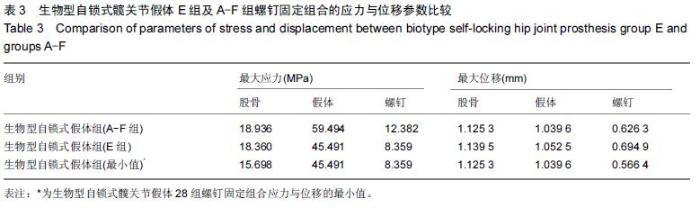
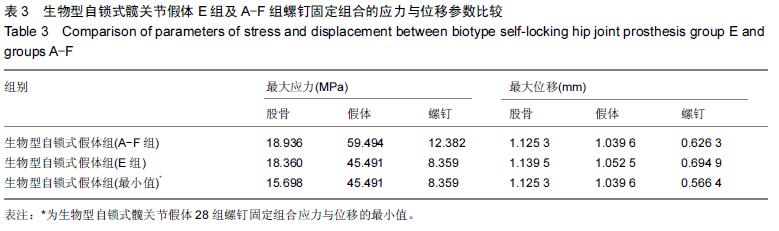
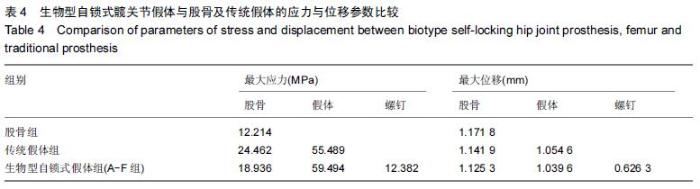
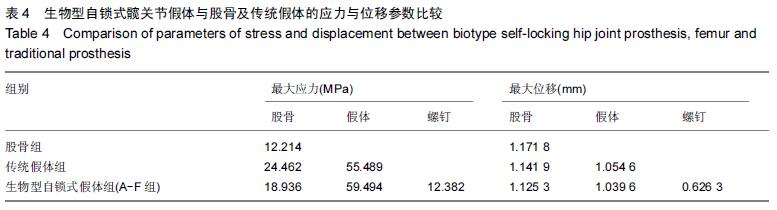
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (17): 2443-2450.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.17.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Modified design of biotype self-locking hip joint prosthesis
Huang Wei-tao1, Li Cai-hua1, Jiang Tuo1, Yang Jun2
- 1Shunde Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528333, Guangdong Province, China; 2the 421 Hospital of PLA, Guangzhou 510318, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2016-03-20Online:2016-04-22Published:2016-04-22 -
About author:Huang Wei-tao, Associate chief physician, Shunde Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528333, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Guangdong Medical Science and Technology Research Foundation, No. A2013460
Cite this article
Huang Wei-tao, Li Cai-hua, Jiang Tuo, Yang Jun. Modified design of biotype self-locking hip joint prosthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(17): 2443-2450.
share this article
| [1] Panagiolopoulos EC,Kallivokas AG,Koulioumpas I,et al.Early failure of a zirconia femoral head prosthesis:fracture orfatigue.Clin Biomech(Bristol,Avon). 2007; 22(7):856-860. [2] Wirtz DC, Pandorf T, Portheine F, et al. Concept and development of an orthotropic FE model of the proximal femur. J Biomech. 2003;36(2): 289-293. [3] Sitthiseripratip K, Van Oosterwyck H, Vander Sloten J, et al. Finite element study of trochanteric gamma nail for trochanteric fracture. Med Eng Phys. 2003;25(2): 99-106. [4] Kobayashi E, Wang TJ, Doi H, et al. Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy dental castings. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1998;9(10): 567-574. [5] Pioletti DP, Rakotomanana LR. Can the increase of bone mineral density following bisphosphonates treatments be explained by biomechanical considerations? Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2004; 19(2): 170-174. [6] Qian BP, Wang XH, Qiu Y, et al. The influence of closing-opening wedge osteotomy on sagittal balance in thoracolumbar kyphosis sencondary to ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison with closing wedge osteoto my. Spine. 2012;37(16):1415-1423. [7] 边焱焱,翁习生,林进,等.多关节置换治疗晚期下肢关节疾患[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(3):296-299. [8] Zielinski SM, Meeuwis MA, Heetveld MJ, et al. Adherence to a femoral neck fracture treatment guideline. Int Orthop. 2013;37(7):1327-1334. [9] Girard J, Glorion C, Bonnomet F, et al. Risk factors for revision of hip arthroplasties in patients younger than 30 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011;469(4): 1141-1147. [10] Xiong DS, Zhan G, Jin ZG. Friction and wear properties of UHMWPE against ion implanted titanium alloy. Surf Coat Techn. 2007;201(15):6487. [11] Zilber S, Lazennec JY, Gorin M, et al. Variations of caudal, central, and cranial acetabular anteversion according to the tilt of the pelvis. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004;26(6):462-465. [12] Millar NL, Halai M, McKenna R, et al. Uncemented ceramic-on-ceramic THA in adults with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics.2010;33(11):795. [13] Xenos JS, Callaghan JJ, Heekin RD, et al. The porous-coated anatomic total hip prosthesis, inserted without cement. A prospective study with a minimum of ten years of follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1999; 81(1):74-82. [14] Engh CA, Culpepper WJ. Femoral fixation options in the 1990s, Femoral fixation in primary total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 1997;20(9):771-773. [15] Swanson TV. The tapered press fit total hip arthroplasty: a European alternative. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(4 Suppl 2):63-67. [16] 罗先正,邱贵兴.人工髋关节学[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社, 2003. [17] 胡侦明,先正.髋关节的生物力学[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006, 26(7): 498-500. [18] 刘文广,李建民,刘凯红,等. 定制肿瘤人工髋关节假体断裂三维有限元分析及套接式翻修假体的初步应用[J]. 