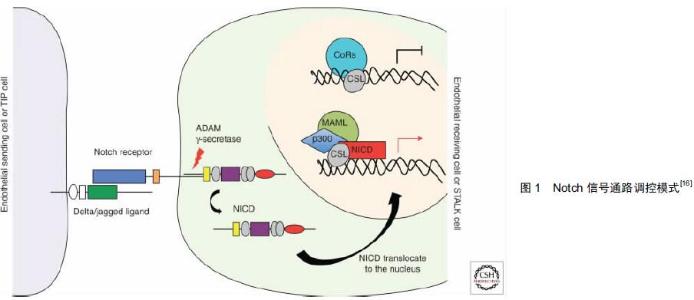
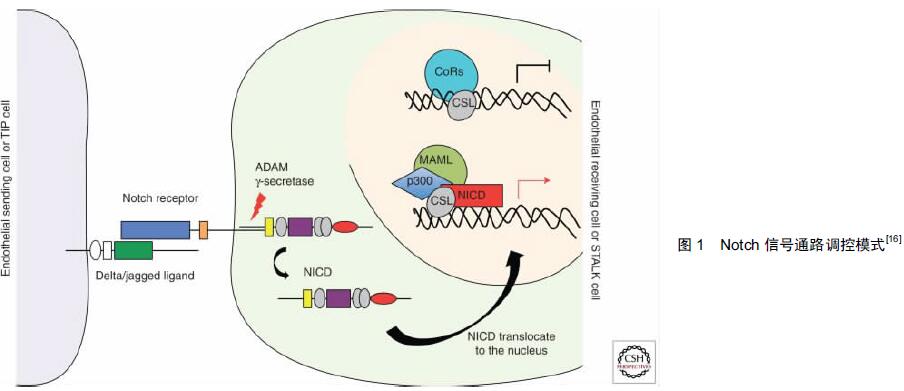
[2] Hillen F, Griffioen AW. Tumour vascularization: sprouting angiogenesis and beyond. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007; 26(3-4): 489-502.
[3] Makanya AN, Hlushchuk R, Djonov VG. Intussusceptive angiogenesis and its role in vascular morphogenesis, patterning, and remodeling. Angiogenesis.2009;12(2):113-123.
[4] Kopan R, Ilagan MX. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell,2009, 137(2):216-233.
[5] Fish JE, Wythe JD.The molecular regulation of arteriovenous specification and maintenance. Dev Dyn.2015;244(3):391-409.
[6] Zhang G, Zhou J, Fan Q, et al. Arterial-venous endothelial cell fate is related to vascular endothelial growth factor and Notch status during human bone mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. FEBS Lett.2008; 582(19):2957-2964.
[7] Lanner F, Sohl M, Farnebo F. Functional Arterial and Venous Fate Is Determined by Graded VEGF Signaling and Notch Status During Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2007;27(3):487-493.
[8] Lamont RE,Childs S.Mapping out arteries and veins.Sci STKE.2006;355:pe39.
[9] Lin FJ, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY. Artery and vein formation: a tug of war between different forces. EMBO Reports. 2007;8(10): 920-924.
[10] Gerhardt H, Golding M, Fruttiger M, et al.VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol. 2003;161(6):1163-1177.
[11] Isogai S, Lawson ND, Torrealday S, et al. Angiogenic network formation in the developing vertebrate trunk. Development. 2003;130(21):5281-5290.
[12] Dejana E, Tournier-Lasserve E, Weinstein BM. The Control of Vascular Integrity by Endothelial Cell Junctions: Molecular Basis and Pathological Implications.Developmental Cell. 2009;16(2):209-221.
[13] Iruela-Arispe ML, Davis GE. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Vascular Lumen Formation. Developmental Cell.2009;16(2):222-231.
[14] Phng LK, Gerhardt H. Angiogenesis: a team effort coordinated by notch. Dev Cell.2009;16(2):196-208.
[15] Benedito R,Hellstrom M.Notch as a hub for signaling in angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res.2013;319(9):1281-1288.
[16] Blanco R,Gerhardt H. VEGF and Notch in Tip and Stalk Cell Selection. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.2013;3(1):a006569.
[17] Jakobsson L, Franco CA, Bentley K, et al. Endothelial cells dynamically compete for the tip cell position during angiogenic sprouting. Nature Cell Biology.20.10;12(10), 943-953.
[18] Hellstrom M, Phng LK, Hofmann JJ,et al. Dll4 signalling through Notch1 regulates formation of tip cells during angiogenesis.Nature. 2007;445(7129):776-780.
[19] Benedito R, Roca C, Sorensen I,et al. The Notch Ligands Dll4 and Jagged1 Have Opposing Effects on Angiogenesis. Cell. 2009;137(6):1124-1135.
[20] Beets K, Huylebroeck D, Moya IM, et al. Robustness in angiogenesis: Notch and BMP shaping waves. Trends In Genetics, 2013,29(3): 140-149.
[21] Leslie JD, Ariza-McNaughton L, Bermange AL,et al. Endothelial signalling by the Notch ligand Delta-like 4 restricts angiogenesis.Development. 2007;134(5), 839-844.
[22] Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P. Basic and Therapeutic Aspects of Angiogenesis. Cell.2011;146(6): 873-887.
[23] Miyamoto A, Lau R, Hein PW, et al. Microfibrillar proteins MAGP-1 and MAGP-2 induce Notch1 extracellular domain dissociation and receptor activation.J Biol Chem.2006;281(15):10089-10097.
[24] Albig AR, Becenti DJ, Roy TG,et al. Microfibril-associate glycoprotein-2 (MAGP-2) promotes angiogenic cell sprouting by blocking notch signaling in endothelial cells. Microvasc Res.2008;76(1):7-14.
[25] Mettouchi A. The role of extracellular matrix in vascular branching morphogenesis. Cell Adh Migr.2012;6(6):528-534.
[26] Trindade A, Kumar SR, Scehnet JS,etal. Overexpression of delta-like 4 induces arterialization and attenuates vessel formation in developing mouse embryos. Blood.2008; 112(5): 1720-1729.
[27] Benedito R, Trindade A, Hirashima M, et al. Loss of Notch signalling induced by Dll4 causes arterial calibre reduction by increasing endothelial cell response to angiogenic stimuli. BMC Dev Biol.2008;8:117.
[28] Harrington LS, Sainson RC, Williams CK, et al.Regulation of multiple angiogenic pathways by Dll4 and Notch in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Microvasc Res.2008; n75(2): 144-154.
[29] Hodkinson PS, Elliott PA, Lad Y, et al. Mammalian NOTCH-1 activates beta1 integrins via the small GTPase R-Ras. J Biol Chem.2007;282(39):28991-29001.
[30] Phng LK, Potente M, Leslie JD, et al. Nrarp coordinates endothelial Notch and Wnt signaling to control vessel density in angiogenesis.Dev Cell. 2009;16(1):70-82.
[31] Pedrosa AR,Trindade A,Fernandes AC,et al.Endothelial Jagged1 antagonizes Dll4 regulation of endothelial branching and promotes vascular maturation downstream of Dll4/Notch1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2015; 35(5): 1134-1146.