Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 1194-1201.doi: 10.12307/2022.223
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cardioprotective effect of 3-nitro-N-methyl salicylamide on the isolated rat heart under cold ischemia preservation
Wang Shuo, Liu Wenying, Lü Chaofan, Li Jiacong, Geng Yi, Zhao Yungang
- Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, Institute of Sports and Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China
-
Received:2021-04-06Revised:2021-04-10Accepted:2021-05-16Online:2022-03-18Published:2021-11-02 -
Contact:Zhao Yungang, PhD, Associate professor, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, Institute of Sports and Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
About author:Wang Shuo, Master, Assistant experimentalist, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, Institute of Sports and Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31971100 (to ZYG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Shuo, Liu Wenying, Lü Chaofan, Li Jiacong, Geng Yi, Zhao Yungang. Cardioprotective effect of 3-nitro-N-methyl salicylamide on the isolated rat heart under cold ischemia preservation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1194-1201.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

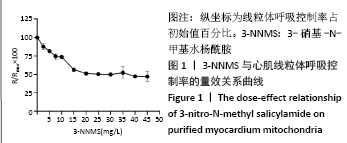
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验采用36只大鼠进行心脏离体保存和再灌注,分为4组,实验过程中部分心脏复灌失败,筛选得到20只再灌成功且心脏血流动力学检测数据稳定的大鼠心脏,每组5只,排除16只失败心脏。 2.2 3-NNMS量效关系测定结果 使用不同质量浓度梯度的3-NNMS抑制提纯心肌线粒体呼吸,当3-NNMS使用质量浓度达到20 mg/L时,对线粒体呼吸控制率的抑制效果达51.29%;之后增加3-NNMS质量浓度直至45 mg/L,线粒体呼吸控制率始终在原始水平的50%上下,未见进一步抑制效果,见图1。证实了3-NNMS对线粒体呼吸链的半抑制效果,并确定动物实验使用质量浓度为25 mg/L。"
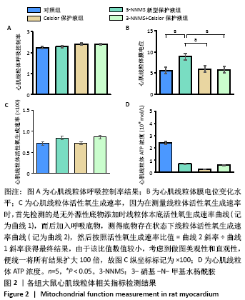
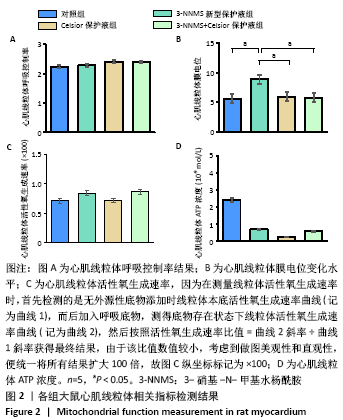
2.3 心肌线粒体相关指标检测结果 与对照组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组、Celsior保护液组、3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组心肌线粒体呼吸控制率、线粒体活性氧生成速率和线粒体ATP含量均无显著变化;3-NNMS新型保护液组和Celsior保护液组、Celsior保护液组和3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组组间线粒体呼吸控制率、活性氧生成速率和ATP含量比较差异也无显著性意义;但与对照组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组心肌线粒体膜电位水平显著升高(P < 0.05);与Celsior保护液组、3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组线粒体膜电位水平也显著升高(P < 0.05),见图2。膜电位的稳定对于维持线粒体正常生理功能至关重要,膜电位升高,有利于促进能量产生和能量转换,抑制凋亡发生。"
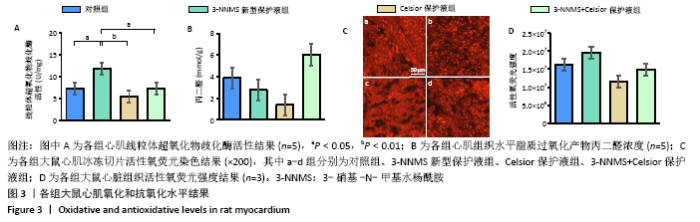
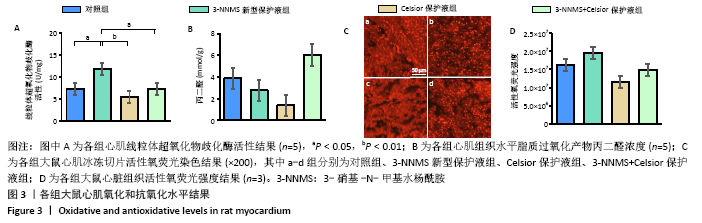
.4 各组大鼠心肌氧化和抗氧化水平结果 3-NNMS新型保护液组心肌线粒体超氧化物歧化酶活性显著高于对照组和3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组(P < 0.05),且显著高于Celsior保护液组(P < 0.01);但脂质过氧化产物丙二醛检测结果显示,与对照组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组、Celsior保护液组、3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组未见显著性差异,3-NNMS新型保护液组、3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组与Celsior保护液组相比也未见显著性差异。而各组左室心肌冰冻切片活性氧荧光染色结果显示,与对照组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组、Celsior保护液组、3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组活性氧荧光强度未见显著性差异;与Celsior保护液组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组和3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组也未见显著性差异,见图3。以上提示,3-NNMS可提高抗氧化酶活性,促进活性氧的清除,从而减轻过量活性氧导致的脂质过氧化。"