山东大学学报:医学版,2008,46(4):431-432. [19] Husson JL, Mallet JF, Huten D, et al. The lumbar- pelvic-femoral complex: applications in hip pathology Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010; 96(4) Suppl:10-16. [20] Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JK. Is disphyseal stem fixation necessary for primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with osteoporotic bone (classc bone)? J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(1):39-46. [21] 王婧.人工髋关节个体化定制设计应用研究[D].新疆:新疆大学硕士学位论文, 2007. [22] Santori FS, Santori N. Mid-term results of a custom-made short proximal loading femoral component. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92:1231. [23] Good V, Ries M, Barrack RL, et al. Reduced wear with oxidized zirconium femoral heads. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2003; 85-A Suppl 4:105-110. [24] 戴克戎.骨溶解与人工髋关节后期松动[J].中华骨科杂志, 1997,17(1): 3-5. [25] 李建龙,李毅中,林金矿,等.股骨近段髓腔的CT测量及股骨假体设计[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(17):3169-3172. [26] 周殿阁,吕厚山,寇伯龙,等.同侧髋、膝关节同时置换术后康复[J].中国康复医学杂志,2003,18(4):204-206. [27] Kim YH, Kim JS, Park JW, et al. Total hip replacement with a short metaphyseal-fitting anatomical cementless femoral component in patients aged 70 years or older. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93:587. [28] 胡孔足,张先龙.有限元分析法与人工髋关节生物力学研究[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2008,29(6):378-380. [29] 戴雪松. 人工髋关节置换术的不同固定方式下的髋臼侧应力分析[D].浙江:浙江大学医学院博士学位论文, 2008. [30] Kleemann RU,Krocker D,Cedraro A,et al. Altered cartilagemechanics and histology in knee osteoarthritis. Relation to clinical assessment (ICRS Grade). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(11):958-963. [31] Dopico-Gonzalez C,New AM,Brown M.Probabilistic analysis of anuncemented total hip replacement. Med Eng Phys. 2009;(31):470-476. [32] Laz PJ,Pal S,Halloran JP,et al.Probabilistic finite element prediction of knee wear simulator mechanics. J Biomech. 2006;(39):2303-2310. [33] Geneser SE,Kirby RM,MacLeod RS.Application of Stochastic Finite Element Methods to Study the Sensitivity of ECG Forward Modeling to Organ Conductivity. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008;55(1): 31-40. [34] Jin ZM,Williams S,Tipper JT,et al. Tribology of Hip Joints from Natural Hip Joints,Cartilage Substitution, Artificial Replacements to Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J Biomed Sci Eng. 2006;(1):69-81. [35] El-Deen M,Garcia-Finana M,Jin ZM.Effect of UHMWPE thickness on contact mechanics in total knee replacement. J Eng Med. 2006;220(7):733-742. [36] Kim YH, Choi YW, Kim JS. Comparison of bone mineral density changes around short, metaphyseal-fitting and conventional cementless anatomical femoral components. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26:931. [37] Haughom BD, Erickson BJ, Hellman MD, et al. Do Complication Rates Differ by Gender After Metal-on-metal Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty? A Systematic Review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473(8): 2521-2529. [38] Kato T, Otani T, Sugiyama H, et al. Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty in Hip Dysplasia with an Extensively Porous-Coated Cylindrical Stem Modified for Asians: A 12-Year Follow-Up Study. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(6): 1014-1018. [39] Agarwala S, Mohrir G, Moonot P. Functional outcome following a large head total hip arthroplasty: A retrospective analysis of mid term results. Indian J Orthop. 2014;48(4):410-414.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [5] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [6] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [7] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [8] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [9] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [10] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [11] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [13] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [14] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [15] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||