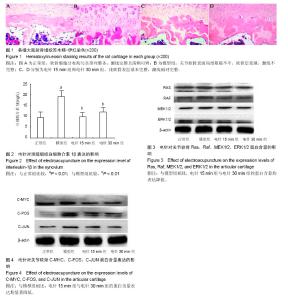
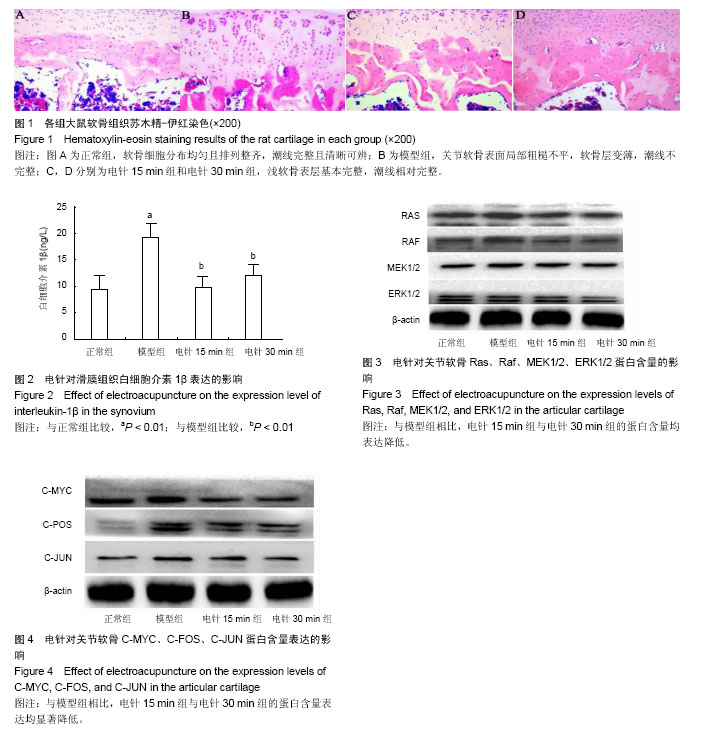
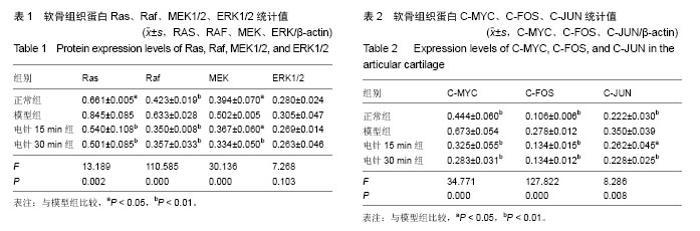
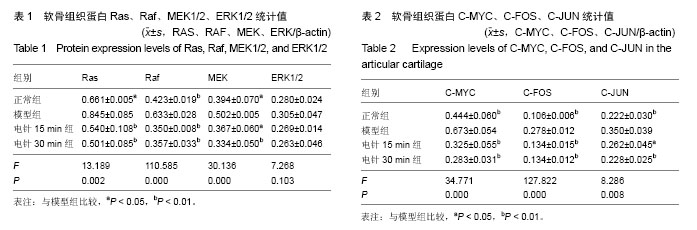
| [1] Chen WH, Liu XX, Tong PJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of knee osteoarthritis Chinese medicine expert consensus (2015).Chin J Integr Med.2016;2:150-153.[2] 刘献祥.基于陈可冀学术思想之骨性关节炎研究[J].康复学报, 2016,26(1):2-5.[3] Li X, Zhen Z, Tang G, et al. MiR-29a and MiR-140 Protect Chondrocytes against the anti-proliferation and cell matrix signaling changes by IL-1β.Mol Cells.2016;39(2):103-110.[4] 林木南,林艳红,刘献祥,等.温热疏密波对膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨细胞RAS/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路的影响[J].中医正骨, 2016,28(2):1-6.[5] Wang X,Li F,Fan C,et al.Effects and relationship of ERK 1 and ERK 2 in interleukin-1β- induced alterations in MMP3,MMP13, type II collagen and aggrecan expression in human chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med.2011;27(4):583-589.[6] 林洁,付长龙,李俐,等.电针治疗膝骨性关节炎疗效的系统评价[J].康复学报,2016,26(4):52-58.[7] Wu MX, Li XH, Lin MN,et al. Clinical study on the treatment of knee osteoarthritis of Shen-Sui insufficiency syndrome type by electroacupuncture. Chin J Integr Med.2010;16(4): 291-297.[8] 李西海,梁文娜,党传鹏,等.补肾壮筋汤抑制炎性细胞因子表达延缓骨关节炎软骨退变的研究[J].风湿病与关节炎,2014,3(5): 20-25.[9] 吴明霞,李西海,吴广文,等.电针后血清对肿瘤坏死因子α诱导软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(46): 8551-8555.[10] Shakoor MA, Rahman MS, Azad AK, et al. Effects of isometric quadriceps muscle strengthening exercise on chronic osteoarthritis of the knee.Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 2010;36 (1):20-22.[11] 杨渠平,范宁,何仁建.膝关节骨性关节炎的性别差异及相关因素[J].中国老年学杂志, 2016,36(1):144-146.[12] 赵昌盛,钟群杰,林剑浩.中国膝关节骨关节炎流行病学调查现状[J].广东医学,2016,37(13):2050-2052.[13] Changlong Fu, Chunsong Zheng, Jie Lin, et al. Cibotium barometz polysaccharides stimulate chondrocyte proliferation in vitro by promoting G1/S cell cycle transition. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(5):3027-3034.[14] 吕苏梅,张瑞丽.中老年膝骨关节炎的流行病学研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(16):4133-4135.[15] Liu F, Liu G, Liang W, et al.Duhuo Jisheng decoction treatment inhibits the sodium nitroprussiate-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes through the mitochondrial dependent signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med.2014;34(6): 1573-1580.