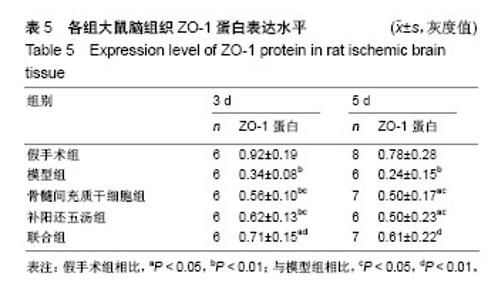
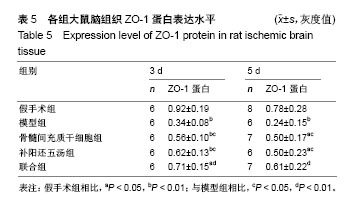
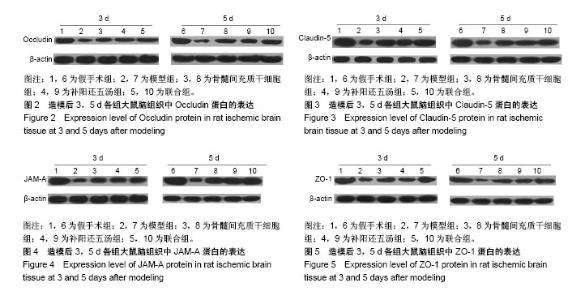
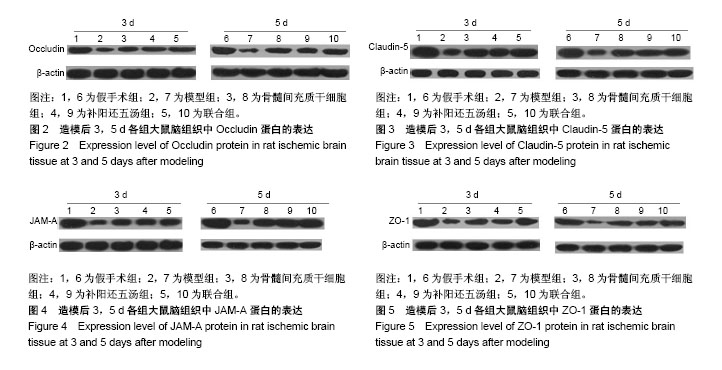
| [1] MacGregor DG, Avshalumov MV, Rice ME. Brain edema induced by in vitro ischemia: causal factors and neuroprotection. J Neurochem. 2003;85(6):1402-1411.[2] Steeg PS, Camphausen KA, Smith QR. Brain metastases as preventive and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(5): 352-363. [3] Day RE, Kitchen P, Owen DS, et al. Human aquaporins: regulators of transcellular water flow. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(5): 1492-1506. [4] 张运克,佟帅.补阳还五汤抗脑缺血及再灌注损伤作用机理研究进展[J].河南中医,2002,22(4):75-76,80.[5] Haas S, Weidner N, Winkler J. Adult stem cell therapy in stroke. Curr Opin Neurol. 2005;18(1):59-64. [6] Wang C, Fei Y, Xu C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate neurological deficits and blood-brain barrier dysfunction after intracerebral hemorrhage in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):4715-4724. [7] Kopen GC, Prockop DJ, Phinney DG. Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum, and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into neonatal mouse brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(19):10711-10716. [8] Liu H, Honmou O, Harada K, et al. Neuroprotection by PlGF gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells after cerebral ischaemia. Brain. 2006;129(Pt 10):2734-2745. [9] Ito M, Kuroda S, Sugiyama T, et al. Transplanted bone marrow stromal cells protect neurovascular units and ameliorate brain damage in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuropathology. 2012; 32(5):522-533. [10] Zhang YK, Han XY, Che ZY. Effects of buyang huanwu tang combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on the expression of VEGF and Ki-67 in the brain tissue of the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model rat. J Tradit Chin Med. 2010;30(4): 278-282. [11] 张运克,高峰,张丹,等.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑组织NSE和GFAP表达的影响[J].中医杂志, 2013,54(23): 2043-2045.[12] 张运克,车志英,梅雪蕊.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血再灌注模型神经细胞凋亡的影响[J].中华中医药学刊, 2009,27(8): 1660-1662.[13] 张运克,车志英,梅雪蕊.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对脑缺血再灌注大鼠行为学及脑梗死体积的影响[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2010,37(2): 366-368.[14] 张运克,张振强,宋军喜.补阳还五汤联合MSCs移植对脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠VEGF及信号通路的影响[J].时珍国医国药, 2016,27(4):806-809.[15] 张运克,宋军营,张振强.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞对大脑中动脉闭塞再灌注治疗的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(50):8120- 8125.[16] Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91. [17] Kiley MA, Oxbury JM, Coley SC. Intracranial hypertension in Sturge-Weber/Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber overlap syndrome due to impairment of cerebral venous outflow. J Clin Neurosci. 2002;9(3): 330-333. [18] 邹伟,孙晓伟,于学平,等.血脑屏障与脑缺血再灌注损伤研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2009,27(3):466-478.[19] 徐姝燕,富建华.紧密连接相关蛋白Occludin的研究进展[J].国际儿科学杂志,2012,39(5):51-454.[20] Jia W, Lu R, Martin TA, et al. The role of claudin-5 in blood-brain barrier (BBB) and brain metastases (review). Mol Med Rep. 2014; 9(3):779-785. [21] Garrido-Urbani S, Bradfield PF, Imhof BA. Tight junction dynamics: the role of junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs). Cell Tissue Res. 2014; 355(3):701-715. [22] Liu W, Wang P, Shang C, et al. Endophilin-1 regulates blood-brain barrier permeability by controlling ZO-1 and occludin expression via the EGFR-ERK1/2 pathway. Brain Res. 2014;1573:17-26. [23] 孙伟,杨鲲鹏,盛利,等.大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注血脑屏障超微结构及紧密连接蛋白Occludin变化的研究[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2007,24(4):425-427.[24] 王静娥,田国萍,周进,等.大鼠脑缺血时紧密连接相关蛋白occludin和claudin-5表达的变化[J].解剖科学进展, 2010,16(2):149-152.[25] Yeung D, Manias JL, Stewart DJ, et al. Decreased junctional adhesion molecule-A expression during blood-brain barrier breakdown. Acta Neuropathol. 2008;115(6):635-642. [26] Musch MW, Walsh-Reitz MM, Chang EB. Roles of ZO-1, occludin, and actin in oxidant-induced barrier disruption. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290(2):G222-231. [27] 陈易简.血脑屏障完整性与中枢神经系统疾病的发展和转归的相关性研究进展[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志, 2017,44(3):319-321.[28] 逯锐锐,龚圆渊,张力华.中医药对血脑屏障通透性影响的研究进展[J].湖南中医杂志,2016,32(7):187-188.[29] 范文涛,王利胜,范有明,等.补阳还五汤对大鼠脑微血管内皮细胞氧糖剥夺再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2016,22(14):111-115.[30] 刘玉晖,易文凤,游宇.补阳还五汤抗动脉粥样硬化作用与紧密连接蛋白的关系[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(24):155-160.[31] 张楠,王思迪,涂盼春,等.紧密连接相关蛋白对血脑屏障通透性影响的研究进展[J].沈阳医学院学报,2017,19(1):72-75. |