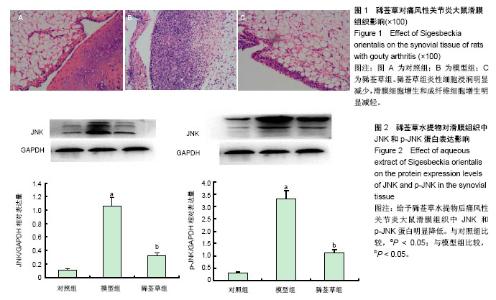
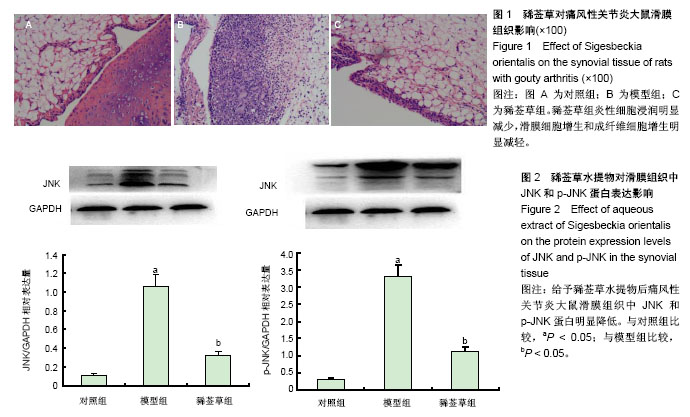
| [1] Gentle MJ. Sodium urate arthritis: effects on the sensory properties of articular afferents in the chicken. Pain.1997;70(2/3):245.[2] Miguélez R,Palacios I,Navarro F, et al.Antiinflammatory effect of a PAF receptor antagonist and a new molecule with antiproteinase activity in an experimental model of acute urate crystal arthritis.J Lipid Mediat Cell Signal.1996;13(1):35.[3] Sabina EP,Rasool M.An in vivo and in vitro potentialof indian ayurvedic herbal formulation triphala onexperimental gouty arthritis in mice.Vascul Pharmacol.2008;48(1):14.[4] Dhawan P, Richmond A. A novel NF- kappa B inducing kinase MAPK signaling pathway up regulates NF- kappa B activity in melanoma cells . J Biol Chem.2002; 277(10):7920-7928.[5] Craig R, Larkin A, Mingo AM, et al. p38 MAPK and NFkappaB collaborate to induce interleukin- gene expression and release. J Biol Chem.2000; 275(31):23814-23824.[6] Joh nson GL,Lapadat R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science.2002; 298(5600):1911-1912.[7] 孙贵才,于学峰,李登宇,等.复方豨莶草胶囊对尿酸钠致大鼠关节炎滑膜IL-1β、IL-8含量的影响[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2007, 2(6): 329-331.[8] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典(一部)[M].北京:中国医药出版社,2010:345.[9] Wang J,Cai Y,Wu Y. Antiinflammatory and analgesic activity of topical administration of Siegesbeckia pubescens.Pak J Pharm Sci.2008;21 (2):89-91.[10] 王发辉,冯起校,黄超文.豨莶草药理研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2011,13(10):102-104.[11] Zhang QB,Qing YF,He YL,et al.Association of NLRP3 polymorphisms with susceptibility to primary gouty arthritis in a Chinese Han population. Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Dec 7.[12] 万春平,李兆福,徐翔峰,等.急性痛风性关节炎免疫学发病机制研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2012,1(4):52-55. [13] Zhou W,Wang Y,Wu R,et al.MicroRNA-488 and -920 regulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines in acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Res.Ther.2017;19(1): 203.[14] Khameneh HJ, Ho AW, Laudisi F, et al.C5a Regulates IL-1β Production and Leukocyte Recruitment in a Murine Model of Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced Peritonitis.Front Pharmacol. 2017; 8:10.[15] Zhou Q, Yu DH, Zhang N, et al.Anti-inflammatory effect of total saponin fraction from Dioscorea nipponica Makino on gouty arthritis and its influence on NALP3 inflammasome. Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Feb 15. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2741-5.[16] Reinwald C, Schauer C, Csepregi JZ,et al. Erratum: Reply to "Neutrophils are not required for resolution of acute gouty arthritis in mice".Nat. Med. 2017; 23(4): 526.[17] Broxmeyer HE.Erythropoietin: multiple targets, actions, and modifying influences for biological and clinical consideration. J Exp Med.2013; 210(2):205-208.[18] Turj an ski AG,V aque JP, Gutk ind JS. MAP kinases and the control of nuclear events. Oncogene.2007; 26(22):3240-3253[19] Han J,Lee JD,Jiang Y,et al.Characterization of the structure and function of a novel MAP kinase kinase (MKK6).J Biol Chem.1996; 271(6): 2886-2891.[20] Liu H, Zhou M. Antitumor effect of Quercetin on Y79 retinoblastoma cells via activation of JNK and p38 MAPK pathways.BMC Complement Altern Med.2017;17(1): 531.[21] Fung TS, Liu DX. Activation of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway by coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus promotes apoptosis independently of c-Jun.Cell Death Dis.2017; 8(12): 3215.[22] Jo AR,Han HS,Seo S,et al.Inhibitory effect of moschamine isolated from Carthamus tinctorius on LPS-induced inflammatory mediators via AP-1 and STAT1/3 inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Bioorg Med Chem Lett.2017; 27(23): 5245-5251.[23] Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP.JNK-signaling: A multiplexing hub in programmed cell death.Genes Cancer.2017;8(9-10): 682-694.[24] Lin CY,Wang WH,Chen SH,et al.Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Nitric Oxide, Prostaglandin E2, and Cytokine Production of Mouse and Human Macrophages Are Suppressed by Pheophytin-b. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(12). pii: E2637.[25] Han Q,Bing W,Di Y,et al.Kinsenoside screening with a microfluidic chip attenuates gouty arthritis through inactivating NF-κB signaling in macrophages and protecting endothelial cells.Cell Death Dis.2016;7(9): e2350 |