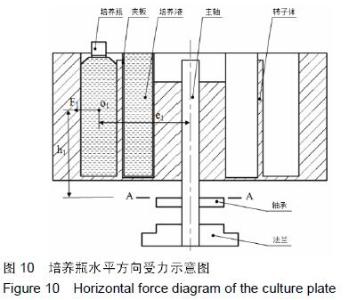
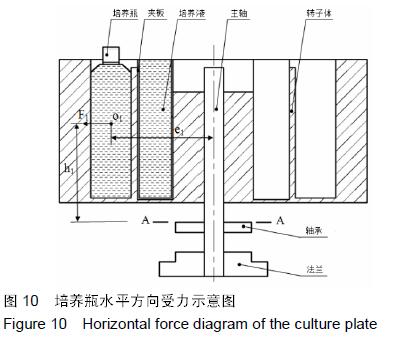
|
[1] 胡深,张洪义,李新慧,等.超高正加速度重复持续性暴露加重对大鼠肝细胞超微结构的损伤[J].中国医刊, 2015,50(2):45-49.
[2] 姚永杰,司高潮.当代载人离心机的现状与发展趋势[J].空军医学杂志,2013,28(1):60.
[3] Gould RK. Syncope as the first sign of complete heart block in a military aviator. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2010;81(4): 431-432.
[4] Catrambone DE, Dawson SW. Vasodilation associated with supplement use: potential concern for military aviators. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2013;84(8):872-873.
[5] 张建,王庆敏,李明皋,等.外军航母舰载机飞行员职业特点分析[J].海军医学杂志,2012,33(2):144-145.
[6] Dancuo Z, Zeljkovic V. High G Training Profiles in a High Performance Human Centrifuge. Scientific Technical Review. 2012;66(1):64-69.
[7] 李莹辉. 21世纪的航天医学细胞分子生物学[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2003,16(z1):588-592
[8] Zorana D, Bosko R, Jelena V, et al. On Mechanics of a High-G Human Centrifuge. PAMM. 2013;13(1):39-40.
[9] Li XM, Li HL. Development and Key Technology of Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System. Journal of academy of Armored Force Engineering. 2014;28(4):1-7.
[10] 吴斌,刘兴华,阚广捍,等.高+Gx作用对猴肺脏的病理学影响[J]. 航天医学与医学工程杂志, 2004,17(6):397-401.
[11] 牛忠英,吴斌,张建中.高+G过载对猴肾脏组织病理学的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2005,30(2):240-244.
[12] 徐冶,李质馨,田洪艳,等.正加速度暴露对大鼠海马星形胶质细胞GFAP表达的影响[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2005, 14(6):644-647.
[13] 常颖,李聪,张风波.离心机转子力学性能的有限元分析及测试[J]. 化工机械, 2012,39(4):478-482. |