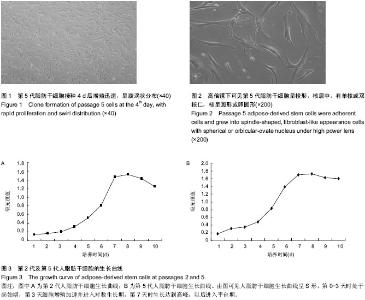
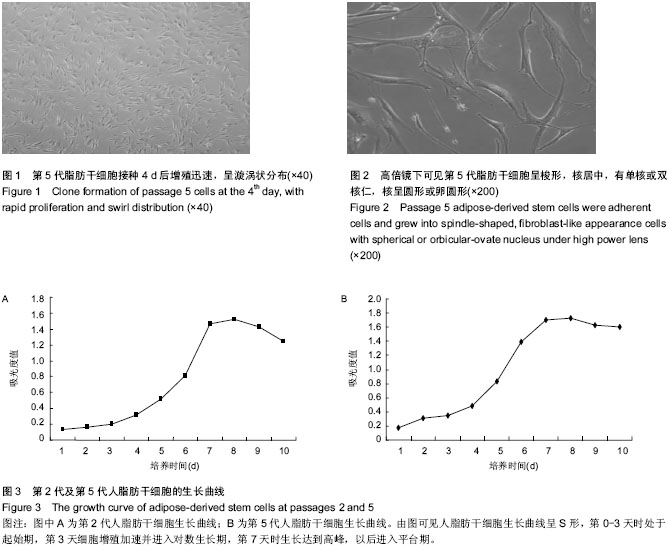
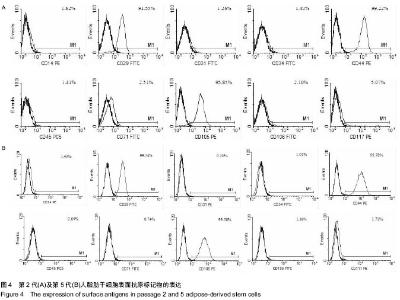
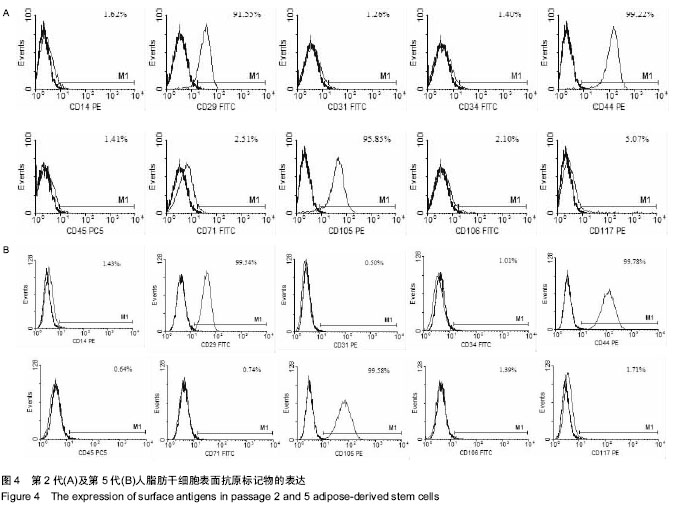
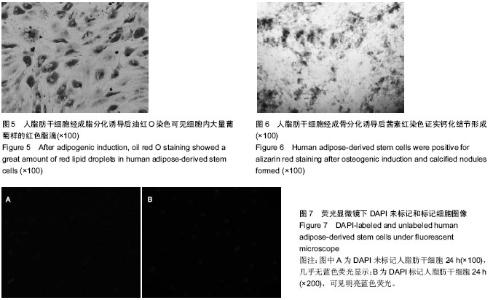
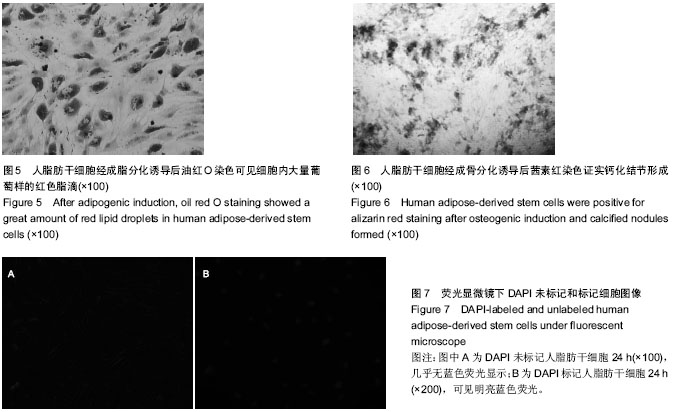
| [1] Gimble J, Guilak F. Adipose-derived adult stem cells: isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential. Cytotherapy. 2003;5(5):362-369.
[2] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295.
[3] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001r;7(2):211-228.
[4] Cherubino M, Marra KG. Adipose-derived stem cells for soft tissue reconstruction. Regen Med. 2009;4(1):109-117.
[5] Zanetti AS, Sabliov C, Gimble JM, et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells and three-dimensional scaffold constructs: a review of the biomaterials and models currently used for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(1):187-199.
[6] Kaewsuwan S, Song SY, Kim JH, et al. Mimicking the functional niche of adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(12): 1575-1588.
[7] Mizuno H, Tobita M, Uysal AC. Concise review: Adipose-derived stem cells as a novel tool for future regenerative medicine. Stem Cells. 2012;30(5):804-810.
[8] Ong WK, Sugii S. Adipose-derived stem cells: fatty potentials for therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(6):1083-1086.
[9] Torres FC, Rodrigues CJ, Stocchero IN, et al. Stem cells from the fat tissue of rabbits: an easy-to-find experimental source. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2007;31(5):574-578.
[10] Peroni D, Scambi I, Pasini A, et al. Stem molecular signature of adipose-derived stromal cells. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(3): 603-615.
[11] Vieira NM, Brandalise V, Zucconi E, et al. Isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential of canine adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(3): 279-289.
[12] Caviggioli F, Vinci V, Salval A, et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, characterization and applications in surgery. ANZ J Surg. 2009;79(11):856.
[13] Yang Q, Wang B, Yu H, et al. TLR7 promotes Th1 polarization in immune thrombocytopenia. Thromb Res. 2011;128(3): 237-242.
[14] Zhu Y, Liu T, Song K, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell: a better stem cell than BMSC. Cell Biochem Funct. 2008;26(6):664- 675.
[15] Chen X, Xu H, Wan C, et al. Bioreactor expansion of human adult bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(9):2052-2059.
[16] Owen TA, Aronow M, Shalhoub V, et al. Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vitro: reciprocal relationships in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1990;143(3):420-430.
[17] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999 2;284(5411):143-147.
[18] Strem BM, Hicok KC, Zhu M, et al. Multipotential differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Keio J Med. 2005;54(3):132-141.
[19] Rubin JP, Marra KG. Adipose stem cell therapy for soft tissue reconstruction. Lancet. 2013;382(9898):1077-1079.
[20] Puissant B, Barreau C, Bourin P, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells: comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Br J Haematol. 2005;129(1):118-129.
[21] Yañez R, Lamana ML, García-Castro J, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells have in vivo immunosuppressive properties applicable for the control of the graft-versus-host disease. Stem Cells. 2006;24(11):2582- 2591.
[22] Cui L, Yin S, Liu W, et al. Expanded adipose-derived stem cells suppress mixed lymphocyte reaction by secretion of prostaglandin E2. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(6):1185-1195. |