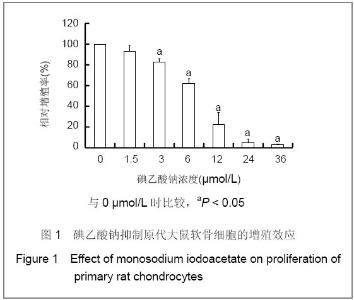
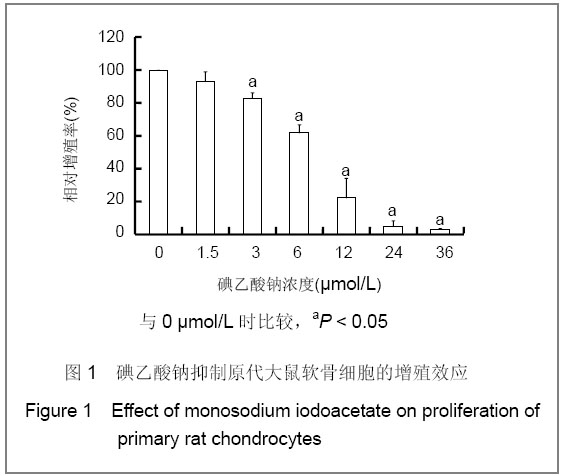
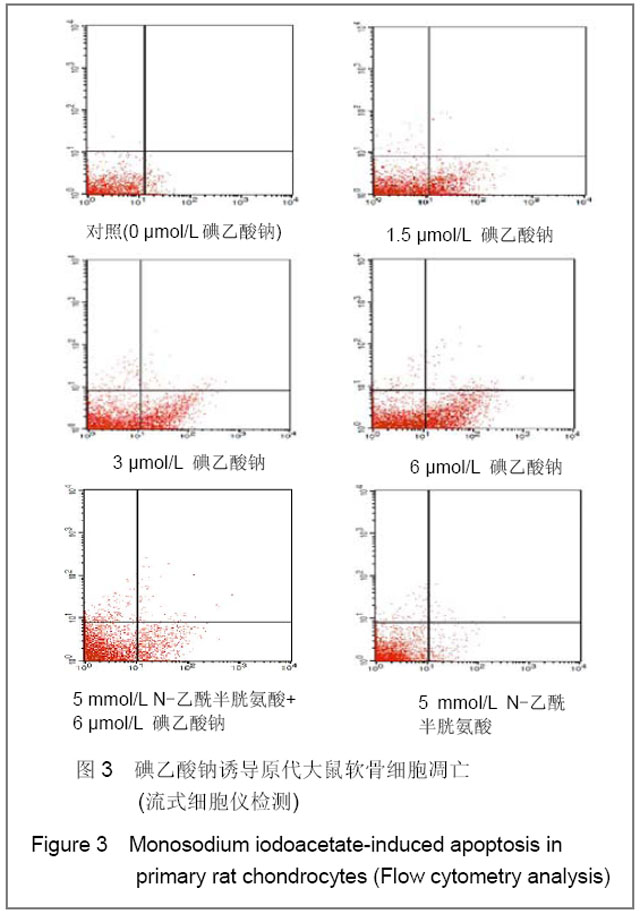
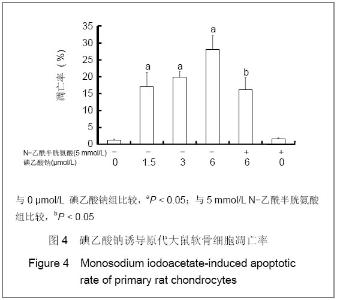
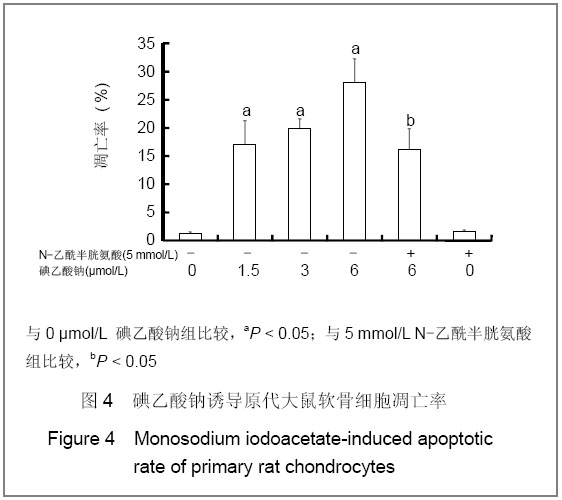
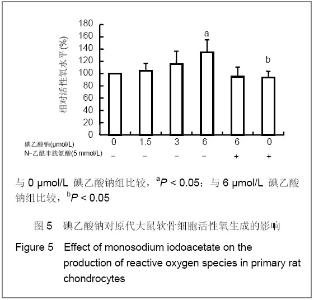
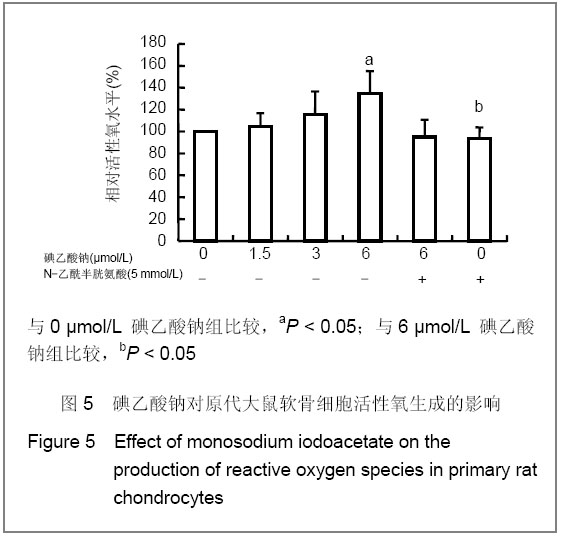
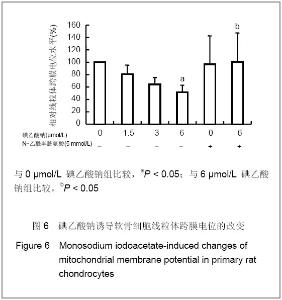
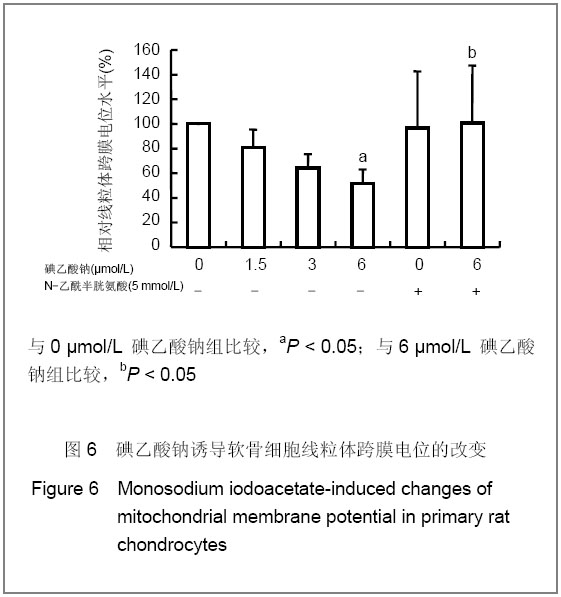
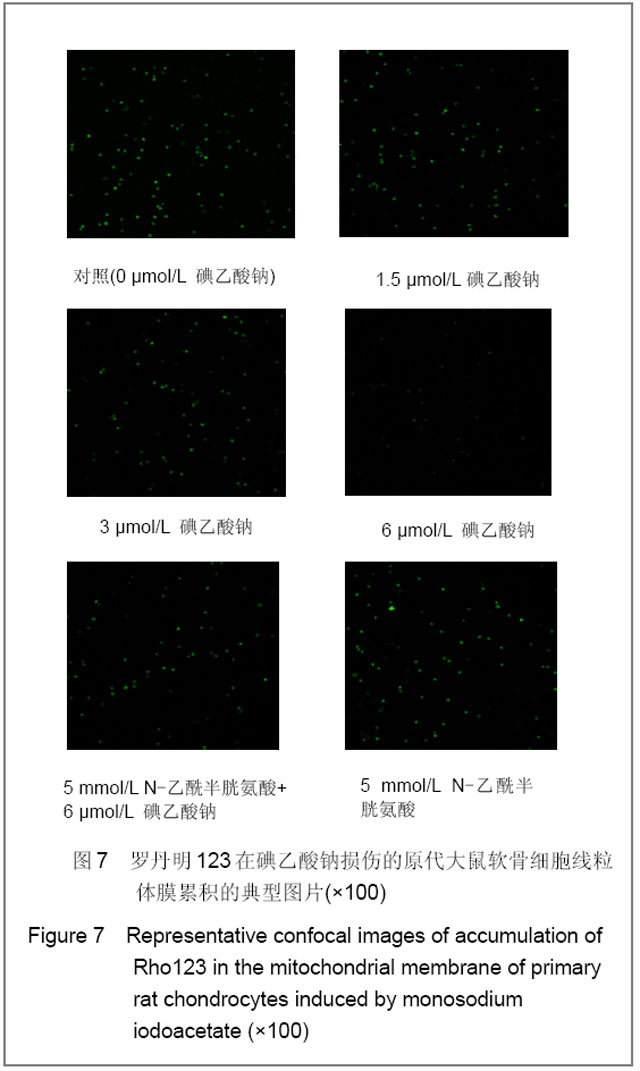
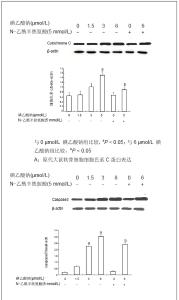
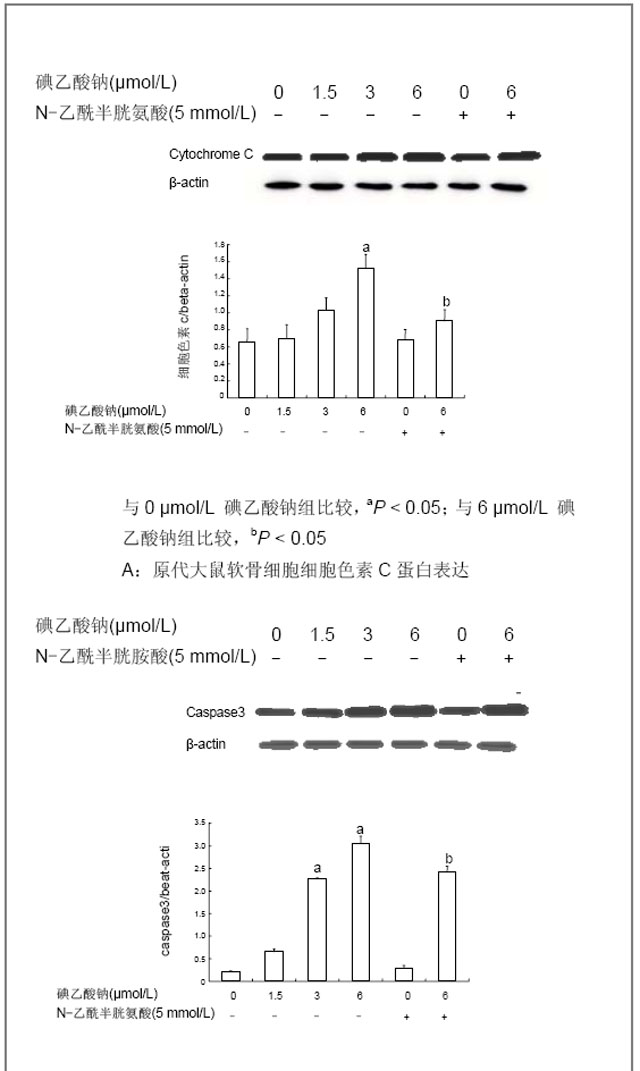
| [1] Krasnokutsky S, Samuels J, Abramson SB. Osteoarthritis in 2007. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007;65(3):222-228.[2] Héraud F, Héraud A, Harmand MF. Apoptosis in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(12):959-965.[3] Malemud CJ, Islam N, Haqqi TM. Pathophysiological mechanisms in osteoarthritis lead to novel therapeutic strategies. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(1-2):34-48.[4] Guingamp C, Gegout-Pottie P, Philippe L,et al. Mono-iodoacetate-induced experimental osteoarthritis: a dose-response study of loss of mobility, morphology, and biochemistry. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Sep;40(9):1670-1679.[5] Parodi AL. Ethical issue in animal experimentation. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2009;193(8):1737-1745.[6] Wu FL,Yu L,Wang ZY. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(20):9973-9976. 