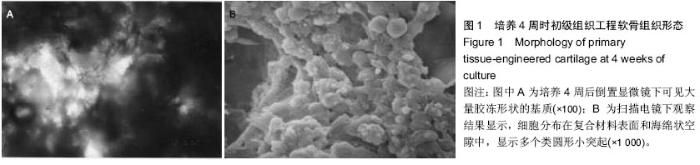
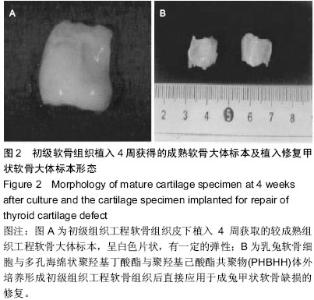
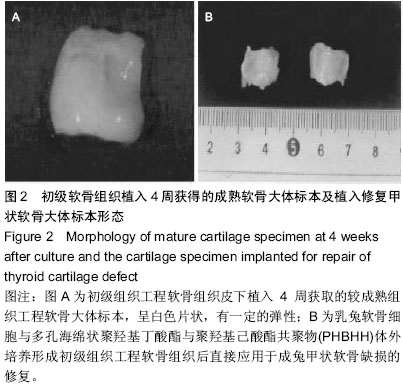
| [1] 张永先,侯春林,王永胜.组织工程技术修复同种异体兔关节软骨缺损实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(29):668-670.
[2] 孙安科,陈文弦,崔鹏程,等.同种异体工程化软骨的构建和修复甲状软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2001,36(43): 278-280.
[3] 孙安科,胡平,李万同,等.组织工程PHBHH多孔材料喉支架的制备与细胞相容性研究[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2011,19(6): 558-561.
[4] 孙安科,李万同,孟庆延,等.带蒂肌筋膜瓣充填与包裹构建喉支架形态组织工程软骨[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2011, 46(12): 1019-1023.
[5] Awad HA, Wickham MQ, Leddy HA, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived adult stem cells in agarose, alginate, and gelatin scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2004;25(16): 3211-3222.
[6] Dunham BP, Koch RJ. Basic fibroblast growth factor and insulinlike growth factor I support the growth of human septal chondrocytes in a serum-free environment. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;124(12):1325-1330.
[7] 孙安科,裴国献,胡平,等.组织工程化喉软骨的构建[J].中华耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2004,39(10):606-611.
[8] 王健,夏万尧,崔磊,等.同种异体组织工程化软骨的免疫学差异[J].中华创伤杂志,2001,17(7):428-430.
[9] 张世浩,朱立新,靳安民,等.软骨细胞复合胶原/壳聚槲/β-磷酸三钙层状梯度修复体的体外培养[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(41):8033-8036.
[10] 姜洪丰,魏巍,解云川,等.组织工程化软骨修复兔膝关节软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华显微外科杂志,2006,29(3):206-208.
[11] 张雷,于洪波,矫晓昆,等.应用液态及凝胶态生物载体材料负载同种异体软骨细胞修复全厚关节软骨缺损[J].中国临床康复, 2006, 10(45):190-193.
[12] 王东武,杨柳,段小军,等.可注射温固化支架复合异体软骨细胞修复关节软骨缺损的初步研究[J].重庆医学,2006,35(12): 1082-1084,1087.
[13] 陈克明,葛宝丰,刘兴炎,等.骨髓间充质干细胞复合纤维蛋白凝胶修复大面积关节软骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(6): 444-446.
[14] 冯万文,莱浙军,李小民,等.骨髓问充质干细胞和软骨细胞共培养种子细胞特征及体内成软骨活性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(3):442-446.
[15] 谭文成,查振刚,张嘉晴,等.动物源性骨软骨支架复合骨髓间充质干细胞/软骨细胞修复兔膝关节骨软骨复合缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(12):2265-2269.
[16] Marlovits S, Hombauer M, Truppe M, et al. Changes in the ratio of type-I and type-II collagen expression during momolayer culture of human chondrocytes. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2004;86(5):286-295.
