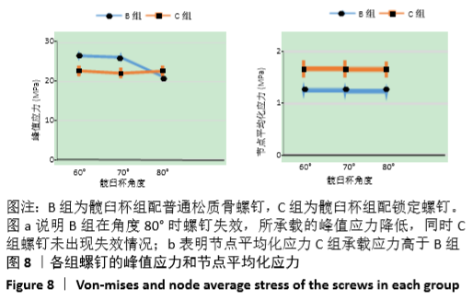
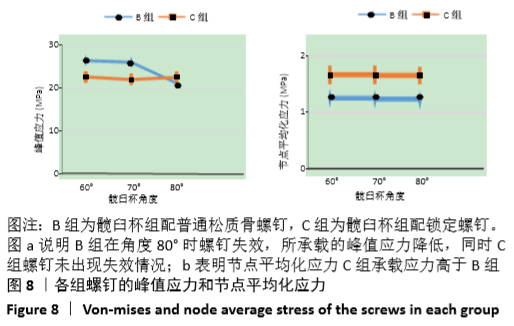
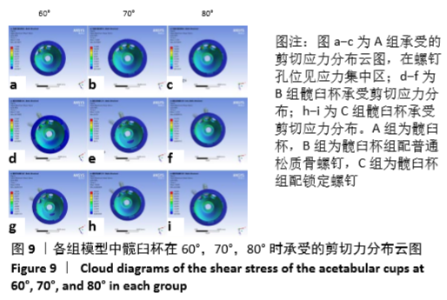
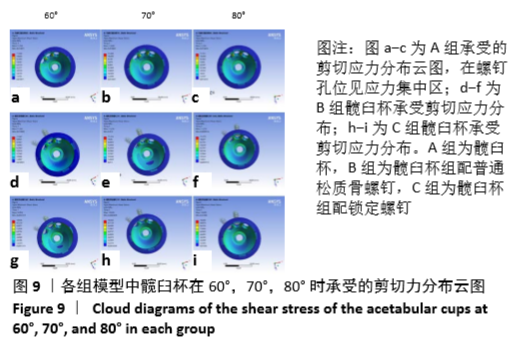
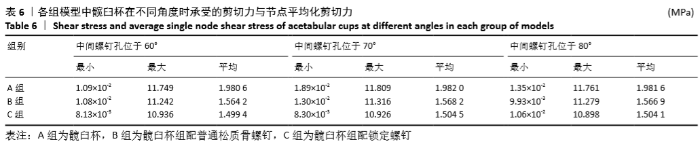
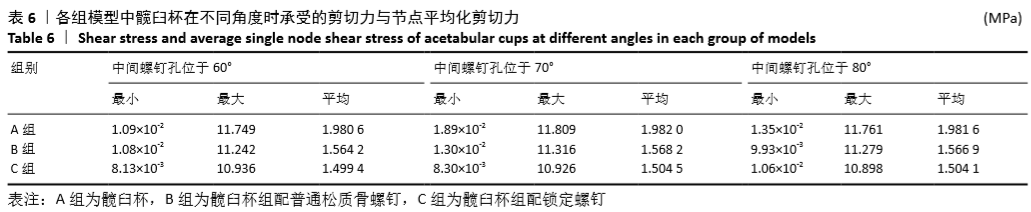
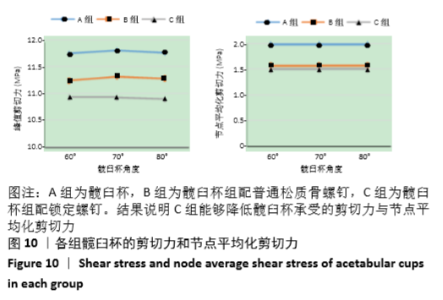
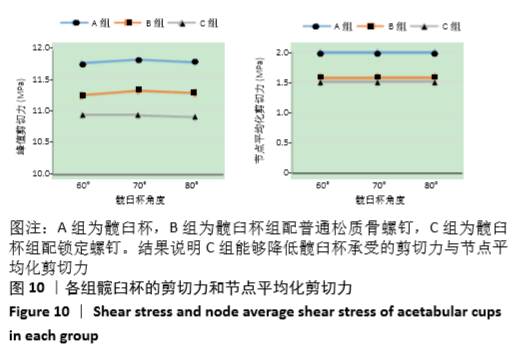
[1] 王俏杰,张先龙.人工髋关节置换术的现状与热点[J].中华关节外科杂志,2015,9(6):718-724.