吴凤麟,宇丽,汪卓赟.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对生长板软骨细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(20): 9973-9976.[7] Jiang L, Cao J, An Y,et al. Genotoxicity of acrylamide in human hepatoma G2 (HepG2) cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2007; 21(8):1486-1492.[8] Fitzpatrick LR, Green C, Maines LW,et al. Experimental osteoarthritis in rats is attenuated by ABC294640, a selective inhibitor of sphingosine kinase-2. Pharmacology. 2011; 87(3-4): 135-143.[9] Horton WE Jr, Bennion P, Yang L. Cellular, molecular, and matrix changes in cartilage during aging and osteoarthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2006;6(4):379-381.[10] Hengartner MO. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature. 2000; 407(6805):770-776.[11] Willis SN, Adams JM. Life in the balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17(6): 617-625.[12] Marchetti P, Castedo M, Susin SA,et al. Mitochondrial permeability transition is a central coordinating event of apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1996;184(3):1155-1160.[13] Kroemer G, Zamzami N, Susin SA. Mitochondrial control of apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1997;18(1):44-51.[14] Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M,et al. Reduction in mitochondrial potential constitutes an early irreversible step of programmed lymphocyte death in vivo. J Exp Med. 1995; 181(5): 1661-1672.[15] Petit PX, Lecoeur H, Zorn E,et al. Alterations in mitochondrial structure and function are early events of dexamethasone-induced thymocyte apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1995;130(1):157-167.[16] Vander Heiden MG, Chandel NS, Li XX,et al. Outer mitochondrial membrane permeability can regulate coupled respiration and cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97(9):4666-4671.[17] Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E,et al. Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature. 2001;410(6828):549-554.[18] Buttke TM, Sandstrom PA. Oxidative stress as a mediator of apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1994;15(1):7-10.[19] Green DR. Death and NF-kappaB in T cell activation: life at the edge. Mol Cell. 2003;11(3):551-552.[20] Garrido C, Gurbuxani S, Ravagnan L, et al. Heat shock proteins: endogenous modulators of apoptotic cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;286(3):433-442.[21] Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2004;55:373-399.[22] Yudoh K, Nguyen T, Nakamura H,et al. Potential involvement of oxidative stress in cartilage senescence and development of osteoarthritis: oxidative stress induces chondrocyte telomere instability and downregulation of chondrocyte function. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(2):R380-391. |