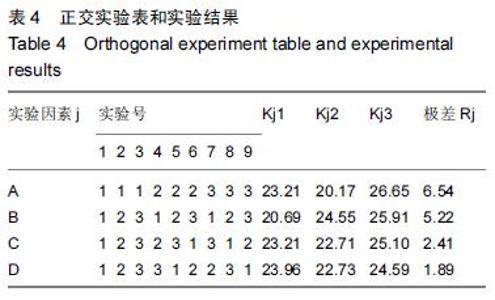
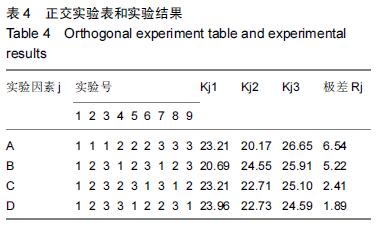
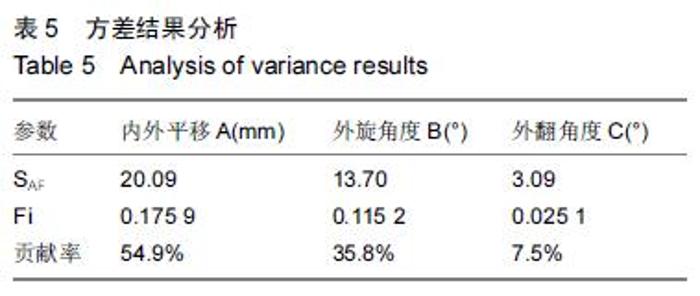
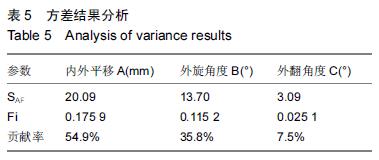
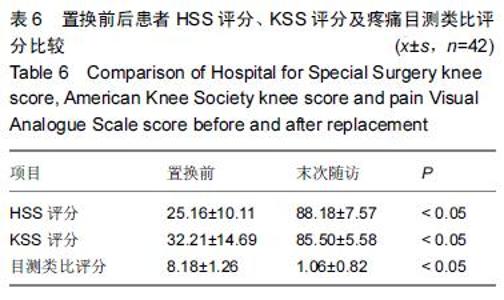
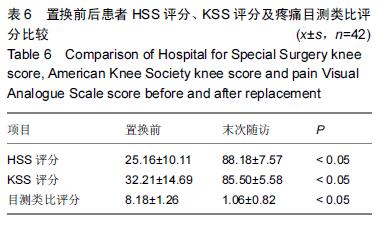
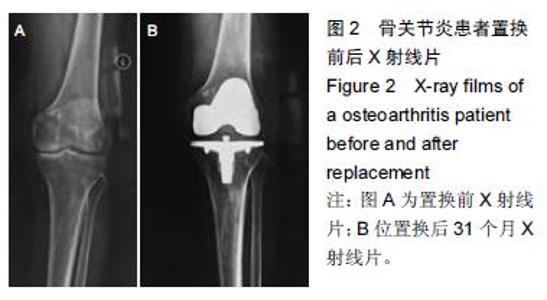
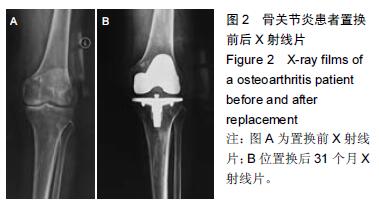
| [1] 刘阳,曹力,李纲,等.固定平台型与活动平台型膝关节假体人工全膝关节置换术后膝前痛的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(3):266-271. [2] 彭侃,姚舒馨,马建兵,等.人工单髁膝关节置换术治疗膝骨关节炎[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(2):106-109. [3] 童培建.复杂全膝关节置换术的手术策略[J].中医正骨, 2013,25(1):3-6. [4] 张催,陈游,张春雷,等.单髁置换术与全膝关节置换术治疗膝单间室骨性关节炎近中期疗效的对比研究[J].中华关节外科杂志,2010,1(2):1092-107. [5] 于水莲,沈鹰.中国组织工程研究与临床康复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(3): 5923-5925. [6] 洪源,冯建民,何川.全膝关节置换术股骨假体旋转力线研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(4): 219-222. [7] 戚盈杰,胡月正,吴剑彬,等.全膝关节置换术股骨及胫骨假体旋转定位研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(4): 221-223. [8] 代宏杰,靳宪辉,崔胜杰,等.人工膝关节置换中髌骨置换效果的Meta 分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(39): 7283-7285. [9] Burnett RS,Boone JL,Rosenzweig SD,et al.Patellar resurfacing compared with nonresurfacing in total knee arthroplasty.A concise follow up of a randomized trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(11):2562-2567. [10] 胡珂,邱红明.现代人工膝关节假体应用进展[J].中西医结合研究,2011,3(5):258-259. [11] 曾长琦,张克.旋转平台型假体全膝关节置换术的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志,2009,3(6):59-60. [12] 魏鸿文,郑诚功.膝关节高屈曲假体的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志,2009,3(4):70-74. [13] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(6):602-604. [14] 赵奇,蒋土.人工膝关节假体设计新进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(32):9838-9842. [15] 符培亮,吴海山.融合或强直膝关节的人工假体置换治疗进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2008,14(3):159-160. [16] 欧光信,李文锐.全膝关节置换后股骨假体周围骨折的研究进展[J].海南医学,2013,24(2):274-276. [17] 陆艳红,石晓兵.膝骨关节炎国内外流行病学研究现状及进展[J].中国中医骨伤杂志,2012,20(6):81-84. [18] 闫海莲.膝关节损伤修复材料及生物力学性能[J].中国组织工程究,2012,16(3):531-534. [19] Seo SS,Kim CW,Kim JH,et al.Clinical results associated with changes of posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013;25(1) : 25-29. [20] 郑红光,黄荣瑛,郑海东,等.TKA 后关节线高度变化对膝关节力学特性影响[J].工程力学,2013,30(增刊) : 298-303. [21] Lützner J,Kirschner S,Günther KP,et al.Patients with no functional improvement after total knee arthroplasty show different kinematics.Int Orthop. 2012;36(9) : 1841-1847. [22] 胡月正,陈彩虹,戚盈杰,等.股骨前轴作为全膝关节置换术中旋转对线标准的磁共振测量实验[J].