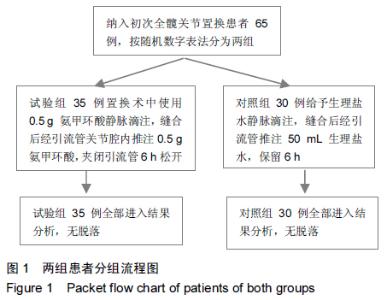
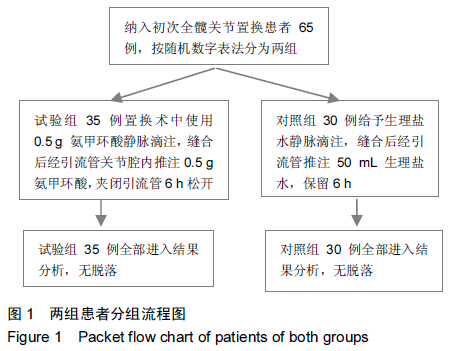
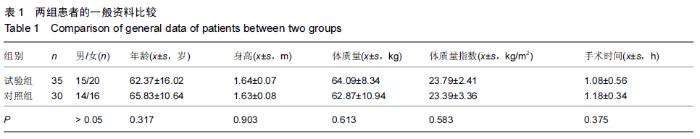
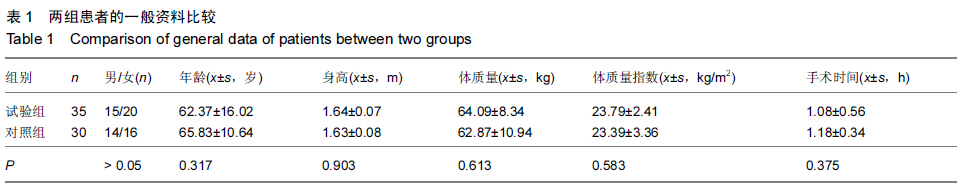
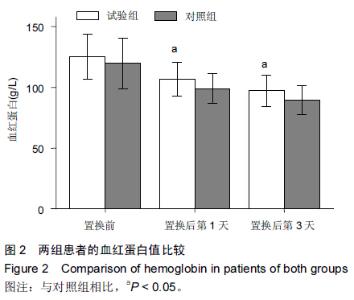
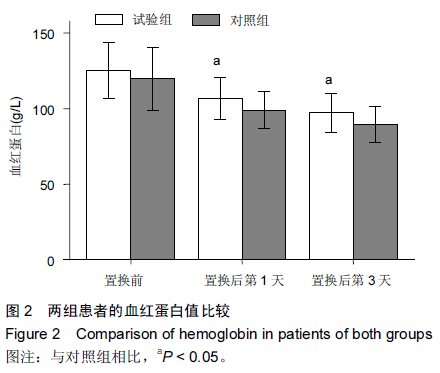
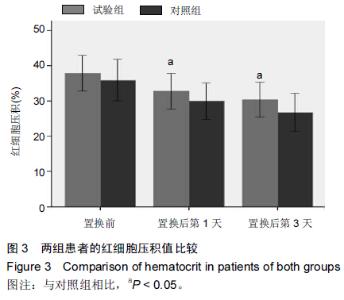
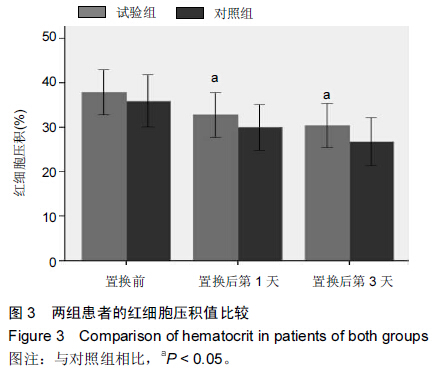
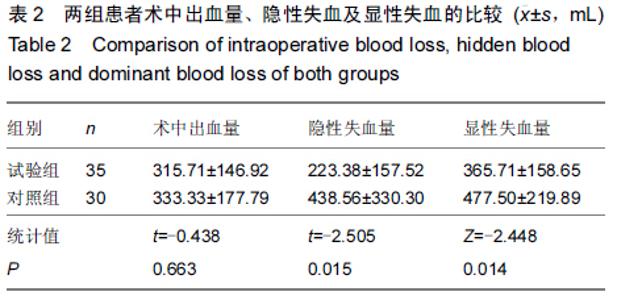
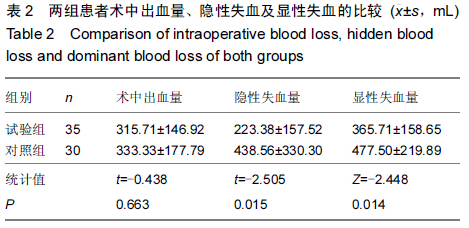
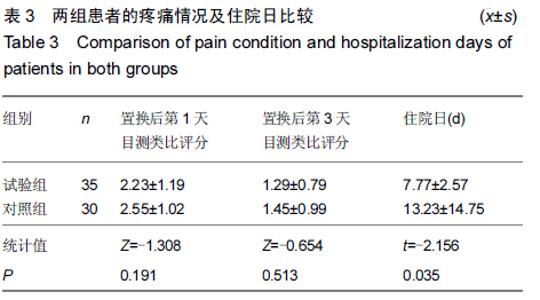
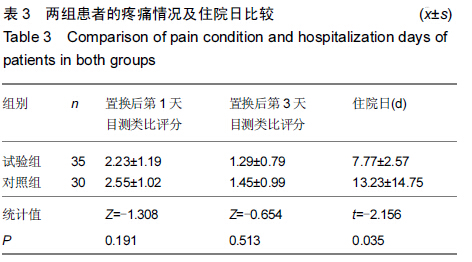
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (44): 7071-7076.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.44.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Intravenous drip and topical application using tranexamic acid decrease hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty
Zhang Cheng-huan1, Liu Yun2, Zhao Jian-ning3, Meng Jia3, Yuan Tao3, Bao Ni-rong3
- 1School of Nursing, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Cadre Training Center, 3Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Region, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-05Online:2015-10-22Published:2015-10-22 -
Contact:Bao Ni-rong, M.D., Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Region, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhang Cheng-huan, Studying for master’s degree, School of Nursing, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Clinical Medical Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province, No. BL2012002; the Science and Technology Project of Nanjing City, No.201402007; the Special Fund for the Prevention and Treatment of Thrombosis after Surgical Operation in Department of Orthopedics of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, No.20150214
Cite this article
Zhang Cheng-huan, Liu Yun, Zhao Jian-ning, Meng Jia, Yuan Tao, Bao Ni-rong. Intravenous drip and topical application using tranexamic acid decrease hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(44): 7071-7076.
share this article
