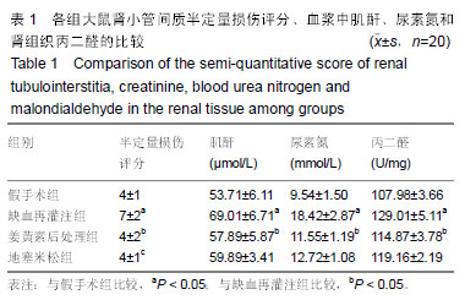
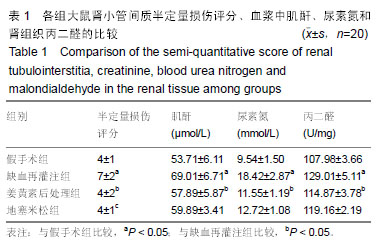
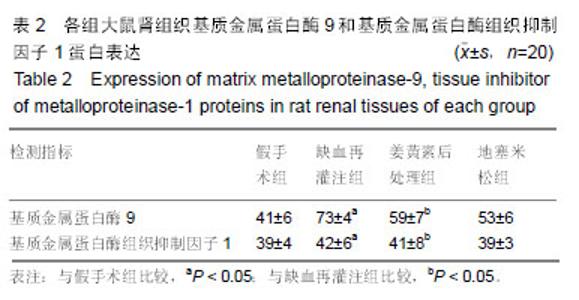
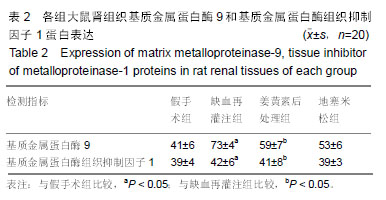
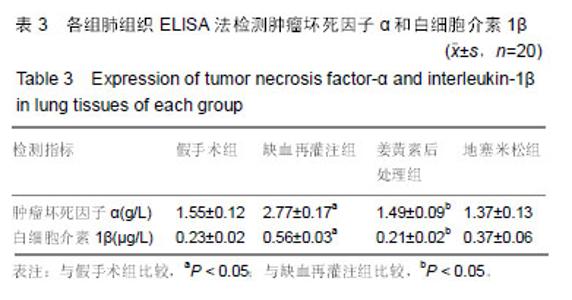
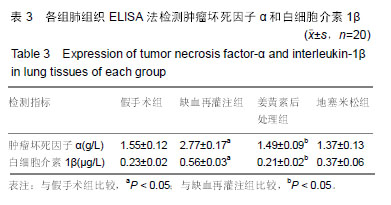
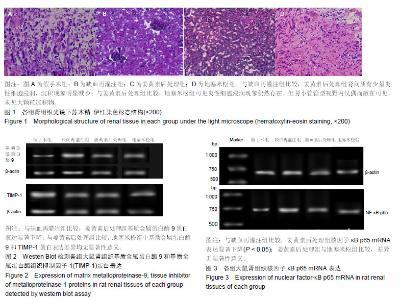
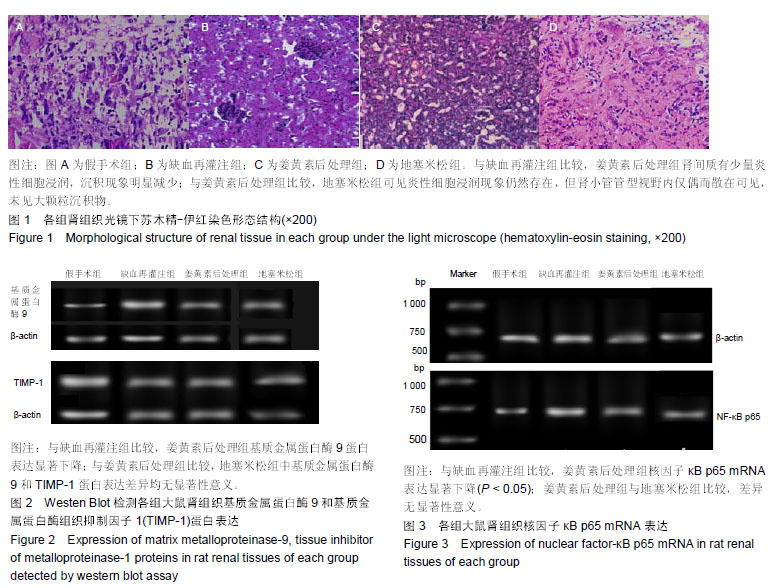
| [1]Karahan MA,Yalcin S,Aydogan H,et al.Curcumin and dexmedetomidine prevents oxidative stress and renal injury in hind limbischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat mode.Ren Fial. 2016;38(5):693-698. [2]Shih JM, Shih YM, Hou YC,et al.Effects of fish oil-based lipid emulsion on inflammation and kidney injury in mice subjected to unilateral hind limb ischemia/reperfusion.Cytokine.2018; (11): 49-57.[3]Takhtfoolad MA,Asghari A,Takhtfooladi HA,et al.The protective role of curcumin on testicular tissue after hindlimb ischemia reperfusion in rats.Int Urol Nephrol.2015;47(10):1605-1610. [4]王子超,赵丽娟.姜黄素对NAFLD大鼠肝组织PPAR-γ和NF-κB p65 mRNA及蛋白表达的影响[J].中国医科大学学报, 2016,45(2): 120-126..[5]孙晓峰,王俊科.姜黄素对肢体缺血再灌注致大鼠肺损伤时MMP-9/ TIMP-1平衡的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2014,34(4):474-476.[6]王光新,李朝芝,夏瑗瑜,等.大鼠肾脏缺血再灌注后IL-6变化及姜黄素预处理的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2012,13(7): 617-619.[7]Kumar K,Rai AK.Proniosomal formulation of curcumin having anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity in different experimental animal models.Pharmazie.2012;67(10):852-857.[8]Cucolas C, Daneasa AI, Olteanu D.Resveratrol and curcumin as protective agents in an experimental rat model of intestinal ischemia and reperfusion.Can J Physiol Pharmacol.2016;94(11): 1151-1158.[9]Liu Y,Chen L,Shen Y,et al.Curcumin Ameliorates Ischemia- Induced Limb Injury Through Immunomodulation.Med Sci Monit.2016;22:2035-2042. [10]张华,吴丛月,王波,等.止血带诱发肢体缺血再灌注损伤不同指标的临床观察[J].全科医学临床与教育,2013,11(2):145-147.[11]邹海波,杨竹,孙晓峰,等.二氧化碳气腹致大鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤及异丙酚诱导核因子E2相关因子表达的保护作用[J].中国小儿急救医学,2016,23(1):33-36.[12]McNally MM, Univers J.Acute Limb Ischemia.Surg Clin North Am. 2018;98(5):1081-1096.[13]POLIGONE B.A role for NF-κB in inflammation and autoimmunity. Raleigh: University of North Carolina.2001.[14]陶佳意.姜黄素预处理、缺血后处理对大鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用及其机制的研究[D]. 南宁:广西医科大学,2012.[15]BOND M,CHASE A J,BAKER A H,et al. Inhibitionof transcription factor NF-kappaB reduces matrixmet metalloproteinase-1,-3 and -9 production by vascular smooth muscle cells.Cardiovsc Res.2001; 50(3): 556-565.[16]王光新,李朝芝,夏瑗瑜,等.大鼠肾脏缺血再灌注后IL-6变化及姜黄素预处理的影响[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2012,34(7):35-41.[17]赵利军,李开济,吴静,等.缺血后处理对大鼠肢体缺血再灌注后肾细胞凋亡的抑制作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2017,43(4):725-728. |