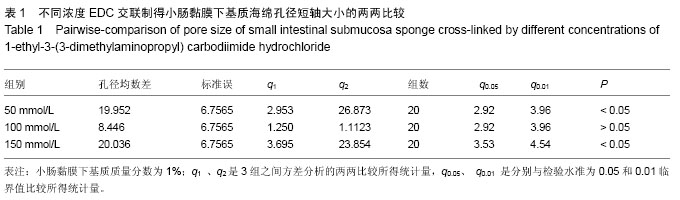
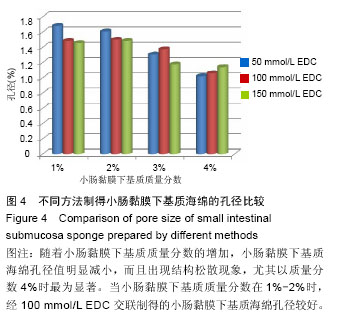
2.3 小肠黏膜下基质海绵经不同浓度EDC交联后的孔径变化 随着小肠黏膜下基质质量分数的增加,小肠黏膜下基质海绵孔壁厚度增加,并且出现了孔径大小和密度的变化。当小肠黏膜下基质质量分数为1%时,小肠黏膜下基质海绵孔径大小为(125±25) μm,但随着小肠黏膜下基质质量分数的增加,小肠黏膜下基质海绵孔径值明显减小,而且出现结构松散现象,尤其以质量分数4%时最为显著。通过实验结果可以得出,当小肠黏膜下基质质量分数在1%-2%时,经100 mmol/L EDC交联制得的小肠黏膜下基质海绵空间结构弹性好,结构规整,无空洞现象。小肠黏膜下基质海绵的孔径与正常小肠黏膜下基质比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图4,表1。"
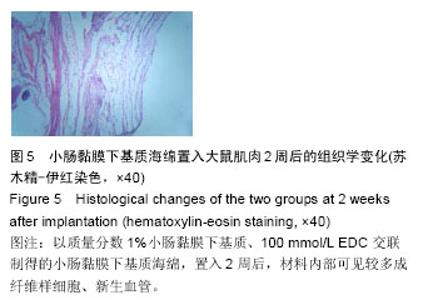
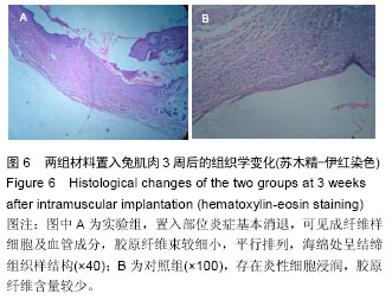
2.4 免疫原性观察结果 术后两组动物状态良好,活动和进食正常,手术切口无红肿、渗血和渗液等,切口一期愈合,无动物死亡,材料周围肌组织均无肿胀、坏死或硬结形成。 置入1周后,可见实验组小肠黏膜下基质海绵网孔状结构保持完整,在材料周围可见轻微炎细胞浸润,少量嗜中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞浸润和巨细胞反应,支架边缘可见周围软组织增殖移行;对照组炎细胞浸润明显,其下创面有粘连,周围软组织增殖移行较少。置入2周后,实验组大小未见明显变化,材料内部可见较多成纤维样细胞、新生血管,见图5;对照组可见明显的粘连,炎性细胞浸润明显,弹性下降,出现局部降解,新增长上皮层次较少,增生欠活跃。置入3周后,实验组置入部位炎症基本消退,可见成纤维样细胞及血管成分,胶原纤维束较细小,平行排列,海绵处呈结缔组织样结构,见图6A;对照组仍然存在炎性细胞浸润,胶原纤维含量较少,见图6B。"
| [1] Otto WR,Sarraf CE.Culturing and differentiating human mesenchymal stem cells for biocompatible scaffolds in regenerative medicine.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;806: 407-426.[2] Shearn JT,Kinneberg KRC,Dyment NA,et al.Tendon tissue engineering: Progress, challenges, and translation to the clinic.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.2011;11(2):163-173.[3] Yang Z,Shi Y,Wei X,et al.Fabrication and Repair of Cartilage Defects with a Novel Acellular Cartilage Matrix Scaffold.Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2010;16(5): 865-876.[4] Jonsson L,Gatzinsky V,Jennische E,et al.Piglet Model for Studying Esophageal Regrowth after Resection and Interposition of a Silicone Stented Small Intestinal Submucosa Tube.Eur Surg Res.2011;46(4):169-179.[5] Kim KS,Lee JY,Kang YM,et al.Small intestine submucosa sponge for in vivo support of tissue-engineered bone formation in the presence of rat bone marrow stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(6): 1104-1113.[6] Xu Y,Wu J,Guan J,et al.Physiochemical and biological properties of modified collagen sponge from porcine skin.J Wuhan Univ Technol.2009;24(4):619-626.[7] Lim JY,Kim SH,Khang G,et al.Preparation and Characterization of Tissue Engineered Scaffold Using Porcine Small Intestinal Submucosa and Hyaluronic Acid. Polym-Korea.2008;32(5):415-420.[8] Huber A,Badylak SF.Phenotypic changes in cultured smooth muscle cells: limitation or opportunity for tissue engineering of hollow organs?J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;6(7):505-511.[9] Hong HK,Lee SK,Song Y,et al.Biodisc Regeneration Using Annulus Fibrosus Cell with Hyaluronic Acid Impregnated Small Intestinal Submucosa Sponge. Polym-Korea.2010;34(3):282-288. [10] Kato H,Suga H,Eto H,et al.Reversible adipose tissue enlargement induced by external tissue suspension: possible contribution of basic fibroblast growth factor in the preservation of enlarged tissue.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6):2029-2040.[11] Marconi S,Castiglione G,Turano E,et al.Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells systemically injected promote peripheral nerve regeneration in the mouse model of sciatic crush.