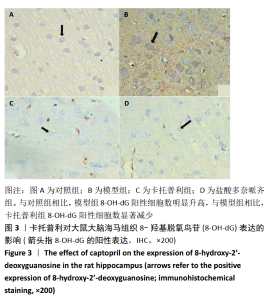
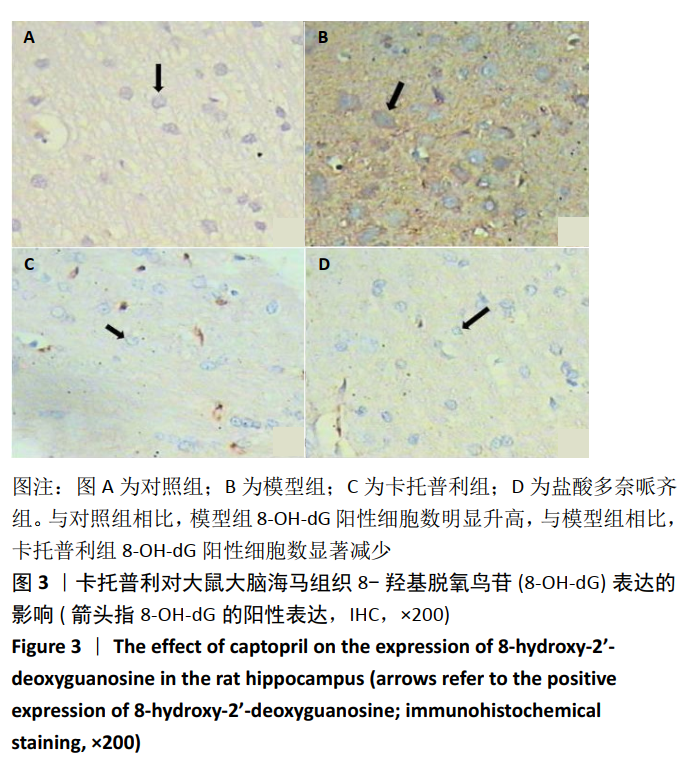
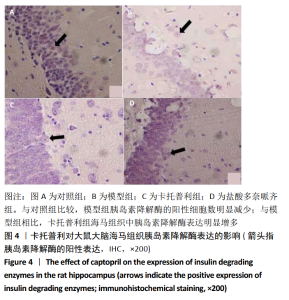
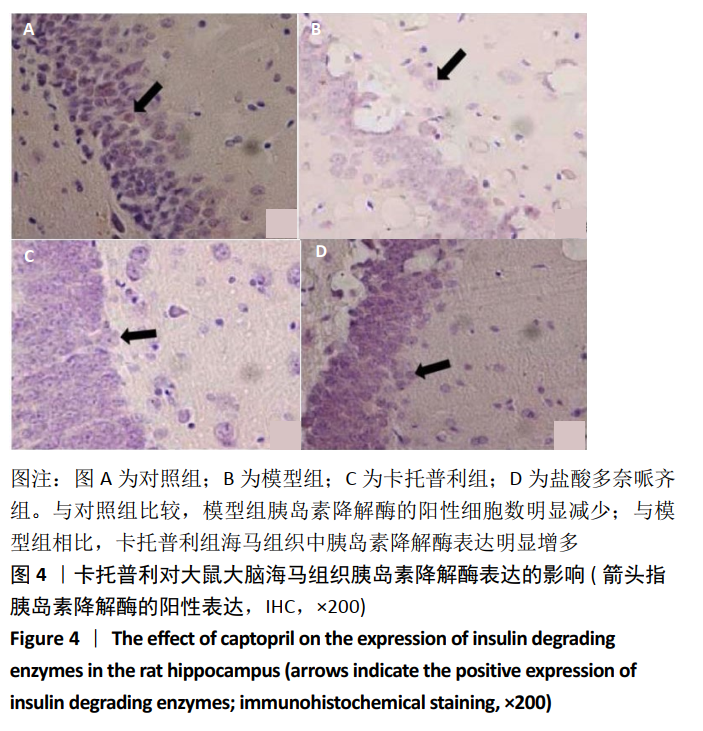
[1] PRINCE M, WIM A, GUICHET M, et al. World Alzheimer report 2015. The global impact of dementia. An analysis of prevalence, incidence, Constant trends-research portal, King`s College. London.2015.