[2] BAYLISS LE, CULLIFORD D, MONK AP, et al. The effect of patient age at intervention on risk of implant revision after total replacement of the hip or knee: a population-based cohort study. Lancet. 2017; 389(1077):1424-1430.
[3] CAPON-GARCIA D,LOPEZ-PARDO A,ALVES-PEREZ MT. Causes for revision surgery in total hip replacement: a retrospective epidemiological analysis. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2016;60(3):160-166.
[4] 朱先洋,尹宗生,陈迪嘉.髋关节置换术后翻修原因及疗效分析[J].安徽医药,2017,21(3):525-528.
[5] 刘冰,廖中亚.全髋关节置换时压配联合髋臼杯螺钉固定效果的分析[J].皖南医学院学报,2018,37(4):356-359.
[6] 王满宜,曾炳芳,主译. 骨折治疗的 AO原则[M]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2018:166-167.
[7] 王岩,主译. 坎贝尔骨科手术学[M]. 北京:人民军医出版社, 2013: 179.
[8] 杨述华,主编.骨科学教程[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2014:62-63.
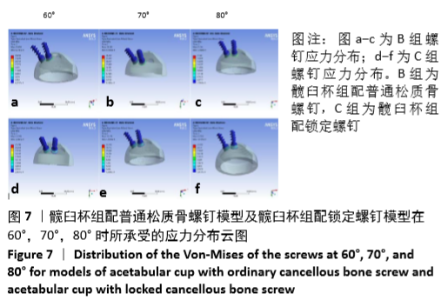
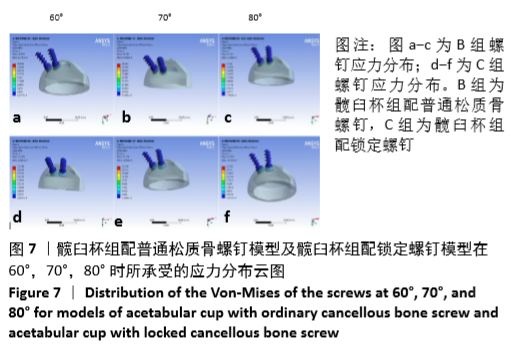
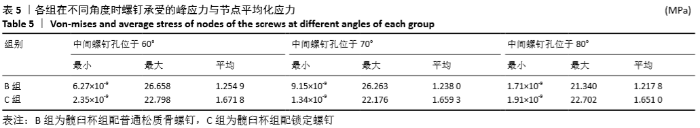
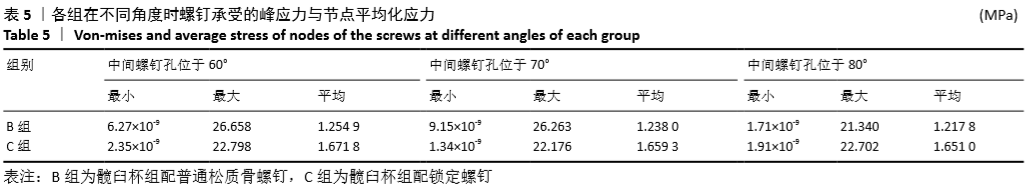
[9] 边逸群.髋关节置换术髋臼假体安装角度的有限元分析[D].泰安:泰山医学院,2013.