[17] 吴雅迪,张刚,宋洪强,等.保存方法对同种异体软骨移植物免疫原性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(2): 201-204.
[18] Schulze-Tanzil G, Mobasheri A, de Souza P, et al. Loss ofchondrogenic potential in dedifferentiated chondrecytes correlates with deficient She-Ed interaction and apoptosis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(6):448-458.
[19] Kinooka M, Maeda Y, Ota Y, et al. Process design of chondrocyte cultures witll monolayer growth for eell expansion and subsequent thtee-dimensional growth for production of cultured cartilage. J Biosci Bioeng. 2005; 100(1): 67-76.
[20] Rasmusson I, Ringdén O, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem ceils inhibit lymphocyte proliferation by mitogens and alloantigens by different mechanisma. Exp Cell Res. 2005; 305(1): 33-41.
[21] 许波,董启榕,伏治国,等.同种异体骨髓基质细胞移植修复兔膝关节骨软骨缺损[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2008,28(1):56-58.
[22] 杨亚冬,张文元,房国坚,等.巢式PCR扩增性别决定基因序列检测兔骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗关节软骨缺损的修复组织来源[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(37):7341-7344.
[23] 张海宁,冷萍,王英振,等.骨软骨镶嵌成形术修复骨软骨复合缺损的比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(4):378-381.
[24] Jakcb RP, Franz T, Gautier E, et al. Autologous osteoehondral grafting in the knee: Indication, results, and reflection. Clin Orthop Ralet Res. 2002;(401):170-184.
[25] Koulalis D, Di Benedetto P, Citak M, et al. Comparative study of navigated versus freehand osteochondral graft transplantation of the knee. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(4): 803-807.
[26] 李文辉,侯筱魁,汤亭亭,等.自体骨软骨镶嵌移植修复猪膝关节骨软骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(6):456-458.
[27] 李旭,孙骏.自体骨髓基质干细胞辅助Mosaicplasty技术促进骨软骨缺损修复整合[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(11): 1067-1071.
[28] 孙骏,侯筱魁,李旭,等.单纯骨软骨镶嵌成形术与联合组织工程方法治疗急性骨软骨缺损的对比研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009,23(4):490-496.
[29] Maccario R, Podest M, Moretta A, et al. Interaction of human mesenchymal stem cells with cells involved in alloantigen- specific immune response favors the differentiation of CD4+ T-cell subsets expressing a regulatory/suppressive phenutype. Haematologica. 2005;90(4):516-525.
[30] Augello A, Tasso R, Negrini SM, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells inhibit lymphocyte proliferation by activation of the programmed death pathway. Eur J Immunol. 2005,35(5):1482-1490.
[31] Le Blanc K, Tammik C, Rosendahl K, et al. HLA expression and immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2003, 31(10):890-896.
[32] 闫磊,李思源,蔡晓玲.SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养及其生物学特性鉴定[J].实用医学杂志,2008,24(17):2945-2947.
[33] Tang QO, Carasco CF, Gamie Z, et al. Preclinical and clinical data for the use of mesenchymal stem cells in articular cartilage tissue engineering. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012; 12(10): 1361-1382.
[34] Xie J, Han Z, Naito M, et al.Articular cartilage tissue engineering based on a mechano-active scaffold made of poly (L-lactide- co-epsilon-caprolactone): in vivo performance in adult rabbits. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010; 94(1):80-88.
[35] Park JS, Yang HN, Woo DG, et al. Chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells in fibrin constructs evaluated in vitro and in nude mouse and rabbit defects models. Biomaterials. 2011;32(6):1495-1507.
[36] Wei B, Jin C, Xu Y, et al. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular matrix scaffold on chondrogenic differentiation of marrow clot after microfracture of bone marrow stimulation in vitro. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(4):464-474.
[37] Bhumiratana S, Eton RE, Oungoulian SR, et al. Large, stratified, and mechanically functional human cartilage grown in vitro by mesenchymal condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(19):6940-6945.
孙安科,胡平,李万同,等.组织工程PHBHH多孔材料喉支架的制备与细胞相容性研究[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2011,19(6): 558-561. |