| [1] Tobias JD. Strategies for minimizing blood loss in orthopedic surgery. Semin Hematol. 2004;41(1 Suppl 1):S145-156. [2] Sabatini L, Trecci A, Imarisio D, et al. Fibrin tissue dhesive reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol. 2012;13(3):145-151.
[3] Liu X, Zhang X, Chen Y, et al. Hidden blood loss after total hip arthoplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(7):1100-1105.
[4] Hawi N, Kendoff DO, Hessling U, et al. Effectiveness of an autologous transfusion system following cemented and non-cemented revisions of total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2014; 38(8):1603.
[5] Horstmann WG, Swierstra MJ, Ohanis D, et al. Favourable results of a new intraoperative and postoperative filtered autologous blood re-transfusion system in total hip arthroplasty: a randomised controlled trial. Int Orthop.2014; 38(1):13.
[6] Alshryda S, Sukeik M, Sarda P, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the topical administration of tranexamic acid in total hip and knee replacement. Bone Joint J. 2014;96(8): 1005-1015.
[7] Zhou X, Tao L, Li J, et al. Do we really need tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of nineteen randomized controlled trials. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133(7):1017-1027.
[8] Singh J, Ballal MS, Mitchell P, et al. Effects of tranexamic acid on blood loss during total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg. 2010;18(3):282.
[9] Kazemi SM, Mosaffa F, Eajazi A, et al. The effect of tranexamic acid on reducing blood loss in cementless total hip arthroplasty under epidural anesthesia. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(1):17.
[10] 周一新.骨科标准新突破手术技术指导规范《人工髋、膝关节置换术》解读[J].中国卫生标准管理,2011,2(4):72-74.
[11] Ward CF, Meathe EA, Benumof JL, et al. A computer nomogram for blood loss replacement. Anesthesiology. 1980;53:126-130.
[12] Gross JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;3:277-280.
[13] Nadler SB,Hidalgo JU,Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;57:224-232.
[14] Dauzat MM, Laroche JP, Charras G, et al. Real-time B-mode ultrasongraphy for better specialty in the noninvesive diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. J Ultrasound Med. 1986;5(11):625-631.