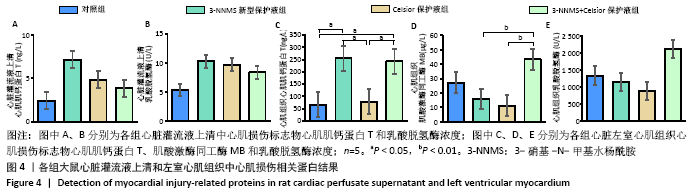
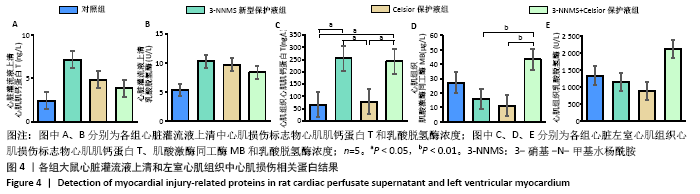
2.5 各组大鼠心脏灌流液上清和左室心肌中心肌损伤标志物结果 各组心脏灌流液上清中心肌损伤标志物结果显示,与对照组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组、Celsior保护液组、3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组心脏灌流液上清中心肌肌钙蛋白T和乳酸脱氢酶浓度均未见显著性差异,3-NNMS新型保护液组与Celsior保护液组相比,Celsior保护液组与3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组相比,也未见显著性差异,见图4A,B;由于上清液中肌酸激酶同工酶MB浓度过低,未能检测到有效数值,故缺少该指标数据。各组左心室组织水平损伤标志物比较结果见图4C-E,3-NNMS新型保护液组和3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组心肌肌钙蛋白T浓度均显著高于对照组和Celsior保护液组(P < 0.05);3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组心肌肌酸激酶同工酶MB水平显著高于3-NNMS新型保护液组和Celsior保护液组 (P < 0.01)。各组间乳酸脱氢酶浓度比较无显著性差异。在正常生理条件下,心肌肌钙蛋白T、肌酸激酶同工酶MB、乳酸脱氢酶主要存在于组织中,当发生心肌损伤或坏死时则释放入血,使血清中相关蛋白浓度上升,因而,此次研究结果显示灌流液上清中心肌损伤标志物水平明显减少,组织水平得到有效保持,提示3-NNMS可有效减轻心肌损伤。"

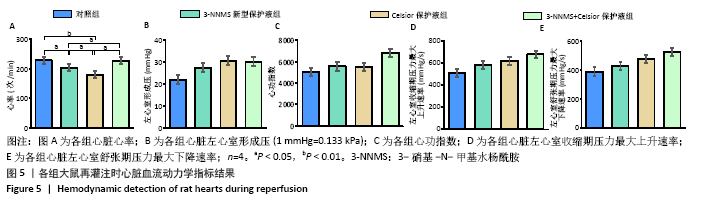
2.6 各组大鼠心脏收缩功能及结构变化结果 血流动力学检测结果显示,与对照组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组大鼠心脏再灌注时心率显著降低(P < 0.05),Celsior保护液组心脏心率也显著降低(P < 0.01);与Celsior保护液组相比,3-NNMS新型保护液组和3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组大鼠心率均显著升高(P < 0.05),而且3-NNMS+Celsior保护液组心率显著高于3-NNMS新型保护液组(P < 0.05),见图5,表明3-NNMS可有效促进再灌注时冷缺血保存心脏心率的恢复。各组心脏左心室形成压、心功指数、+dp/dtmax和-dp/dtmax比较差异均无显著性意义,提示经过8 h冷缺血保存后,各组心脏收缩功能基本一致。显微镜下观察苏木精-伊红染色心肌石蜡切片,各冷缺血保存组心脏形态均未见明显结构性变化,见图6。"
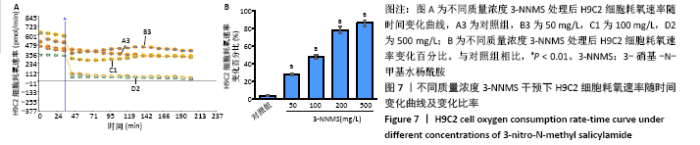
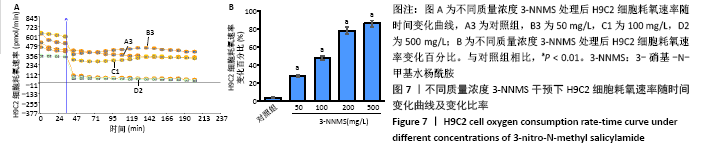
2.7 3-NNMS对H9C2细胞呼吸氧耗速率和细胞活力的影响 在不同质量浓度3-NNMS处理下,H9C2细胞氧耗速率与3-NNMS质量浓度呈现负相关关系;当3-NNMS质量浓度达100 mg/L时,其对H9C2细胞氧耗速率抑制效率达到47.76%,接近半抑制效果;继续增加3-NNMS质量浓度,细胞呼吸氧耗速率被严重抑制(P < 0.01),见图7。而通过MTT实验检测显示,当3-NNMS质量浓度达到500 mg/L时,才对细胞活力造成显著性影响(P < 0.01),且与500 mmol/L的二甲基亚砜干预结果一致,见图8。因此,高质量浓度3-NNMS对细胞活性的影响是由二甲基亚砜造成而非3-NNMS造成,即3-NNMS在细胞培养和呼吸抑制效果上不存在剂量相关安全性问题。"
| [1] SOARES ROS, LOSADA DM, JORDANI MC, et al. Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Revisited: An Overview of the Latest Pharmacological Strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5034. [2] CHOUCHANI ET, PELL VR, JAMES AM, et al. A Unifying Mechanism for Mitochondrial Superoxide Production during Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Cell Metab. 2016;23(2):254-263. [3] MARIN W, MARIN D, AO X, et al. Mitochondria as a therapeutic target for cardiac ischemia‑reperfusion injury (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2021; 47(2):485-499. [4] SUN MS, JIN H, SUN X, et al. Free Radical Damage in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: An Obstacle in Acute Ischemic Stroke after Revascularization Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:3804979. [5] GONZÁLEZ-MONTERO J, BRITO R, GAJARDO AI, et al. Myocardial reperfusion injury and oxidative stress: Therapeutic opportunities. World J Cardiol. 