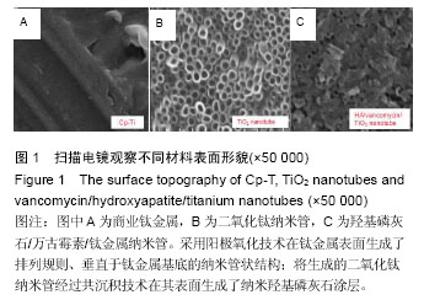
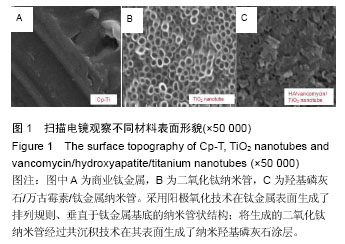
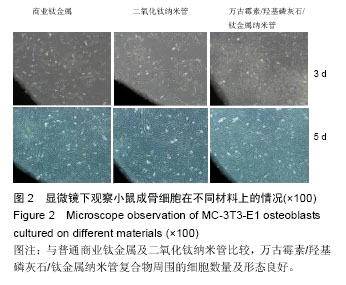
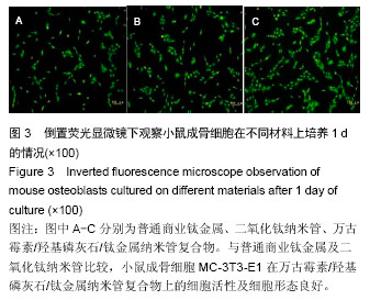
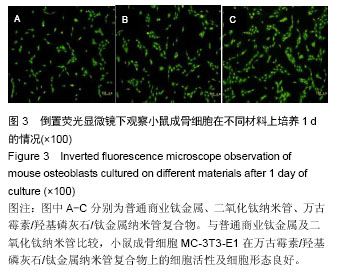
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (21): 3097-3103.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.21.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biocompatibility of vancomycin/hydroxyapatite/titanium nanotubes
Zhang Hang-zhou1, Tian Ang2, Liang Qing-wei1, Bai Xi-zhuang3, Xue Xiang-xin2
- 1Department of Sports Medicine and Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China; 2School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China; 3Department of Sports Medicine and Joint Surgery, People’s Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110006, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2016-03-13Online:2016-05-20Published:2016-05-20 -
About author:Zhang Hang-zhou, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Sports Medicine and Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81071449, 81501857; Provincial-Level Hospital Reform Project for Construction of Key Clinical Department in Liaoning Province, No. LNCCC-A03-2014
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Hang-zhou, Tian Ang, Liang Qing-wei, Bai Xi-zhuang, Xue Xiang-xin. Biocompatibility of vancomycin/hydroxyapatite/titanium nanotubes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(21): 3097-3103.
share this article
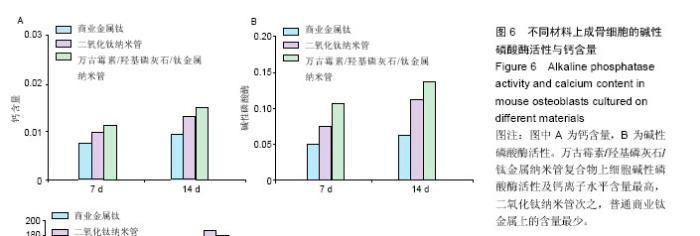
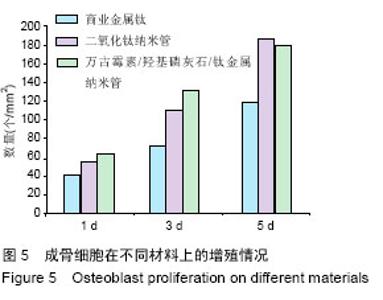
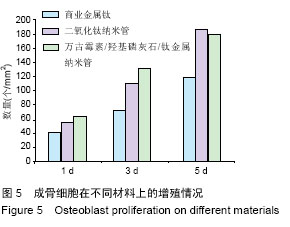
2.4 成骨细胞在不同材料上的碱性磷酸酶活性与钙含量 共培养7 d时,商业钛金属组、二氧化钛纳米管组、万古霉素/羟基磷灰石/钛金属纳米管组钙质量浓度分别为0.008,0.01,0.013 µg/L;共培养14 d时,商业钛金属组、二氧化钛纳米管组、万古霉素/羟基磷灰石/钛金属纳米管组钙质量浓度分别0.009,0.015,0.017 µg/L,见图6A。 共培养7 d时,商业钛金属组、二氧化钛纳米管组、万古霉素/羟基磷灰石/钛金属纳米管组碱性磷酸酶活性分别为0.05、0.08、0.11;共培养14 d时,商业钛金属组、二氧化钛纳米管组、万古霉素/羟基磷灰石/钛金属纳米管组碱性磷酸酶活性分别为0.06、0.12、0.14,见图6B。万古霉素/羟基磷灰石/钛金属纳米管复合物上细胞碱性磷酸酶活性及钙离子水平含量最高,二氧化钛纳米管次之,普通商业钛金属上的含量最少。"

| [1] Glibert M,De Bruyn H,Östman PO.Six-Year Radiographic, Clinical, and Soft Tissue Outcomes of Immediately Loaded, Straight-Walled, Platform-Switched, Titanium-Alloy Implants with Nanosurface Topography.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(1):167-171.[2] Raphel J,Karlsson J,Galli S,et al.Engineered protein coatings to improve the osseointegration of dental and orthopaedic implants. Biomaterials. 2016;83(6): 269-282.[3] Ataya A,Kline KP,Cope J,et al.Titanium exposure and yellow nail syndrome.Respir Med Case Rep. 2015;16: 146-147.[4] Hara D, Nakashima Y, Sato T, et al. Bone bonding strength of diamond-structured porous titanium-alloy implants manufactured using the electron beam-melting technique.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;59:1047-1052.[5] Hara D,Nakashima Y,Sato T,et al. Bone bonding strength of diamond-structured porous titanium-alloy implants manufactured using the electron beam-melting technique.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;59:1047-1052.[6] Choi JY,Lee HJ,Jang JU,et al.Comparison between bioactive fluoride modified and bioinert anodically oxidized implant surfaces in early bone response using rabbit tibia model.Implant Dent. 2012;21(2): 124-128.