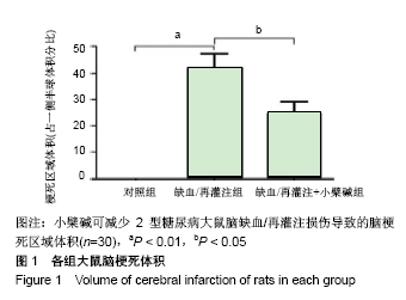
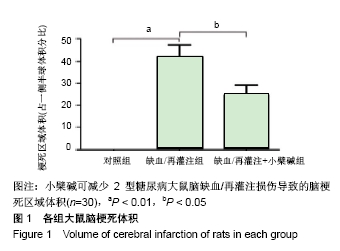
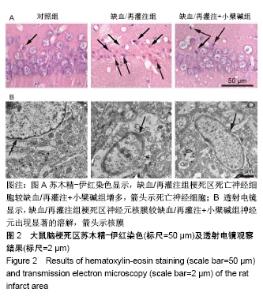
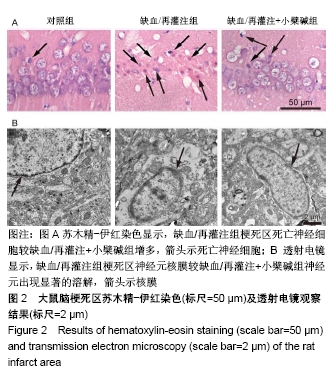
[1] UMEMURA T, KAWAMURA T, HOTTA N.Pathogenesis and neuroimaging of cerebral large and small vessel disease in type 2 diabetes: A possible link between cerebral and retinal microvascular abnormalities.J Diabetes Investig. 2017;8(2):134-148.
[2] HASHIMOTO T, MATSUMOTO S, ANDO M, et al.Cerebral Hyperperfusion Syndrome After Endovascular Reperfusion Therapy in a Patient with Acute Internal Carotid Artery and Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusions. World Neurosurg.2018;110:145-151.
[3] BLAIR M.Diabetes Mellitus Review. Urol Nurs.2016;36(1):27-36.
[4] FRIER BM. Hypoglycaemia in diabetes mellitus: epidemiology and clinical implications.Nat Rev Endocrinol.2014;10(12):711-722.
[5] DAI HB, XU MM, LV J, et al. Mild Hypothermia Combined with Hydrogen Sulfide Treatment During Resuscitation Reduces Hippocampal Neuron Apoptosis Via NR2A, NR2B, and PI3K-Akt Signaling in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(7):4865-4873.
[6] 武嘉庚.葛根素对H_2O_2诱导的海马神经元损伤的保护作用[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2017,33(14):1324-1327.
[7] 王欢欢,薛茜,邹玉安. 内源性抗氧化应激机制在缺血预处理与缺血再灌注损伤中的研究进展[J].神经药理学报, 2016,6(02):46-52.
[8] 颜思阳,陈瑶,周德生,等. 线粒体自噬在脑缺血再灌注损伤中的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2019,25(4):659-664.
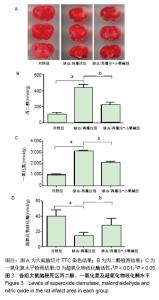
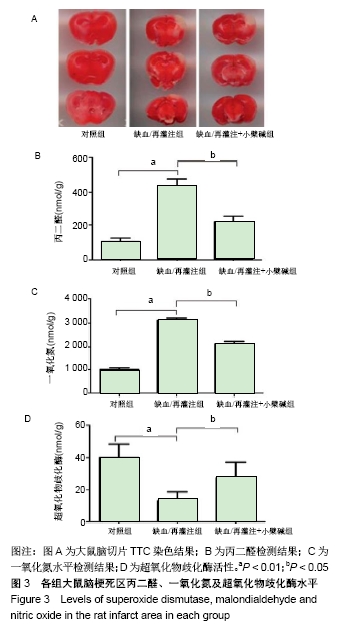
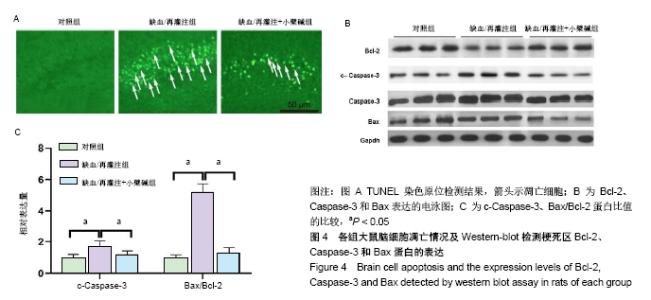
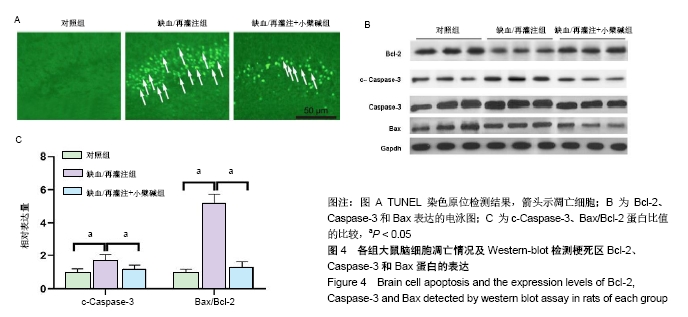
[9] 尚远宏,田金凤,刘庆,等.梓葛冻干粉针对脑缺血/再灌注损伤大鼠脑微血管舒缩功能异常的改善作用[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,39(6): 21-27.
