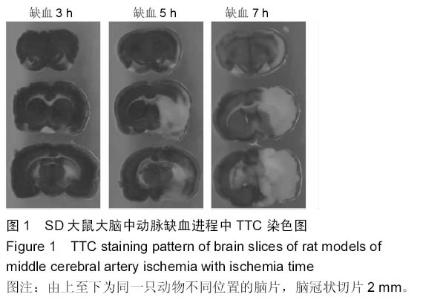
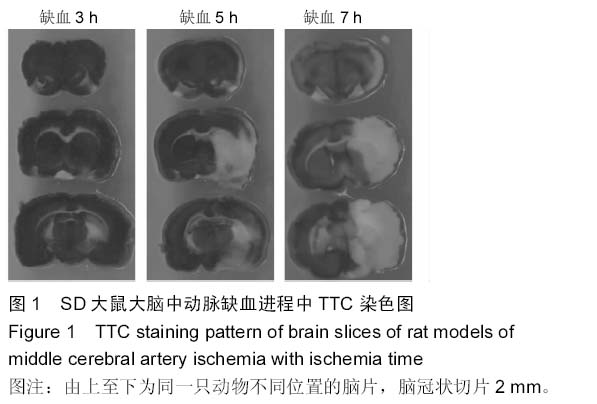
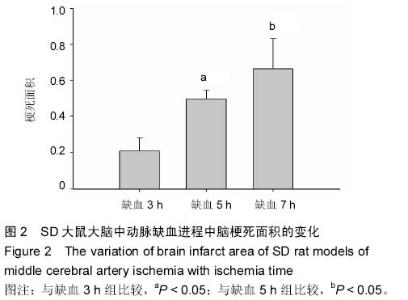
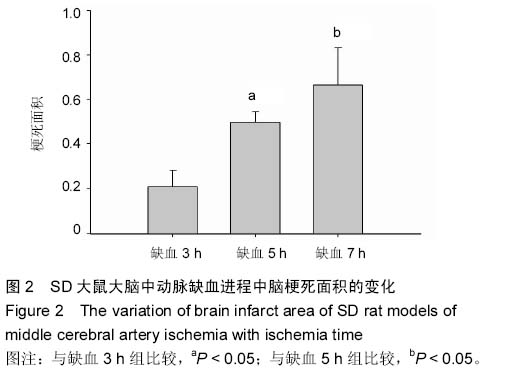
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (27): 4322-4327.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.27.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
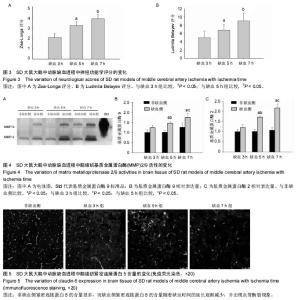
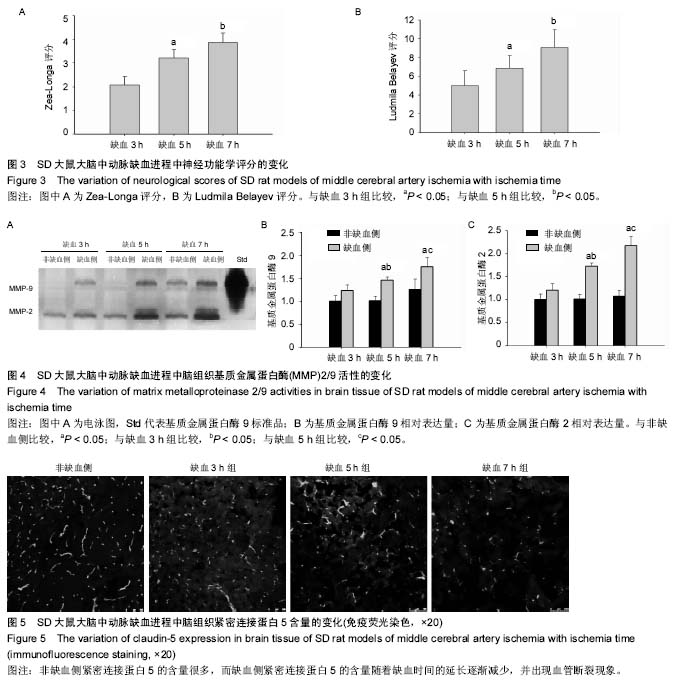
The increased activation of matrix metalloproteinase 2/9 and gradual degradation of claudin in rat models of middle cerebral artery ischemia
Liang Jia1,Qi Zhi-feng2, Shi Wen-juan2, Liu Ke-jian2
- 1Science Experimental Center of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China;
2Cerebrovascular Diseases Research Institute, Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing 100053, Chin
-
Online:2015-06-30Published:2015-06-30 -
Contact:Liu Ke-jian, Professor, Cerebrovascular Diseases Research Institute, Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing 100053, China -
About author:Liang Jia, Studying for doctorate, Science Experimental Center of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171242; a grant from Principal Foundation of Liaoning Medical University of China, No. XZJJ20140105
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Jia,Qi Zhi-feng, Shi Wen-juan, Liu Ke-jian. The increased activation of matrix metalloproteinase 2/9 and gradual degradation of claudin in rat models of middle cerebral artery ischemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(27): 4322-4327.
share this article
| [1] Banerjee P,Jana S,Chakraborty S,et al.Inflammation and MMPs in alcohol-induced liver diseases and protective action of antioxidants.Indian J Biochem Biophys.2013; 50(5): 377-386.