[7] Liu Y,Jiang T,Zhou Y,et al.Evaluation of the attachment, proliferation, and differentiation of osteoblast on a calcium carbonate coating on titanium surface. Materials Science and Engineering C. 2011;31:1055-1061.[8] Park JW,Suh JY,Chung HJ.Effects of calcium ion incorporation on osteoblast gene expression in MC3T3-E1 cells cultured on microstructured titanium surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A.2008;86(1):117-126.[9] Anselme K.Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials.2000;21(7):667-681.[10] Aw MS,Simovic S,Addai-Mensah J,Losic D:.Polymeric micelles in porous and nanotubular implants as a new system for extended delivery of poorly soluble drugs. J Mater Chem.2011;21(20):7082-7089.[11] Bjursten LM,Rasmusson L,Oh S,et al.Titanium dioxide nanotubes enhance bone bonding in vivo.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;92(3):1218-1224. [12] Burns K,Yao C,Webster TJ.Increased chondrocyte adhesion on nanotubular anodized titanium.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;88(3):561-568. [13] Chang CH,Lee HC,Chen CC, et al.A novel rotating electrochemically anodizing process to fabricate titanium oxide surface nanostructures enhancing the bioactivity of osteoblastic cells.J Biomed Mater Res A.2012;100(7):1687-1695. [14] Gulati K,Aw MS,Findlay D,et al.Local drug delivery to the bone by drug-releasing implants: perspectives of nano-engineered titania nanotube arrays.Ther Deliv. 2012;3(7):857-873.[15] Gulati K,Ramakrishnan S,Aw MS,et al.Biocompatible polymer coating of titania nanotube arrays for improved drug elution and osteoblast adhesion.Acta Biomater.2012;8(1):449-456.[16] Hu Y,Cai K,Luo Z,et al.TiO2 nanotubes as drug nanoreservoirs for the regulation of mobility and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Acta Biomater. 2012;8(1):439-448. [17] Jayaraman M,Meyer U,Bühner M,et al.Influence of titanium surfaces on attachment of osteoblast-like cells in vitro.Biomaterials.2004;25(4):625-631.[18] Popat KC,Eltgroth M,LaTempa TJ,et al.Titania nanotubes: a novel platform for drug-eluting coatings for medical implants.Small.2007;3(11):1878-1881. [19] Shrestha NK,Macak JM,Schmidt-Stein F,et al. Magnetically guided titania nanotubes for site-selective photocatalysis and drug release.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48(5):969-972. [20] Peng L,Mendelsohn AD,LaTempa TJ,et al.Long-term small molecule and protein elution from TiO2 nanotubes. Nano Lett.2009;9(5):1932-1926.[21] Wang Y,Yuan L,Yao C,et al.Cytotoxicity Evaluation of pH-Controlled Antitumor Drug Release System of Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(6):4143-4148.[22] Doadrio AL,Conde A,Arenas MA,et al.Use of anodized titanium alloy as drug carrier: Ibuprofen as model of drug releasing.Int J Pharm. 2015;492(1-2): 207-212[23] Przekora A,Benko A,Nocun M,et al.Titanium coated with functionalized carbon nanotubes--a promising novel material for biomedical application as an implantable orthopaedic electronic device.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014;45:287-296.[24] Yan L,Jiang DM.Study of bone-like hydroxyapatite/polyamino acid composite materials for their biological properties and effects on the reconstruction of long bone defects.Drug Des Devel Ther.2015;17(9):6497-6508[25] Clauss M,Van Der Straeten C,Goossens M. Prospective five-year subsidence analysis of a cementless fully hydroxyapatite-coated femoral hip arthroplasty component.Hip Int. 2014;24(1):91-97.