2018;10(9):74-86. [6] ELTZSCHIG HK, ECKLE T. Ischemia and reperfusion--from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17(11):1391-1401. [7] BERNARDI P, RASOLA A, FORTE M, et al. The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore: Channel Formation by F-ATP Synthase, Integration in Signal Transduction, and Role in Pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2015; 95(4):1111-1155. [8] DARE AJ, LOGAN A, PRIME TA, et al. The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ decreases ischemia-reperfusion injury in a murine syngeneic heart transplant model. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015; 34(11):1471-1480. [9] BASILI S, TANZILLI G, MANGIERI E, et al. Intravenous ascorbic acid infusion improves myocardial perfusion grade during elective percutaneous coronary intervention: relationship with oxidative stress markers. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3(2):221-229. [10] PANISELLO-ROSELLÓ A, LOPEZ A, FOLCH-PUY E, et al. Role of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in ischemia reperfusion injury: An update. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(27):2984-2994. [11] SOLIMAN S, ISHRAT T, FOUDA AY, et al. Sequential Therapy with Minocycline and Candesartan Improves Long-Term Recovery After Experimental Stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 2015;6(4):309-322. [12] YU L, GONG B, DUAN W, et al. Melatonin ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 1 diabetic rats by preserving mitochondrial function: role of AMPK-PGC-1α-SIRT3 signaling. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41337. [13] CHEN C, LU W, WU G, et al. Cardioprotective effects of combined therapy with diltiazem and superoxide dismutase on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Life Sci. 2017;183:50-59. [14] Kalimeris K, Briassoulis P, Ntzouvani A, et al. N-acetylcysteine ameliorates liver injury in a rat model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion. J Surg Res. 2016;206(2):263-272. [15] TSUJITA K, SHIMOMURA H, KAIKITA K, et al. Long-term efficacy of edaravone in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circ J. 2006; 70(7):832-837. [16] 徐建兴,钟永利,肖燕,等. 3-硝基-N-甲基水杨酰胺对琥珀酸-细胞色素C还原酶的抑制作用[J]. 生物化学杂志,1987,3(2):139-145. [17] 沈明,徐建兴,陈清棠. 3-硝基-N-甲基-水杨酰胺对大鼠局灶脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 中风与神经疾病,2002,19(1):17-19. [18] WÖLKART G, SCHRAMMEL A, KOYANI CN, et al. Cardioprotective effects of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural mediated by inhibition of L-type Ca2+ currents. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(20):3640-3653. [19] KWAN JC, GAO L, MACDONALD PS, et al. Cardio-protective signalling by glyceryl trinitrate and cariporide in a model of donor heart preservation. Heart Lung Circ. 2015;24(3):306-318. [20] CHAMBERS DC, YUSEN RD, CHERIKH WS, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-fourth Adult Lung And Heart-Lung Transplantation Report-2017;Focus Theme: Allograft ischemic time. