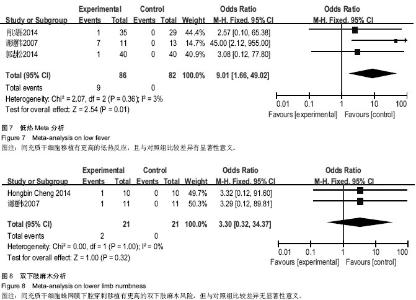
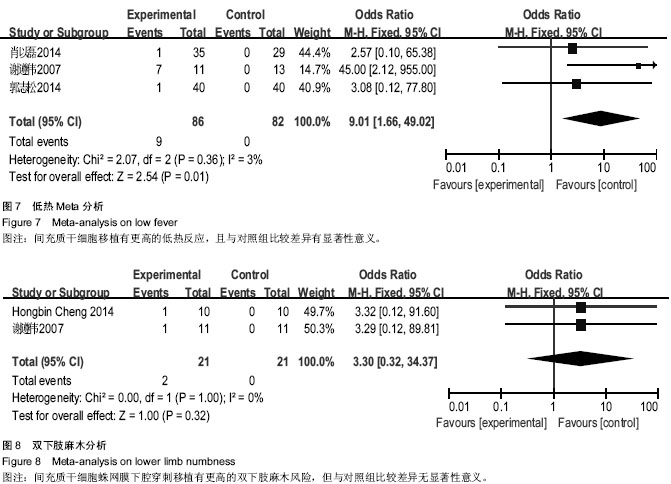
| [1] Sarmento CA, Rodrigues MN, Bocabello RZ, et al. Pilot study: bone marrow stem cells as a treatment for dogs with chronic spinal cord injury. Regen Med Res. 2014;2(1):9-11.
[2] Burns TC, Verfaillie CM. From mice to mind: Strategies and progress in translating neuroregeneration. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;759:90-100.
[3] Vawda R, Fehlings MG. Mesenchymal cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: current & future perspectives. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 2013; 8(10): 25-38.
[4] Yip PK, Malaspina A. Spinal cord trauma and the molecular point of no return. Mol Neurodegener. 2012 Feb 8;7:6-10.
[5] Wakao S, Matsuse D, Dezawa M. Mesenchymal stem cells as a source of Schwann cells: their anticipated use in peripheral nerve regeneration. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014;200(1): 31-41.
[6] Ghosh M, Pearse DD. The role of the serotonergic system in locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury. Front Neural Circuits. 2015;8:151-154.
[7] Goodarzi P, Aghayan HR, Larijani B, et al. Stem cell-based approach for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015;29:168-170.
[8] Wakao S, Matsuse D, Dezawa M. Mesenchymal stem cells as a source of Schwann cells: their anticipated use in peripheral nerve regeneration. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014;200(1): 31-41.
[9] Wang A, Brown EG, Lankford L, et al. Placental mesenchymal stromal cells rescue ambulation in ovine myelomeningocele. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(6):659-669.
[10] Siddiqui AM, Khazaei M, Fehlings MG. Translating mechanisms of neuroprotection, regeneration, and repair to treatment of spinal cord injury. Prog Brain Res. 2015;218: 15-54.
[11] Brazelton TR, Rossi FM, Keshet GI, et al. From marrow to brain: expression of neuronal phenotypes in adult mice. Science. 2000;290(5497):1775-1779.
[12] Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM, et al. Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Blood. 2004;103(5):1669-1675.
[13] Ninomiya K, Iwatsuki K, Ohnishi Y, et al. Intranasal delivery of bone marrow stromal cells to spinal cord lesions. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23(1):111-119.
