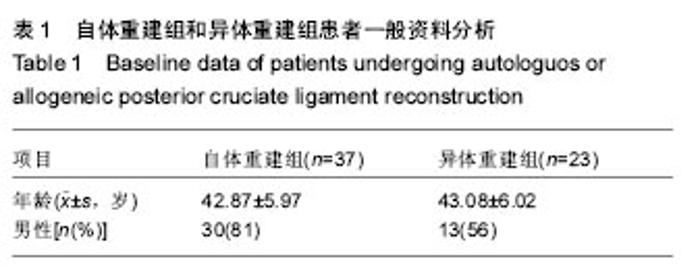
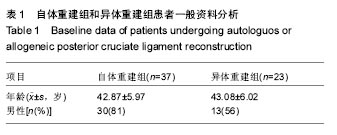
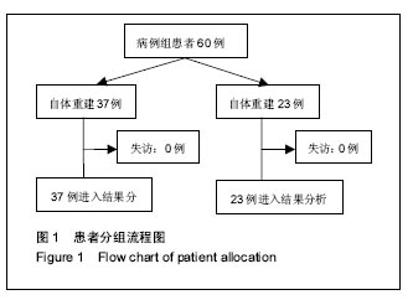
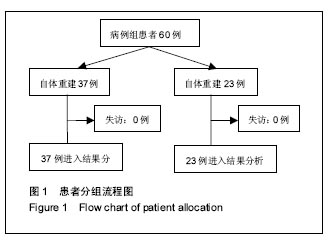
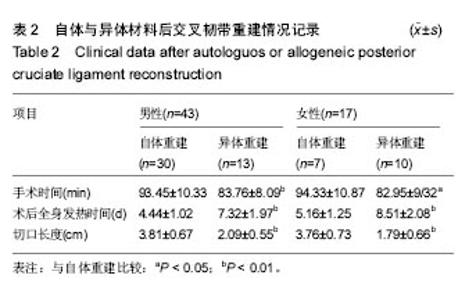
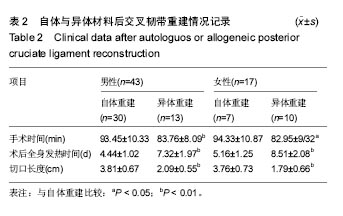
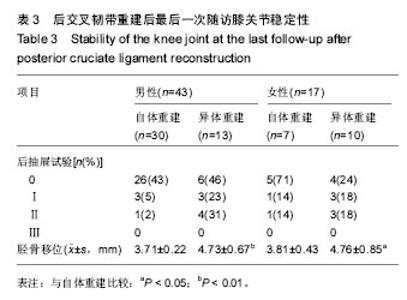
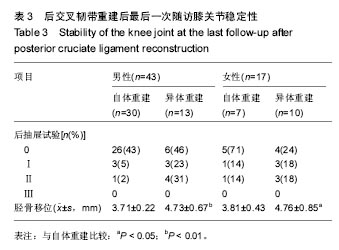
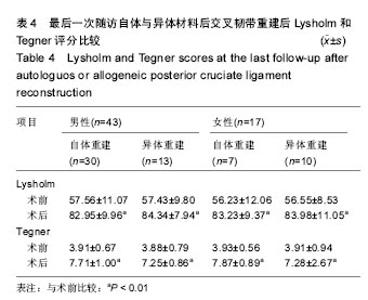
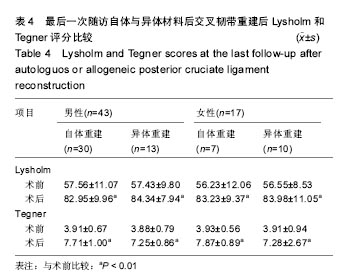
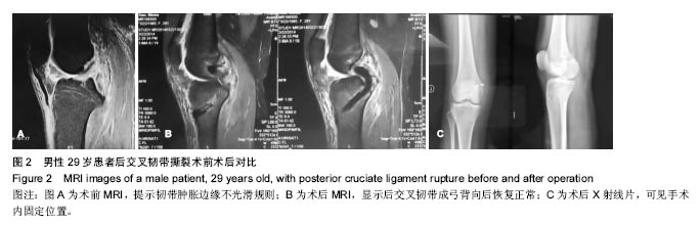
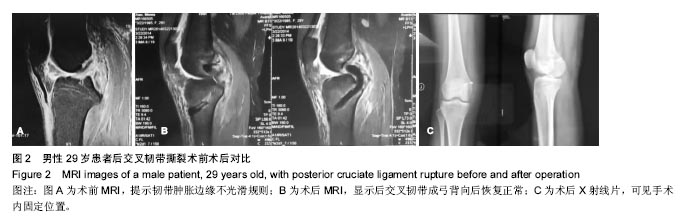
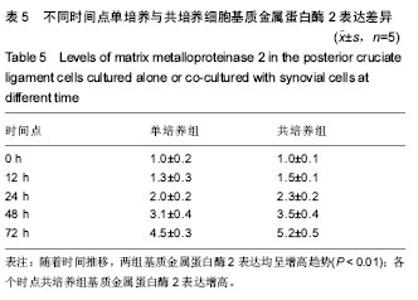
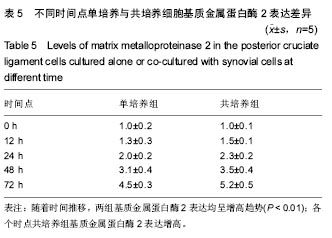
| [1]尤田,张新涛,张文涛,等. 中国成人前交叉韧带胫骨止点的解剖研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(6):730-733.[2]李劼若,查振刚,潘锐,等. 前交叉韧带重建术中胫骨骨道定位的应用解剖研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016, 24(12):1118-1120.[3]孙正宇,李箭.组织工程韧带的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(9):1160-1166.[4]Rahr-Wagner L, Lind M. The Danish Knee Ligament Reconstruction Registry. Clin Epidemiol. 2016;8:531-535.[5]Liechti DJ, Chahla J, Dean CS, et al.Outcomes and Risk Factors of Rerevision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Arthroscopy. 2016; 32(10):2151-2159.[6]楼华.运动员前交叉韧带重建术后再损伤预防的研究进展[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2014, 40(11):90-94.[7]傅捷,王晓宇,周密,等. 关节镜下前交叉韧带重建术后感染的诊断与治疗要点[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014, 29(6): 550-552.[8]袁思捷,陈鹏,田京.单束和双束后交叉韧带重建术的对比:系统综述及meta分析[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2015, 15(2):149-155.[9]王春莉,梅虎,谢静,等. 共培养下后交叉韧带成纤维细胞中MMPs的基因表达[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2012, 34(16): 1600-1603.[10]Xie J, Wang CL, Yang W, et al. Modulation of MMP-2 and -9 through connected pathways and growth factors is critical for extracellular matrix balance of intra-articular ligaments. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016 Sep 29.[11]Tegner Y,Lysholm J. Rating system in the evaluation of knee ligament injuries.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1985;1(198): 43-49.