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2017;36(10): 1047-1059. [21] CADENAS S. ROS and redox signaling in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018; 117:76-89. [22] VENKAT P, SHEN Y, CHOPP M, et al. Cell-based and pharmacological neurorestorative therapies for ischemic stroke. Neuropharmacology. 2018;134(Pt B):310-322. [23] ZHOU H, MA Q, ZHU P, et al. Protective role of melatonin in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: From pathogenesis to targeted therapy. J Pineal Res. 2018;64(3):10.1111/jpi.12471. [24] ZHOU H, ZHANG Y, HU S, et al. Melatonin protects cardiac microvasculature against ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of mitochondrial fission-VDAC1-HK2mPTP-mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res. 2017;63(1): e12413. [25] KALIMERIS K, BRIASSOULIS P, NTZOUVANI A, et al. N-acetylcysteine ameliorates liver injury in a rat model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion. J Surg Res. 2016;206(2):263-272. [26] VALLS-LACALLE L, BARBA I, MIRÓ-CASAS E, et al. Succinate dehydrogenase inhibition with malonate during reperfusion reduces infarct size by preventing mitochondrial permeability transition. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;109(3):374-384. [27] GUO L, SHESTOV AA, WORTH AJ, et al. Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex II by the Anticancer Agent Lonidamine. J Biol Chem. 2016; 291(1):42-57. [28] VANDEN HOEK TL, BECKER LB, SHAO Z, et al. Reactive oxygen species released from mitochondria during brief hypoxia induce preconditioning in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(29): 18092-18098. [29] SUZUKI C, HATAYAMA N, OGAWA T, et al. Cardioprotection via metabolism for rat heart preservation using the high-pressure gaseous mixture of carbon monoxide and oxygen. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(22):8858. [30] ELGEBALY SA, POSTON R, TODD R, et al. Cyclocreatine protects against ischemic injury and enhances cardiac recovery during early reperfusion. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2019;17(9):683-697. [31] YANG C, XU H, CAI L, et al. Donor pretreatment with adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activator protects cardiac grafts from cold ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;49(5):1354-1360. [32] WU MY, YIANG GT, LIAO WT, et al. Current mechanistic concepts in ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(4):1650-1667. [33] ZOROVA LD, POPKOV VA, PLOTNIKOV EY, et al. Mitochondrial membrane potential. Anal Biochem. 2018; 552:50-59. [34] ZHOU HY, ZHANG LN, ZHENG MZ, et al. Improved myocardial function with supplement of levosimendan to Celsior solution. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014;64(3):256-265. |