[10] 丁锋,主编.ANSYS Workbench 19.0结构分析入门到精通[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2019:188.
[11] ZIELINSKI SM, MEEUWIS MA, HEETVELD MJ, et al. Adherence to a femoral neck fracture treatment guideline. Int Orthop.2013;37(7): 1327-1334.
[12] 戴雪松.人工髋关节置换术的不同固定方式下的髋臼侧应力分析[D].杭州:浙江大学医学院,2008.
[13] 屈瑾,雷新玮,展影,等.髋关节表面置换术假体柄固定方式对股骨近端骨密度及应力影响[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(35): 2769-2771.
[14] 徐佳明,李星亮,王韬.髋臼高位放置对股骨假体应力影响的有限元分析[J]. 临床外科杂志,2019,27(3):239-242.
[15] SCHNEIDER D, WEBER FE, GRUNDER U, et al. A randomized controlled clinical multicenter trial comparing the clinical and histological performance of a new, modified polylactide-co-glycolide acid membrane to an expanded polytetrafluorethylene membrane in guided bone regeneration procedures. Clin Oral Implants Res.2014;25(2):150-158.
[16] ANNEN BM, RAMEL CF, HÄMMERLE CH, et al. Use of a new cross-linked collagen membrane for the treatment of peri-implant dehiscence defects: a randomised controlled double-blinded clinical trial. Eur J Oral Implantol.2011;4(2):87-100.
[17] RONDA M, REBAUDI A, TORELLI L, et al. Expanded vs.dense polytetrafluoroethylene membranes in vertical ridge augmentation around dental implants: a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res.2014;25(7):859-866.
[18] TODISCO M. Early loading of implants in vertically augmented bone with non-resorbable membranes and deproteinised anorganic bovine bone. An uncontrolled prospective cohort study. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010;3(1):47-58.
[19] CHIAPASCO M, ZANIBONI M. Clinical outcomes of GBR procedures to correct peri-implant dehiscences and fenestrations: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(4):113-123.
[20] 丁秀敏,侯丽丽,郭子学,等.半球与椭球髋臼假体对骨性髋臼应力分布的对比分析[J].医用生物力,2008,23(6):465-470.
[21] 胡如印. 3D打印多孔钛金属骨小梁髋臼杯的临床应用、体内基础研究与生物力学研究[D]. 南宁:广西医科大学,2018.
[22] 杨宾宾. 股骨头坏死三维有限元研究[D]. 北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院,2017.
[23] 朱海泉. 第二掌骨、食指近中节指骨骨折的有限元分析[D]. 南京:南京医科大学,2018.
[24] 姚楚亮,陈少文,杨焱鑫,等.全髋关节置换术髋臼杯螺钉固定与镶嵌固定的疗效分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(4): 468-471.
[25] ZILKENS C, DJALALI S, BITTERSOHL B, et al. Migration pattern of cementless press fitcups in the presence of stabilizing screws in total hip arthroplasty. Eur J Med Res. 2011;16(3):127-132.
[26] 吴浩波.经髋白螺钉固定髋臼假体的改良钉道参数、力学价值、临床分析[D].杭州:浙江大学,2011.
[27] 白波,罗林聪,彭缣侨.有限元法在髋关节运动力学研究中的应用进展[J].国际骨科杂志,2018,39(1):24-27.
[28] LERCH M, WEIGEL N, WINDHAGEN H, et al. Finite element model of a novel short stemmed total hip arthroplasty implant developed from cross sectional CT scans. Technol Health Care. 2013;21(5):493-500.
[29] 李翰祥,董黎敏,叶金铎,等.骨小梁结构对髋关节置换的应力分布影响的研究[J].天津理工大学学报,2019,35(3):1-9.
[30] 王志坚,李彦旭,韩青,等.髋关节置换术中2种不同髋关节假体的有限元分析:应力集中和位移变化比较[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2019,45(2):347-352. |