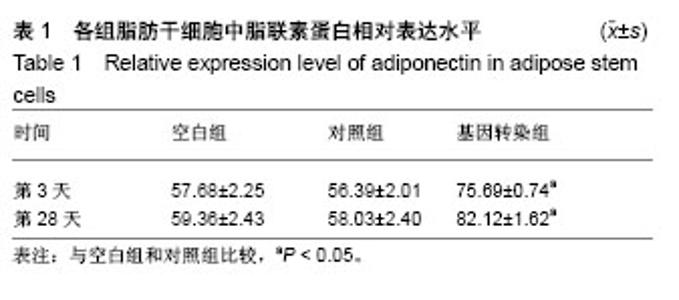
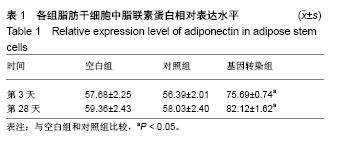
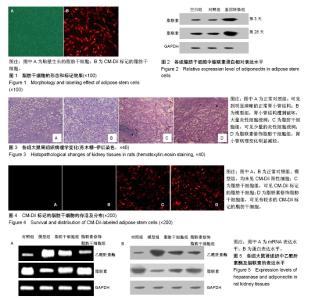
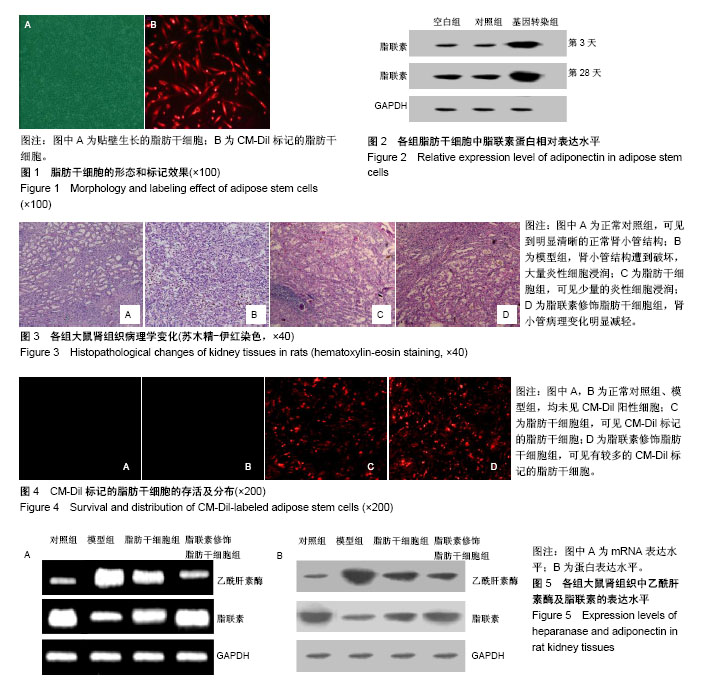
| [1] 管娜.儿童原发性肾病综合征治疗进展[J].中华儿科杂志, 2017,55(8): 638-640.[2] 郑秉暄,李金存,王慧,等.原发性肾病综合征高脂血症发生机制的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(8):1572-1575.[3] 陈琪,朱彩风,朱斌.原发性肾病综合征的治疗机制研究进展[J].温州医科大学学报,2014,44(1):71-74.[4] Kishida K, Funahashi T, Shimomura I. Adiponectin as a routine clinical biomarker. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;28(1):119-130.[5] Lim S, Quon MJ, Koh KK. Modulation of adiponectin as a potential therapeutic strategy. Atherosclerosis. 2014;233(2): 721-728.[6] Lippi G, Meschi T, Mattiuzzi C, et al. Adiponectin and migraine: systematic review of clinical evidence. Neurol Sci. 2014;35(8):1167- 1171.[7] Tang Y, Gan X, Cheheltani R, et al. Targeted delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor improves stem cell therapy in a rat myocardial infarction model. Nanomedicine. 2014;10(8):1711-1718.[8] Atashi F, Modarressi A, Pepper MS. The role of reactive oxygen species in mesenchymal stem cell adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation: a review. Stem Cells Dev. 2015; 24(10):1150-1163.[9] Jeong H, Yim HW, Cho YS, et al. Efficacy and safety of stem cell therapies for patients with stroke: a systematic review and single arm meta-analysis. Int J Stem Cells. 2014;7(2):63-69.[10] Bruin JE, Saber N, Braun N, et al. Treating diet-induced diabetes and obesity with human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitor cells and antidiabetic drugs. Stem Cell Reports. 2015;4(4):605-620.[11] Morigi M, De Coppi P. Cell therapy for kidney injury: different options and mechanisms--mesenchymal and amniotic fluid stem cells. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2014;126(2):59.[12] Ma T, Sun J, Zhao Z, et al. A brief review: adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):124.[13] Tabatabaei Qomi R, Sheykhhasan M. Adipose-derived stromal cell in regenerative medicine: A review. World J Stem Cells. 2017;9(8):107-117.