[2] DEVI S, YADAV R, CHINANA P, et al. Fighting the Cause of Alzheimer’s and GNE Myopathy. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:669-682.
[3] KIM DH, LEE D, LIM H, et al. Effect of growth differentiation factor-15 secreted by human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells on amyloid beta levels in in vitro and in vivo models of Alzheimer’s disease. Bio Chum Biophysics Res Commune. 2018; 504(4):933-940.
[4] YANG JS, JEON S, YOON KD, et al . Cyanidin-3-glucoside inhibits amyloid β25-35-induced neuronal cell death in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Korean J Physio Pharmacia. 2018;22(6):689-696.
[5] EDERER KA, JIN K, BOUSLOG S, et al. Age- and genotype-specific effects of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor lisinopril on mitochondrial and metabolic parameters in drosophila melanogaster. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(11):3351.
[6] ROUCH L, CESTAC P, HANON O, et al. Antihypertensive drugs, prevention of cognitive decline and dementia: a systematic review of observational studies, randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses, with discussion of potential mechanisms. CNS drugs. 2015;29(2):113-130.
[7] SAVASKAN E, HOCK C, OLIVIERI G, et al. Cortical alterations of angiotensinconverting enzyme, angiotensin II and AT1 receptor in Alzheimer’s dementia. Neurobiol Aging. 2001;22:541-546.
[8] HIRAWA N, UEHARA Y, KAWABATA Y, et al. Long-Term Inhibition of Renin-Angiotensin System Sustains Memory Function in Aged Dahl Rats. Hypertension. 1999;34(3):496-502.
[9] FENG T, YAMASHITA T, ZHAI Y, et al . Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion accelerates Alzheimer’s disease pathology with the change of mitochondrial fission and fusion proteins expression in a novel mouse model.Brain Res. 2018;1696:63-70.
[10] KRASINSKI CA, IVANCIC VA, ZHENG Q, et al. Resveratrol Sustains Insulin-Degrading Enzyme Activity toward Aβ42. Acs Omega. 2018;3(10): 13275-13282.
[11] Marpillat NL, Macquin-Mavier I, Tropeano AI, et al. Antihypertensive classes, cognitive decline and incidence of dementia: a network meta-analysis. J Hypertens. 2013;31(6):1073-1082.
[12] Abdalla S, Langer A, Fu X, et al. ACE Inhibition with Captopril Retards the Development of Signs of Neurodegeneration in an Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(8):16917-16942.
[13] AbdAlla S, El Hakim A, Abdelbaset A, et al.Inhibition of ACE retards tau hyperphosphorylation and signs of neuronal degeneration in aged rats subjected to chronic mild stress. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:917156.
[14] Lynn SA, keeling E, Munday R, et al. The complexities underlying age-related macular degeneration: could amyloid beta play an important role? Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(4):538-548.