[26] Li S,Huang B,Chen Y,et al. Hydroxyapatite-coated femoral stems in primary total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int J Surg. 2013;11(6):477-482.[27] Oonishi H. A long term histological analysis of effect of interposed hydroxyapatite between bone and bone cement in THA and TKA.J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2012;22(2):165-176.[28] Rajesh P,Muraleedharan CV,Komath M,et al.Laser surface modification of titanium substrate for pulsed laser deposition of highly adherent hydroxyapatite.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2011;22(7):1671-1679.[29] Cooper LF. A role for surface topography in creating and maintaining bone at titanium endosseous implants.J Prosthet Dent.2000;84(5):522-534.[30] von Wilmowsky C,Bauer S,Lutz R,et al.In vivo evaluation of anodic TiO2 nanotubes: an experimental study in the pig. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;89(1):165-171.[31] Bjursten LM, Rasmusson L, Oh S, et al. Titanium dioxide nanotubes enhance bone bonding in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010; 92(3):1218-1224.[32] Tang J,Hu J,Kang L,et al.The use of vancomycin in the treatment of adult patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection: a survey in a tertiary hospital in China.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(10): 19436-19441.[33] Jeon YL,Kim MH,Yang HS,et al.Optimum initial loading dose of vancomycin for pneumonia caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Infect. 2016;72(1):115-118.[34] Kim SH,Kim MG,Kim SS,et al.Change in Detection Rate of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Their Antibiotic Sensitivities in Patients with Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media.J Int Adv Otol.2015;11(2):151-156.[35] Hahn A,Frenck RW Jr,Allen-Staat M,et al.Evaluation of Target Attainment of Vancomycin Area Under the Curve in Children With Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteremia.Ther Drug Monit. 2015;37(5):619-625. [36] Hanrahan TP,Kotapati C,Roberts MJ,et al.Factors associated with vancomycin nephrotoxicity in the critically ill.Anaesth Intensive Care. 2015;43(5): 594-599.[37] Jacqz-Aigrain E,Leroux S,Zhao W,et al.How to use vancomycin optimally in neonates: remaining questions. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015;8(5): 635-648. [38] Hanrahan T,Whitehouse T,Lipman J,et al. Vancomycin-associated nephrotoxicity: A meta-analysis of administration by continuous versus intermittent infusion.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015; 46(3):249-253. [39] Liu Y,Yin Y,Liu XZ,et al.Retrospective Analysis of Vancomycin Nephrotoxicity in Elderly Chinese Patients.Pharmacology.2015;95(5-6):279-284. [40] Edin ML,Miclau T,Lester GE,et al.Effect of cefazolin and vancomycin on osteoblasts in vitro. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1996;(333):245-251.[41] Rathbone CR,Cross JD,Brown KV,et al. Effect of various concentrations of antibiotics on osteogenic cell viability and activity.J Orthop Res. 2011;29(7): 1070-1074. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||