温州医学院学报, 2013,43(12) : 800-803. [23] van Jonbergen HP,Innocenti B,Gervasi GL,et al. Differences in the stress distribution in the distal femur between patellofemoral joint replacement and total knee replacement: a finite element study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2012;7:28. [24] Steinbrück A,Schroder C,Woiczinski M,et al. Patellofemoral contact patterns before and after total knee arthroplasty: an in vitro measurement.Biomed Eng Online. 2013;12: 58. [25] Kainz H, Reng W,Augat T,et al.Influence of total knee arthroplasty on patellar kinematics and contact characteristics.Int Orthop. 2012;36(1):73-78. [26] 张绪树,郭媛,安美文,等.不同运动状态下国产人工膝关节接触压力分布有限元分析[J].计算机辅助工程,2013, 22(2):61-65. [27] 卫晓东,张高龙,黄荣瑛,等.假体植入偏差对TKA 后膝关节面间力学特性的影响[J].工程力学,2013,29(增刊Ⅱ): 226-232. [28] 胡杨,董跃福,徐卿荣,等.全膝关节置换股骨假体植入定位参数有限元分析及优化[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(3) : 334-338. [29] 刘志宏,刘利,韦林,等.不同型号配对固定平台型膝关节假体生物力学有限元分析研究[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2012, 33(5):322-325. [30] 马军,牛东生,孙玺淳,等.个体化的软组织平衡技术在膝外翻全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中华关节外科杂志, 2012, 6(5): 695-701. [31] 徐美涛,查振刚,刘宁,等.人工全膝关节置换术在外翻膝的临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(2):109-112. [32] 卿忠,姚剑锋,张育民,等.屈曲挛缩畸形全膝关节置换的软组织平衡[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(10):923-925. [33] Camarata DA.Soft tissue balance in total knee arthroplasty with a force sensor. Orthop Clin North Am.2014;45(2):175-184. [34] 祝钧.全膝关节置换术中股骨假体内置外置对膝关节生物力学影响的实验研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2009. [35] Girard J, Amzallag M, Pasquier G, et al.Total knee arthroplasty in valgus knees: predictive preoperative parameters influencing a constrained design selection. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009;95(4): 260-266. [36] Mihalko W, Fishkin Z, Krakow K.Patellofemoral overstuff and its relationship to flexion after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;449: 283-287. [37] 何毓珏,冯明光,徐长明,等.矢状面髌骨形位参数变化对伸膝机构影响研究[J] .东南大学学报:自然科学版,2004, 34(6):806-809. [38] Scott RD.Femoral and tibial component rotation in total knee arthroplasty:methods and consequences . Bone Joint J. 2013;95B(11 Suppl): 140-143. [39] Bell SW, Young P, Drury C, et al.Component rotational alignment in unexplained painful primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2014;21(1):272-277. [40] Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JS, et al. The relationship between the survival of total knee arthroplasty and postoperative coronal, sagittal and rotational alignment ofknee prosthesis. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2): 379-385. Catani F,Innocenti B,Belvedere C,et al.Articular contact estimation in TKA using in vivo kinematics and finite element analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(1): 19-28. |