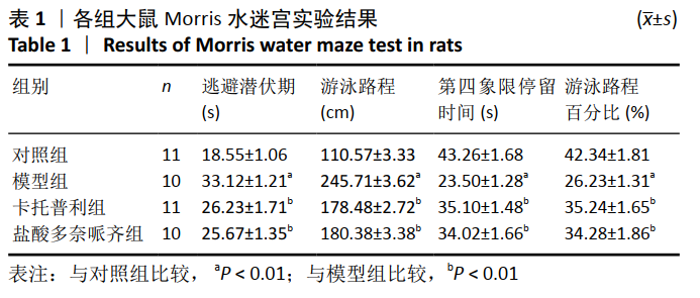
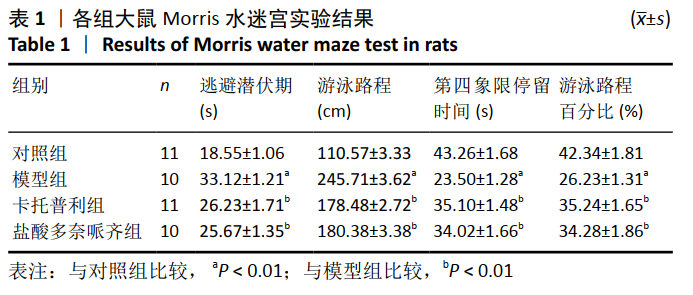
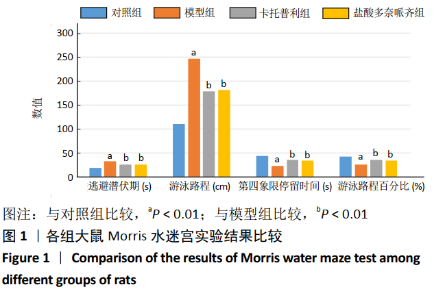
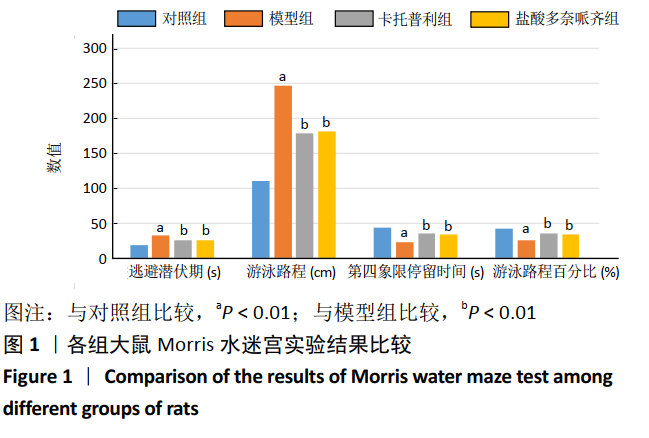
[15] 周娇娇,阙建宇,于雯雯,等.Morris水迷宫检测动物学习记忆水平的方法学[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(24):6274-6277.
[16] YANG JD, FENG GY, ZHANG J, et al. Association between angiotensin-converting enzyme gene and late-onset Alzheimer’ s disease in Han Chinese. Neurosci Lett. 2000;295(1-2):41-44.
[17] WRIGHT JW, YAMAMOTO BJ, HARDING JW. Angiotensin receptor sub type mediated physiologies and behaviors:new discoveries and clin ical targets. Prog Neurobiol. 2008;84(2):157-181.
[18] MARPILLAT NL, MACQUIN-MAVIER I, TROPEANO A, et al. Antihypertensive classes, cognitive decline and incidence of dementia: a network meta-analysis. Hypertension. 2013;31(6):1073-1082.
[19] LI NM, LIU KF, QIU YJ, et al. Mutations of beta-amyloid precursor protein alter the consequence of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(4):658-665.
[20] DELAMONTE SM, TONG M, WANDS JR, et al. The 20-yeatvoyagea-board the journal of Alzheimer`s disease: docking at “type 3 diabetes”, environmental/exposure factors, pathogenic mechnisms, and potential treatments . J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;62(3):1381-1390.
[21] BARTHOLD D, JOYCE G, WHARTON W, et al. The association of multiple anti-hypertensive medication classes with Alzheimer’s disease incidence across sex, race, and ethnicity. P Los One.2018;13(11): e0206705.
[22] Rosenberg PB, Mielke MM, Tschanz J, et al.Effects of cardiovascular medications on rate of functional decline in Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2008;16(11):883-892.
[23] 段晓宇,蒋建华,孔岩,等.ACEI和ARB类药物对AD大鼠认知功能的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2012,29(5):412-414.
[24] 王建峰,张晨红,王婉,等.尼莫地平联合盐酸多奈哌齐对脑梗死认知障碍患者的疗效及对生活质量的影响[J].河北医学,2018,24(8): 1273-1277.
[25] Ohrui T, Tomita N, Sato-Nakagawa T, et al. Effects of brain-pene trating ACE inhibitors on Alzheimer disease progression. Neurology. 2004;63(67):1324-1325. |