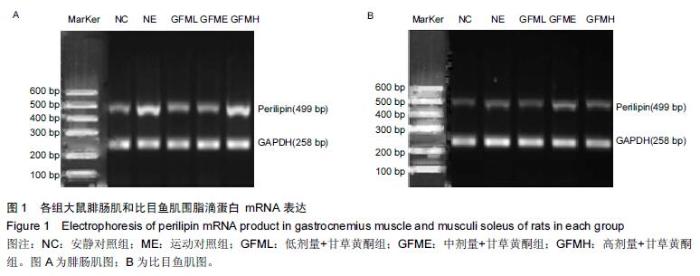
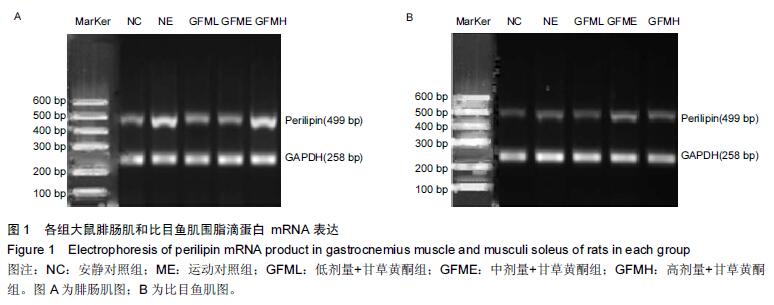
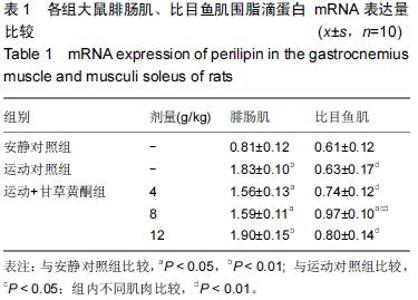
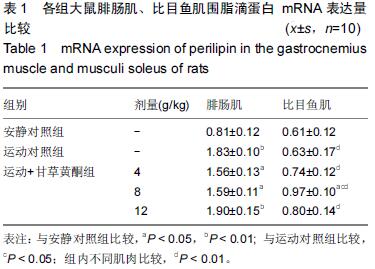
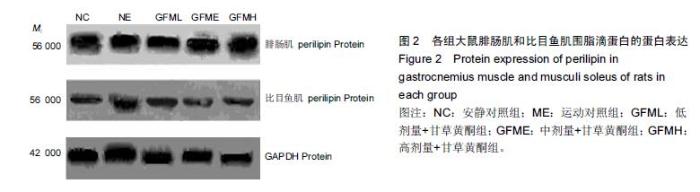
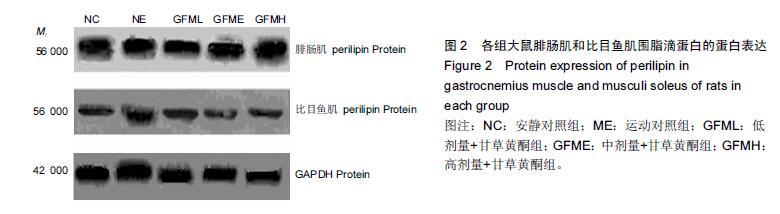
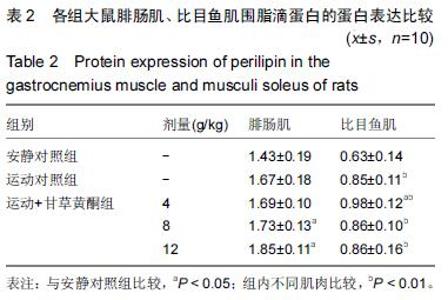
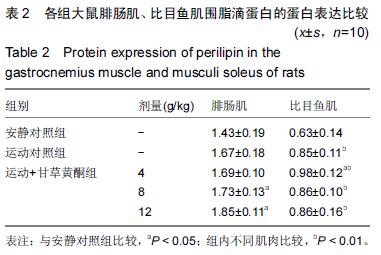
| [1] Schiaffino S, Sandri M, Murgia M. Activity-dependent signalingpathways controlling muscle diversity and plasticity. Physiology.2007;22(8): 269-278. [2] 张国华,陈淑妆,李素萍.大强度耐力运动抑制骨骼肌线粒体的生物合成[J],中国组织工程研究,2015,19(46): 7419-7424. [3] Li L, Chen Y, Gibson SB.Starvation-induced autophagy is regulated by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species leading to AMPK activation. Cell Signal.2013;25(1): 50-65. [4] 孙晓娟,薛海涛.构建运动预适应力竭运动损伤模型大鼠心脏JAK2的表达变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(20): 3216-3220. [5] Tamer A,Mohamed S, Nassan MA.Molecular and immunohistochemical effects of metformin in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9(5):1921-1930. [6] Tansey JT,Sztalryd C,Gruia-Gray J,et al.Perilipin ablation results in a lean mouse with aberrant adipocyte lipolysis,enhanced leptin production,and resistance to diet-indueed obesity. Proc NatI Aead Sci USA. 2001;98:6494-6469. [7] Londos C, Sztalryd C, Tansey JT, et al.Role of PAT proteins in lipid metabolism. Biochimie.2005;87:45-49. [8] Xie YC, Dong XW, Wu XM. et al. Inhibitory effects of flavonoids extracted from licorice on lipopolysaccharide induces acute pulmonary inflammation in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 9(2):194-200. [9] 阳毅,莫伟彬,李启畅.甘草黄酮对运动大鼠肝组织自由基代谢及P53 mRNA表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2013,19(19):228. [10] 黄东,卜凯,阳毅.甘草黄酮对运动大鼠体内糖及脂肪组织RBP4 mRNA表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2014, 20(2): 124-1128. [11] 黄东,李跃林,卜凯,等.甘草黄酮对力竭运动大鼠脂肪代谢酶、ERRαmRNA及蛋白表达的影响[J].广西师范大学学报:自然科学版,2016,34(1):17-23. [12] Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, etal. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol. 1979; 47(6):1278. [13] 李永峰,韩勇,郭勇力,等.黄芪注射液和有氧运动对一次力竭运动大鼠外周血T 淋巴细胞亚群的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2010,16(14): 181-184. [14] 莫伟彬,卜凯,黄丽丽,等.罗汉果甜苷对力竭运动大鼠胃组织HSP70 mRNA及蛋白表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2015, 21(7): 103-106. [15] Li L, Yang G, Shi S, et al. The adipose triglyceride lipase, adiponectin and visfatin are downregulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in vivo. Cytokine. 2009;45(1): 12-19. [16] Bosma M, Minnaard R, Lauren ML, et al.The lipid droplet coat protein perilipin 5 also localizes to muscle mitochondria. Histochem Cell Biol.2012;137(2): 205-216. [17] Abidov MT, del Rio MJ, Ramazanov TZ, et al. Effects of Aralia mandshurica and Engelhardtia chrysolepis extracts on some parameters of lipid metabolism in women with nondiabetic obesity. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2006;141(3): 343-346. [18] Conte M, Vasuri F, Bertaggia E, et al. Differential expression of perilipin 2 and 5 in human skeletal muscle during aging and their association with atrophyrelated genes. Biogerontology.2015;16(3): 329-340. [19] Pourteymour S, Sindre L, Torgrim M.Perilipin 4 in human skeletal muscle: localization and effect of physical activity.Physiological Reports.2015;3 (8): 12481-12496. [20] 田吉明,汪军,张瑞林.一次性运动对肥胖大鼠脂肪水解调节因素的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2008,31(11): 1504-1506. |