[10] 葛宇松,刘雪松,薛俊燕,等.丁苯酞注射液预处理通过PI3K/Akt通路对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的神经保护作用[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2013,30(1):32-36.
[11] CICERO AF, BAGGIONI A.Berberine and Its Role in Chronic Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol.2016;928:27-45.
[12] LAN J, ZHAO Y, DONG F, et al.Meta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and hypertension.J Ethnopharmacol.2015;161:69-81.
[13] HUANG Z, HAN Z, YE B, et al.Berberine alleviates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting excessive autophagy in cardiomyocytes.Eur J Pharmacol.2015;762:1-10.
[14] YANG J, YAN H, LI S, et al. Berberine Ameliorates MCAO Induced Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Activation of the BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2018;43(3):702-710.
[15] REED MJ,MESZAROS K,ENTES LJ,et al.A new rat model of type 2 diabetes: the fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism. 2000; 49(11):1390-1394.
[16] LIU X, XU Y, ZHOU Q, et al.PI3K in cancer: its structure, activation modes and role in shaping tumor microenvironment. Future Oncol. 2018;14(7):665-674.
[17] ZHANG YP, LIU SY, SUN QY, et al.Proanthocyanidin B2 attenuates high-glucose-induced neurotoxicity of dorsal root ganglion neurons through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(9):1628-1636.
[18] LIEN EC, DIBBLE CC, TOKER A.PI3K signaling in cancer: beyond AKT. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017;45:62-71.
[19] FAES S, DORMOND O.PI3K and AKT: Unfaithful Partners in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):21138-21152.
[20] JUSTICIA C, SALAS-PERDOMO A, Pérez-de-Puig I, et al.Uric Acid Is Protective After Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion in Hyperglycemic Mice. Transl Stroke Res.2017;8(3):294-305.
[21] GONG L, TANG Y, AN R, et al.RTN1-C mediates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via ER stress and mitochondria- associated apoptosis pathways. Cell Death Dis.2017;8(10): e3080.
[22] DONG P, ZHANG X, ZHAO J, et al.Anti-microRNA-132 causes sevofluraneinduced neuronal apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/ FOXO3a pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(6):3238-3246.
[23] TANG L, MO Y, LI Y, et al.Urolithin A alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2017;486(3):774-780.
[24] WANG YK, DENG F, MIAO J,et al. Neuroprotection by Carbenoxolone Against Ischemia Injury Involves PI3K/Akt Pathway. Clin Lab.2015;61(10):1561-1568.
[25] ZHOU S, FANG Z, WANG G, et al.Gap junctional intercellular communication dysfunction mediates the cognitive impairment induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: PI3K/Akt pathway involved. Am J Transl Res.2017;9(12):5442-5451.
[26] WANG K, FENG X, CHAI L, et al.The metabolism of berberine and its contribution to the pharmacological effects.Drug Metab Rev.2017; 49(2):139-157.
[27] KUMAR A, EKAVALI, CHOPRA K, et al. Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: An update. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;761:288-297.
[28] COELHO AR, MARTINS TR, COUTO R, et al.Berberine-induced cardioprotection and Sirt3 modulation in doxorubicin-treated H9c2 cardiomyoblasts.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017; 1863 (11):2904-2923.
[29] HAWKINS PT, STEPHENS LR.PI3K signalling in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1851(6):882-897.
|