[12]Wodowski AJ, Swigler CW, Liu H, et al. Proprioception and Knee Arthroplasty: A Literature Review. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47(2):301-309.[13]李盛,吴冰,崔家鸣,等.前交叉韧带三维空间结构的研究进展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2016(8):780-783.[14]莫成敏,林秋喜.自体腘绳肌腱、同种异体肌腱重建后交叉韧带的疗效比较[J]. 中国医药导报, 2015, 12(10):98-102.[15]Zhang L, Li Z. Primary reconstruction of ACL and PMC of the knee. Asia-Pacific Journal of Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation and Technology. 2016; 6(12):31-31.[16]徐雁,敖英芳,余家阔,等.自体腘绳肌腱单、双束重建前交叉韧带临床比较研究[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2015, 46(3):274-276.[17]LaPrade CM, Civitarese DM, Rasmussen MT,et al. Emerging Updates on the Posterior Cruciate Ligament: A Review of the Current Literature. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(12):3077-3092.[18]Patel SA, Hageman J, Quatman CE, et al. Prevalence and location of bone bruises associated with anterior cruciate ligament injury and implications for mechanism of injury: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2014;44(2):281-293.[19]张承昊,李棋,唐新,等. 促进腱-骨愈合方法的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(7):912-916.[20]Wang Y, Tang Z, Xue R,et al. TGF-β1 promoted MMP-2 mediated wound healing of anterior cruciate ligament fibroblasts through NF-κB. Connect Tissue Res. 2011; 52(3): 218-225.[21]Wang Y, Yang L, Zhang J, et al. Differential MMP-2 activity induced by mechanical compression and inflammatory factors in human synoviocytes. Mol Cell Biomech. 2010;7(2): 105-114.[22]Tourville TW, Poynter M E, Desarno M J, et al. Relationship between synovial fluid ARGS‐aggrecan fragments, cytokines, MMPs, and TIMPs following acute ACL injury: A cross-sectional study. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(12):1796-1803.[23]王靖,戴畅,王愉思. MMPs 在膝前交叉韧带不同分束表达水平的实验研究[J]. 医学临床研究, 2016, 33(6):102-105.[24]沙永强,吕永钢.力生长因子E肽对前交叉韧带成纤维细胞活力、迁移与侵袭的影响[J]. 医用生物力学, 2016, 31(3):227-234. |