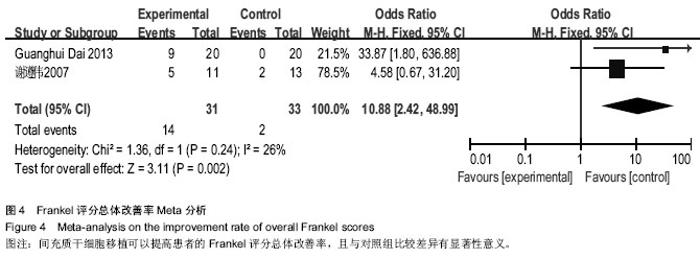
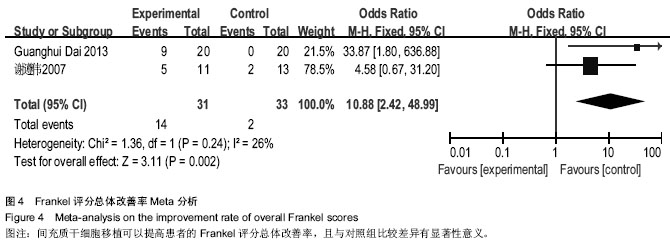
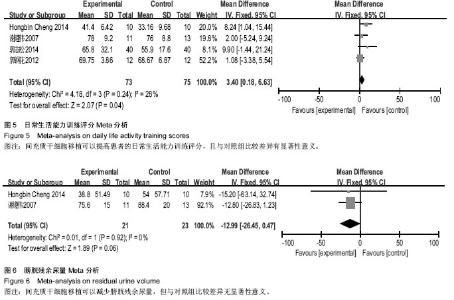
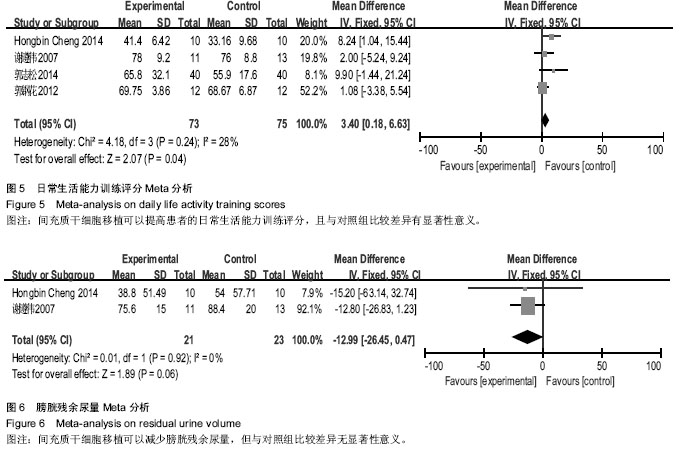
[14] 谢遵伟,崔贵祥,李义召,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤疗效观察[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(7): 1277-1279.
[15] 肖以磊,李忠民,朱建新,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗早期脊髓损伤疗效观察[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2014,20(1):7-11.
[16] 郭志松,秦秉玉,代荣钦,等.髓间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(11):2605-2607.
[17] 郭钢花,申利坊,李哲.血间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤临床研究[J].中国实用医刊,2012,39(10):58-60.
[18] Cheng H, Liu X, Hua R, et al. Clinical observation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in treatment for sequelae of thoracolumbar spinal cord injury. J Transl Med. 2014;12:253.
[19] Dai G, Liu X, Zhang Z, et al. Transplantation of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of complete and chronic cervical spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2013;1533:73-79.
[20] Zehendner CM, Sebastiani A, Hugonnet A, et al. Traumatic brain injury results in rapid pericyte loss followed by reactive pericytosis in the cerebral cortex. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13497.
[21] Bracken MB. Steroids for acute spinal cord injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;1:CD001046.
[22] Vawda R, Fehlings MG. Mesenchymal cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: current & future perspectives. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(1):25-38.
[23] National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center. Spinal cord injury facts and figures at a glance. J Spinal Cord Med. 2013;36(1):1-2.
[24] Misra K, Sabaawy HE. Minimally manipulated autologous adherent bone marrow cells (ABMCs): a promising cell therapy of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(7): 1058-1060.
[25] Wang WX, Springer JE. Role of mitochondria in regulating microRNA activity and its relevance to the central nervous system. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(7):1026-1028.
[26] Joaquim AF, Patel AA, Vaccaro AR. Cervical injuries scored according to the Subaxial Injury Classification system: An analysis of the literature. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2014;5(2):65-70.
[27] Rowland JW, Hawryluk GW, Kwon B, et al. Current status of acute spinal cord injury pathophysiology and emerging therapies: promise on the horizon Neurosurg Focus. 2008; 25(5):E2.
[28] Darian-Smith C, Lilak A, Garner J, et al. Corticospinal sprouting differs according to spinal injury location and cortical origin in macaque monkeys. J Neurosci. 2014;34(37): 12267-12279.
[29] Li Z, Zhang Z, Zhao L, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with Nogo-66 receptor gene silencing for repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(8):806-814.
[30] Liu S, Li C, Xing Y, et al. Effect of microenvironment modulation on stem cell therapy for spinal cord injury pain. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(5):458-459.
[31] Carrade DD, Affolter VK, Outerbridge CA, et al. Intradermal injections of equine allogeneic umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells are well tolerated and do not elicit immediate or delayed hypersensitivity reactions. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(10):1180-1192.
[32] Dasari VR, Veeravalli KK, Rao JS, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Apoptosis After Spinal Cord Injury. In: Chang RCC, ed. Advanced Understanding of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Croatia: InTech, 2011;10(8):365-394. |