[2] Cavdar Z,Ozbal S,Celik A,et al.The effects of alpha-lipoic acid on MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities in a rat renal ischemia and re-perfusion model. Biotech Histochem.2014; 89(4):304-314.
[3] Tang X,Zhong W,Tu Q,et al.NADPH oxidase mediates the expression of MMP-9 in cerebral tissue after ischemia- reperfusion damage.Neurol Res.2014;36(2):118-125.
[4] Li M,Ma RN,Li LH,et al.Astragaloside IV reduces cerebral edemapost-ischemia/reperfusion correlating the suppression of MMP-9 and AQP4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;715(1-3): 189-195.
[5] Cao J,Geng L,Wu Q,et al. Spatiotemporal expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) is regulated by the Ca2+-signal transducer S100A4 in the pathogenesis of thoracic aortic aneurysm.PLoS One.2013;8(7):e70057.
[6] Moniche F,Montaner J,Gonzalez-Marcos JR,et al.Intra-arterial bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation correlates with GM-CSF, PDGF-BB, and MMP-2 serum levels in stroke patients: results from a clinical trial. Cell Transplant.2014;23 Suppl 1:S57-S64.
[7] Bai X,Zhang X,Chen L,et al. Protective effect of naringenin in experimental ischemic stroke: down-regulated NOD2, RIP2, NF-kappaB, MMP-9 and up-regulated claudin-5 expression. Neurochem Res.2014;39(8):1405-1415.
[8] Sapojnikova N,Kartvelishvili T,Asatiani N,et al.Correlation between MMP-9 and extracellular cytokine HMGB1 in prediction of human ischemic stroke outcome. Biochim Biophys Acta.2014;1842(9):1379-1384.
[9] Tsuji K,Aoki T,Tejima E,et al.Tissue plasminogen activator promotes matrix metalloproteinase-9 upregulation after focal cerebral ischemia.Stroke.2005; 36(9):1954-1959.
[10] Zhao H,Wang R,Wu X,et al.Erythropoietin delivered via intra-arterial infusion reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress in brain microvessels of rats following cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015;10(1): 153-161.
[11] Wang R, Wu X, Liang J et al.Intra-artery infusion of recombinant human erythropoietin reduces blood-brain barrier disruption in rats following cerebral ischemia and reperfusion.Int J Neurosci.2014.[Epub ahead of print]
[12] Won S,Lee JH,Wali B,et al.Progesterone attenuates hemorrhagic transformation after delayed tPA treatment in an experimental model of stroke in rats: involvement of the VEGF-MMP pathway.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2014;34(1): 72-80.
[13] Wang L,Li Z,Zhang X,et al.Protective effect of shikonin in experimental ischemic stroke: attenuated TLR4, p-p38MAPK, NF-kappaB, TNF-alpha and MMP-9 expression, up-regulated claudin-5 expression, ameliorated BBB permeability. Neurochem Res.2014; 39(1):97-106.
[14] Dong W, Qi Z, Liang J,et al.Reduction of zinc accumulation in mitochondria contributes to decreased cerebral ischemic injury by normobaric hyperoxia treatment in an experimental stroke model.Exp Neurol.2015.[Epub ahead of print]
[15] Marinescu M,Bouley J,Chueh J,et al.Clot injection technique affects thrombolytic efficacy in a rat embolic stroke model: implications for translaboratory collaborations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2014;34(4):677-682.
[16] Bai X,Zhang X,Chen L,et al.Protective effect of naringenin in experimental ischemic stroke: down-regulated NOD2, RIP2, NF-kappaB, MMP-9 and up-regulated claudin-5 expression. Neurochem Res.2014;39(8):1405-1415.
[17] Golab P,Boguszewska-Czubara A,Kielbus M,et al.The rtPA increases MMP-9 activity in serum during ischaemic stroke. Neurol Neurochir Pol.2014;48(5):309-314.
[18] Maradni A,Khoshnevisan A,Mousavi SH,et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and MMP inhibitors on intracranial aneurysms: a review article. Med J Islam Repub Iran.2013;27(4):249-254.
[19] Lukaszewicz-Zajac M, Mroczko B, Slowik A. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J Neural Transm. 2014; 121(11):1387-1397.
[20] Chao HM,Chuang MJ,Liu JH,et al.Baicalein protects against retinal ischemia by antioxidation, antiapoptosis, downregulation of HIF-1alpha, VEGF, and MMP-9 and upregulation of HO-1.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2013;29(6): 539-549.
[21] Lukaszewicz-Zajac M,Mroczko B,Kornhuber J,et al.Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in the tumors of central nervous system (CNS). J Neural Transm.2014;121(5):469-477.
[22] Rosell A,Ortega-Aznar A,varez-Sabin J,et al.Increased brain expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 after ischemic and hemorrhagic human stroke.Stroke.2006; 37(6):1399-1406.