| [1] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [2] | Li Qin, Mao Shuangfa, Li Min, Cheng Jiyan. Protective effect and mechanism of dendrobium on fibroblasts damaged by ultraviolet B [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1228-1233. |
| [3] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [4] | Duan Zhaoyuan, Wu Mingli, Luo Meng, Gao Jing, Li Ruiqing, Feng Xiaodong. Glutathione peroxidase 4 regulates neuronal ferroptosis after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1956-1962. |
| [5] | Cai Shengsheng, Mei Heng, Zhang Xuequan, Deng Jin, Cao Jun, He Bin. Prepared HPe6DF composite nanoparticles enhance the effect of photodynamic therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1566-1573. |
| [6] | Zhang Shuping, Dai Lingli, Wang Yajun, Liu Wenjuan, Huang Zuoyi. Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors on oxidative stress related factors in a rat model of beta-amyloid 1-42 dementia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5650-5655. |
| [7] | Zhu Rui, Zeng Qing, Huang Guozhi. Ferroptosis and stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739. |
| [8] | Xie Wenjie, Zhou Gang, Xie Jinmei, Liu Jiao, Li Pengfei, Yang Fan, Cui Di. Mechanism of myocardial oxidative damage in a rat model of one-time exhaustive exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 247-252. |
| [9] | Bai Zhenjun, Liu Tong, Wang Zirun, Zhang Huiyu, Xu Peng. Effect of “Lumbar Three Needles” on expression of oxidative stress factors in rats with multifidus muscles injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5145-5150. |
| [10] | Zhao Yilang, Liu Tao, Yang Huilin, He Fan. Extracellular matrix improves antioxidant capacity of human umbilical cord stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3953-3958. |
| [11] |
Zhong Ping, Cui Xing.
Baicalin protects intestinal mucosal barrier and intervenes acute graft-versus-host disease by regulating autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4028-4032. |
| [12] | Liu Wenhua, Liang Jinfeng, Deng Shaojie. Resveratrol reduces tumor nuclear factor-α expression in wear-particle-treated macrophages by regulating the level of intracellular oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(26): 4115-4120. |
| [13] | Huang Chao, Huang Qinghua, You Di, Guo Wenlai, Qu Wenrui, Zhu Zhe, Li Rui . Molecular mechanism of quercetin in the treatment of traumatic brain injury: its feasibility of clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3760-3766. |
| [14] | Zhang Chunqiang, Zhang Tong, Zhang Guiying, Liu Yu, Wang Shuying, Liu Gaiping, Zhang Jiaxin. Embryonic development of C-type natriuretic peptide-pretreated mouse oocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2722-2727. |
| [15] | Jiang Li-ping, Li Long-jie, Gong De-zheng, Geng Cheng-yan, Jiang Li-jie, Zhong Lai-fu. Monosodium iodoacetate induces apoptosis of primary rat chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(2): 247-253. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||