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012; 18(11-12):1264-1272.[12] Ackbar R,Ainoedhofer H,Gugatschka M,et al.Decellularized ovine esophageal mucosa for esophageal tissue engineering.Technol Health Care. 2012;20(3):215-223.[13] Morey AF.Re:Small Intestinal Submucosa Urethral Wrap at the Time of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Placement as a Salvage Treatment Option for Patients with Persistent/Recurrent Incontinence Following Multiple Prior Sphincter Failures and Erosions.J Urol. 2012;188(3):865-866.[14] Mcadams PD,Jordan G H.Re: Long-term Results of Small Intestinal Submucosa Graft in Bulbar Urethral Reconstruction.Eur Urol.2012;62(4):728.[15] Owen TJ,Lantz GC,Hiles MC,et al.Cal cifi cati on pot en tial of small int es tinal s ubmucosa in a rat s ubcut aneous model.J Surg Res.1997;71(2):179. [16] Wissink MJ,Beernink R,Pieper JS,et al.Bingding and release of basic fibroblast growth factor from heparinized cllagen matrices.Biomaterials. 2001;22: 2291-2292.[17] Tanaka Y,Kubotal A,Yokokural S,et al.Optical mechanical refinement of human amniotic membrane by dehydration and cross-linking.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;9(6):731-737.[18] Cholasa RH,Hsu HP,Spectorb M.The reparative response to cross-linked collagen-based scaffolds in a rat spinal cordgap model.Biomaterials. 2012;33(7): 2050-2059.[19] Cintron JR,Abcarian H,Chaudhry V,et al.Treatment of fistula-in-ano using a porcine small intestinal submucosa anal fistula plug.Tech Coloproctol. 2013; 17(2):187-191.[20] Kalaji N,Deloge A,Sheibat-Othman N,et al.Controlled release carriers of growth factors FGF-2 and TGF beta1: synthesis,characterization and kinetic modelling. J Biomed Nanotechnol.2010;6(2):106-116.[21] Hodde JP,Record RD,Liang HA,et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor in porcine-derived extracellular matrix.Endothelium.2001;8(1):11.[22] Chen MK,Badylak SF.Small bowel tissue engineering using small intestinal submucosa as a scaffold.J Surg Res.2001;99(2):352.[23] McPherson TB,Badylak SF.Characterization of fibronectin derived from porcine small intestinal submucosa.Tissue Eng.1998;4(1):75.[24] Liatsikos EN,Dinlenc CZ,Kapoor R,et al.Laparoscopic ureteral reconstruction with small intestinal submucosa. J Endourol.2001;15(2):217.[25] McDevitt CA,Wildey GM,Catrone RM.Transforming growth factor- beta1 in a sterilized tissue derived from the pig small intestine submucosa.J Biomed Mater Res A.2003;67(2): 637-640.[26] Hurst RE,Bonner RB.Mapping of the distribution of significant proteins and proteoglycans in small intestinal submucosa by fluorescence microscopy.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2001;12(11):1267-1279.[27] Layman H,Li X,Nagar E,et al.Enhanced angiogenic efficacy through controlled and sustained delivery of FGF-2 and G-CSF from fibrin hydrogels containing ionic-albumin microspheres.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2012;23(1-4):185-206.[28] Leeuwenburgh SC,Jo J,Wang H,et al.Mineralization,biodegradation,and drug release behavior of gelatin apatite composite microspheres for bone regeneration. iomacromolecules.2010;11(10):2653-2659. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||