[23] Liang J,Qi Z,Liu W,et al.Normobaric hyperoxia slows blood-brain barrier damage and expands the therapeutic time window for tissue-type plasminogen activator treatment in cerebral ischemia. Stroke.2015;46(5):1344-1351.
[24] Zhao H,Wang R,Wu X,et al.Erythropoietin delivered via intra-arterial infusion reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress in brain microvessels of rats following cerebral ischemia and reperfusion.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.2015;10(1):153-161.
[25] Inzitari D, Giusti B, Nencini P,et al. MMP9 variation after thrombolysis is associated with hemorrhagic transformation of lesion and death.Stroke.2013;44(10):2901-2903.
[26] Jin X,Liu J,Yang Y,et al.Spatiotemporal evolution of blood brain barrier damage and tissue infarction within the first 3h after ischemia onset.Neurobiol Dis.2012; 48(3):309-316.
[27] Liu J,Jin X,Liu KJ,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated occludin degradation and caveolin-1-mediated claudin-5 redistribution contribute to blood-brain barrier damage in early ischemic stroke stage.J Neurosci.2012;32(9):3044-3057.
[28] Yang Y,Estrada EY,Thompson JF,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2007; 27(4):697-709.
[29] Latour LL,Kang DW,Ezzeddine MA,et al. Early blood-brain barrier disruption in human focal brain ischemia Ann Neurol. 2004;56(4):468-477.
[30] Yang Y, Thompson JF, Taheri S,et al.Early inhibition of MMP activity in ischemic rat brain promotes expression of tight junction proteins and angiogenesis during recovery. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013;33(7):1104-1114.
[31] Asahi M,Asahi K,Jung JC,et al. Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal cerebral ischemia: effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition with BB-94. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2000;20(12):1681-1689.
[32] Wang X,Tsuji K, Lee SR,et al. Mechanisms of hemorrhagic transformation after tissue plasminogen activator reperfusion therapy for ischemic stroke. Stroke.2004; 35(11 Suppl 1): 2726-2730. |
| [1] | Zhu Rui, Zeng Qing, Huang Guozhi. Ferroptosis and stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739. |
| [2] | Li Siyu, Wang Qingsong. Effect of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion on expression of Occludin and Claudin-2 in rat ileum mucosa [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5186-5191. |
| [3] | Min Dongyu, Li Hongyan, Guan Le, Chang Jiang, Zhang Haining, Cui Xinyue, Wang Peng, Cao Yonggang. Protective mechanism of Naoxinqing Capsule in rat models of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 215-222. |
| [4] | Long Yanfang1, 2, Wang Xinlei2, Wang Mingpu3, Tang Xingjiang2. Effects of androgen on the expression of Bcl-2, Bax and Cyt-C in brain tissue of adult rat models of middle cerebral artery occlusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(27): 4344-4349. |
| [5] | Zou Haibo, Sun Xiaofeng. Effects of curcumin post-conditioning on the balance of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in a rat model of renal injury induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3643-3648. |
| [6] | Zhang Yunke, Che Zhiying, Li Ke. Effect of Buyang Huanwu Decoction combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on expression of tight junction proteins in the brain of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 55-60. |
| [7] | Chen Bo1, Liang Jie1, Chen Zhen-bing2. Expression and effects of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 and 2 in the denervated skeletal muscle of rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 516-522. |
| [8] | Sun Feng. Role of ABCG2 gene in proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(13): 2057-2062. |
| [9] |
Tang Ju, Lou Fang-yong, Zhu Wei, Jiang Hai-tao, Zhang Zhen-xiang.
Arthroscopic posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using autologous and allogeneic materials and the association with matrix metalloproteinases 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(30): 4879-4884. |
| [10] | Wang Cheng, Bo Qi-yu, Dai Guo-feng, Yang Wei-wei. Variation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 levels during Kartogenin-induced directional differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(50): 7475-7480. |
| [11] | Li Guang, Guo Qi-fa, Huang Ning-qing, Li Ling-wei. Correlation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 with the early performance of knee osteoarthritis cartilage under MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(37): 5518-5523. |
| [12] | Wang Lu, Huo Shuai, Wang Ya-fei, Zhao Lin, Liu Bo-feng, Ruan Cai-lian, Hui Xue-feng. The regulating effect of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor on neural synaptic plasticity in a rat model of chronic cerebral ischemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(40): 6498-6503. |
| [13] | Sun Ya-nan. The expression of connective tissue growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase 9 in the ovary of rat models of polycystic ovarian syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(27): 4412-4416. |
| [14] | Zhao Lu, Liu Lei, Mao Jian-xiong, Wang Jian-yao, Xu Jin-yong, Ye Xiao-shuo. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase in rats with cavernous transformation of portal vein and their role in peripheral angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(18): 2884-2890. |
| [15] | Tang Pei-juan, Wang Chang-lei, Gong Chun-mei, Tang Pei-qian, Hao Jian-zhong. c-fos/c-jun regulates extracellular matrix metalloproteinase 20 expression in ameloblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1673-1677. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||