[14] Saidi RF, Rajeshkumar B, Shariftabrizi A, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate liver ischemia-reperfusion injury and promote liver regeneration. Surgery. 2014;156(5):1225-1231.[15] Chen L, Qin F, Ge M, et al. Application of adipose-derived stem cells in heart disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2014; 7(7):651-663.[16] Kho MC, Park JH, Han BH, et al. Plantago asiatica L. Ameliorates Puromycin Aminonucleoside-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome by Suppressing Inflammation and Apoptosis. Nutrients. 2017;9(4): E386.[17] 高大维,杨鹏.血管内皮生长因子基因修饰羊膜间充质干细胞移植治疗肾病综合征[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):83-88.[18] Chru?ciel P, Sahebkar A, Rembek-Wieliczko M, et al. Impact of statin therapy on plasma adiponectin concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 randomized controlled trial arms. Atherosclerosis. 2016;253:194-208.[19] Kawwass JF, Summer R, Kallen CB. Direct effects of leptin and adiponectin on peripheral reproductive tissues: a critical review. Mol Hum Reprod. 2015;21(8):617-632.[20] 程捷瑶,王美娟,马红,等.脂联素通过腺苷酸激活蛋白激酶途径抑制大鼠肝星状细胞氧化应激并调控转化生长因子β1和Ⅰ型胶原表达[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2015,23(1):69-72.[21] 王林,解汝娟,刘晓刚.脂代谢异常对肾病的影响[J].现代生物医学进展, 2015,15(13):2577-2580.[22] 朱磊,解德琼,张臣丽,等.肾病综合征患者外周血T细胞亚群及血清脂联素水平与患者激素治疗效果的关系[J].河北医学, 2017, 23(10):1646-1649.[23] 陈海天,叶景光,吴淑端,等.妊娠期糖尿病孕妇胎盘组织中脂联素的表达及滋养细胞增殖的变化[J].中华围产医学杂志,2014, 17(11):760-763.[24] 陈海天,王冬昱,耿慧珍,等.脂联素对体外高糖诱导的滋养细胞增殖的抑制作用[J].中华妇产科杂志,2016,51(3):204-208.[25] 屠叶平,施辉.脂联素和胱抑素C在糖尿病肾病早期诊断中的临床意义[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2014,23(20):2191-2194.[26] 杨笑云,常宝成,单春艳,等.“亚临床”2型糖尿病肾病患者尿血管紧张素原水平及相关因素分析[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2015,31(5):395-399.[27] 王丽,郭宏,王曦,等.不同分期老年2型糖尿病肾病患者外周血调节性和辅助性T细胞的表达[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014,34(18): 5142-5143.[28] 李美花.盐酸川芎嗪联合螺内酯治疗糖尿病肾病的疗效观察[J].中国实用医刊,2016,43(3):127-128.[29] 潘锡正,林芳.肾小球电荷屏障研究的新进展[J].医学综述,2014, 20(12): 2138-2140.[30] 郭倩,张肖,刘利飞,等.化瘀通络中药对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾小球电荷屏障的影响[J].中医杂志,2016,57(8):690-695.[31] 刘增波,梅长林,胡惠民,等.乙酰肝素酶对脓毒症肾小球内皮细胞糖萼的影响[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2014,30(7):524-529. |