[16] Ye JX, Wu GW, Li XH, et al.Millimeter Wave Treatment Inhibits Apoptosis of Chondrocytes via regulation Dynamic Equilibrium of Intracellular Free Ca2+.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2015:464161.[17] 邵翔,陈后煌,陈达,等.透骨消痛胶囊抑制脂多糖诱导软骨细胞炎症反应的机制研究[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(6):406-410.[18] Li X,Zhen Z,Tang G,et al.MiR-29a and MiR-140 Protect Chondrocytes against the anti-proliferation and cell matrix signaling changes by IL-1β.Mol Cells.2016;39(2):103-110.[19] Quan YY,Qin GQ,Huang H, et al. Dominant roles of fenton reaction in sodium nitroprusside-induced chondrocyte apoptosis.Free Radic Biol Med.2016; 94:135-144.[20] 吴明霞,李西海,李俐,等.电针对骨性关节炎软骨细胞JAK-STAT信号通路表达的影响[J].福建中医药大学学报,2011,21(6): 21-23.[21] 吴明霞,李西海,李俐,等.电针后血清对TNF-α诱导凋亡软骨细胞MAPK信号通路的影响[J].福建中医药,2011,42(6):43-45.[22] O'Neill E, Kolch W. Conferring specificity on the ubiquitous Raf/MEK signalling pathway. Br J Cancer.2004;90(2): 283-288.[23] Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, et al. Sorafenib blocks the raf/mek/erk pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res.2006;66(24): 11851-11858.[24] 蒋成英,戴广海.Ras/Raf/Mek/Erk信号传导通路在肝细胞癌发生中的作用机制及在靶向治疗中的应用[J].中国肿瘤临床,2008, 35(23):1377-1380.[25] Karnoub AE, Weinberg RA. Ras oncogenes: split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2008;9(7):517-531.[26] Roskoski R. ERK1 /2 MAP kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res.2012;66(2):105-143.[27] Yatsugi N,Tsukazaki T,Osaki M,et al.Apoptosis of articular chondrocytes in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: correlation of apoptosis with degree of cartilage destruction and expression of apoptosis-related proteins of p53 and c-myc. J Orthop Sci.2000;5:150-156.[28] Gustems M,Woellmer A,Rothbauer U, et al.c-Jun/c-Fos heterodimers regulate cellular genes via a newly identified class of methylated DNA sequence motifs . Nucleic Acids Res.2014;42(5):3059-3072.[29] Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Osteoarthritis.J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:626-634.[30] Schuenrwegh AJ, Dombrecht E, Stevens WJ, et al. Influence of proinflammatory (IL-1 alpha, IL-6, TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4) cytokines on chondrocyte function. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2003; 11: 681-687.[31] 王宁,龙迪,孟晓娜.IL-1β对小鼠软骨细胞中c-myc蛋白表达的影响[J].中华临床医师杂志,2013,7(23):11486-11490. |