[15] 谢锦伟,岳辰,裴福兴.氨甲环酸在全髋关节置换术中的有效性与安全性研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(20):1856-1860.
[16] 刘志刚,张上上,陈如见,等. 全髋关节置换后的隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13):2305-2313.
[17] 徐海永,张明,方怀玺,等.初次全髋关节置换后的隐性失血:影响因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(13):1974-1978.
[18] 李少斐,郭亭,赵建宁,等. 围髋关节置换期隐性失血相关危险因素及预后[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(13):2006-2011.
[19] McManus KT, Velchik MG, Alavi A, et al. Non-invasive assessment of postoperative bleeding in TKA patients with Tc-99m RNCs. J Nuclear Med. 1987;28:565-567.
[20] Bao N, Zhou L,Cong Y,et al. Free fatty acids are responsible for the hidden blood loss in total hip and knee arthroplasty. Med Hypotheses. 2013;133(1)104-107.
[21] 丛宇,赵建宁,包倪荣,等.隐性失血对全髋关节置换术后功能恢复影响的临床观察[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(6):466-468.
[22] Bowditch MG, Villar RN. Do obese patients bleed more?A prospective study of blood loss at total hip replacement. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1999;81(3):198-200.
[23] 覃健,余存泰,徐中和,等.全髋关节及全膝关节置换术后隐性失血的临床影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(5):323-326.
[24] Prasad NP,admanabhan V,Mullajj A.Blood loss in total knee arthroplasty an analysis of risk factors. Int Orthop. 2007; 31(1):39-44.
[25] Oremus K, Sostaric S, Trkulja V, et al. Influence of tranexamic acid on postoperative autologous blood retransfusion in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Transfusion. 2014; 54(1):31-41.
[26] McConnell JS, Shewale S,Munro NA, et al. Reduction of blood loss in primary hip arthroplasty with tranexamic acid or fibrin spray: a randomized controlled trial Acta Orthopaedica. 2011;82(6):660-663.
[27] Nishihara S, Hamada M. Does tranexamic acid alter the risk of thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty in the absence of routine chemical thromboprophylaxis? Bone Joint J. 2015; 97(4):458-462.
[28] Gillette BP, DeSimone LJ, Trousdale RT, et al.Low risk of thromboembolic complications with tranexamic acid after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):150-154.
[29] Rajesparan K, Biant LC, Ahmad M, et al. The effect of an intravenous bolus of tranexamic acid on blood loss in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91:776.
[30] Irwin A, Khan SK, Jameson SS, et al. Oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid in enhanced-recovery primary total hip and knee replacement Results of 3000 procedures. Bone Joint J. 2013;95(11):1556-1561.
[31] Machin JT, Batta V, Soler JA, et al. Comparison of Intra-operative Regimes of Tranexamic Acid Administration in Primary Total Hip Replacement. Acta Orthopedica Belgica. 2014;80: 228-233.
[32] Seo JG, Moon YW, Park SH, et al. The comparative efficacies of intra-articular and IV tranexamic acid for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(8):1869-1874.
[33] Alshryda S, Mason J, Vaghela M, et al. Topical (intra-articular) tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates following total kneereplacement: a randomized controlled trial (TRANX-K). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(21):1961-1968.
[34] Hourlier H, Fennema P.Single tranexamic acid dose to reduce perioperative morbidity in primary total hip replacement: a randomised clinical trial. Hip Int.2013;24(1):63-68.
[35] Rajesparam K,Binat LC,Ahmad M,et al.The effect of an intravenous bolus of tranexamic acid on blood loss in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91:776-783.
[36] Soni A, Saini R, Gulati A, et al. Comparison Between Intravenous and Intra-articular Regimens of Tranexamic Acid in Reducing Blood Loss During Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014.
[37] Patel JN, Spanyer JM, Smith LS, et al. Comparison of Intravenous versus Topical Tranexamic Acid in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Randomized Study. J Arthroplasty. 2014.
[38] Tyler C, Wind MD, William R, et al. The Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Transfusion Rate in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:387-389.
[39] 马云青,张轶超,张洪.氨甲环酸在单侧全膝关节置换术中局部应用的止血效果分析[J].中华外科杂志, 2013, 51(1):40-43.
[40] Gandhi R, Evans HM, Mahomed SR, et al.Tranexamic acid and the reduction of blood loss in total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. BMC Res Notes. 2013;6:184.
|
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [3] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [9] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [10] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [11] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [12] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [13] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [14] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [15] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||