Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1956-1962.doi: 10.12307/2022.523
Previous Articles Next Articles
Glutathione peroxidase 4 regulates neuronal ferroptosis after spinal cord injury
Duan Zhaoyuan1, Wu Mingli2, Luo Meng1, Gao Jing2, Li Ruiqing1, 2, Feng Xiaodong1, 2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Rehabilitation Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-28Revised:2021-07-30Accepted:2021-09-08Online:2022-04-28Published:2021-12-15 -
Contact:Feng Xiaodong, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; Rehabilitation Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine , Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Duan Zhaoyuan, Master candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Key Research and Development Promotional Project of Department of Science and Technology of Henan Province, No. 202102311130 (to WML); 2019 Henan Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Special Project, No. 2019ZY2132 (to WML); National Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Research Base Scientific Research Special Project of Henan Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Administration, No. 2018JDZX083 (to WML)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Duan Zhaoyuan, Wu Mingli, Luo Meng, Gao Jing, Li Ruiqing, Feng Xiaodong. Glutathione peroxidase 4 regulates neuronal ferroptosis after spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1956-1962.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
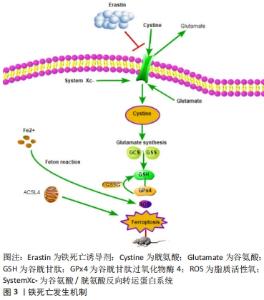
2.1 脊髓损伤与铁死亡 2.1.1 铁死亡 铁死亡是一种非典型的程序性细胞死亡形式,其主要标志是铁过载和活性氧积累,并伴有线粒体缩小和膜密度增加等形态学改变[3]。从本质上讲,铁死亡的发生取决于富铁诱导的脂质活性氧和防止脂质过氧化的抗氧化系统之间的平衡。一旦发生失衡,脂质活性氧产生过多或抗氧化系统活性降低,就会引发严重的脂质过氧化,造成蛋白质和DNA的氧化损伤以及损伤部位神经纤维的变性和脱髓鞘,导致神经细胞铁死亡的发生[11]。 脂质活性氧的形成是铁催化脂质过氧化过程,包括非酶机制(芬顿反应)和酶机制(脂氧合酶)诱导[12]。生理情况下,细胞内的铁浓度保持相对稳定的状态,血液中的游离Fe3+先与细胞外转铁蛋白形成复合物,再与细胞膜上转铁蛋白受体1结合,经过内吞过程转移到细胞内[13]。当细胞内聚集大量的游离铁时,游离铁中的亚铁可通过芬顿反应产生羟基自由基(?OH),诱导氧化应激,造成细胞损伤。铁死亡发生的另一条重要途径是酶促脂质过氧化,脂氧合酶在这一过程中起着不可或缺的作用,它能催化多不饱和脂肪酸脱氢生成磷脂氢过氧化物;其次在Fe2+的存在下,磷脂氢过氧化物被分解成烷氧基自由基(RO-),它还可以攻击其他多聚不饱和脂肪酸引发脂质过氧化的连锁反应。另一方面,磷脂氢过氧化物可以分解成4-羟基壬烯醛和丙二醛,通过交联反应使膜蛋白失活。多聚不饱和脂肪酸、4-羟基壬烯醛和丙二醛会降低细胞膜的稳定性,增加细胞膜的通透性,从而导致细胞死亡[11]。此外后两种醛类末端产物可与细胞蛋白质中的碱性氨基酸(如赖氨酸、组氨酸、精氨酸、半胱氨酸)共价结合,从而改变其结构和功能特性[14]。 GPx4是调控铁死亡的重要中枢因子,能够通过将激活的磷脂氢过氧化物转化为失活的磷脂酰胆碱来消除多聚不饱和脂肪酸的磷脂氢过氧化物,从而干扰自由基的连锁反应,抑制脂质过氧化过程,减少铁死亡的发生,见图3。"
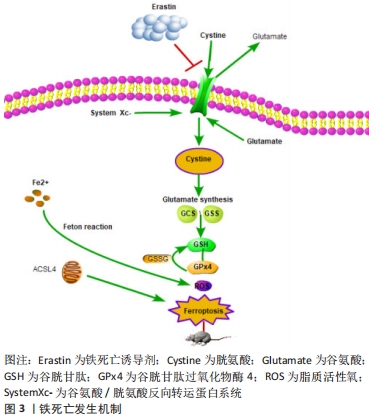

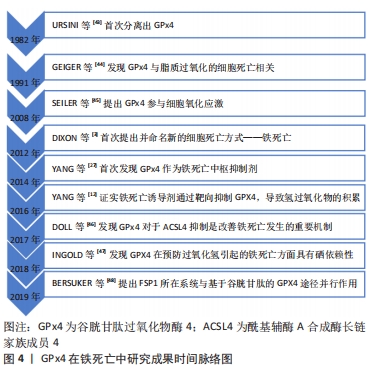
2.1.2 脊髓损伤中铁死亡的发生机制 脊髓损伤后继发性损伤是一个复杂的级联放大反应,也是原发性损伤的延续和发展,涉及多种细胞损伤机制,其危害甚至超过原发性损伤[15]。铁和脂质的代谢与脊髓损伤的病理生理密切相关,因此铁死亡在脊髓损伤的病理生理过程中起着重要的作用。脊髓损伤后红细胞碎裂溶血,释放大量游离铁,形成局部铁过载[16-17];同时,损伤应激反应激活了大量的脂质活性氧,导致脂质活性氧聚集[16],而铁过载又进一步增加了脂质活性氧积聚。脊髓损伤后的病理过程是铁死亡发生的先决条件,近年来先后有学者从不同层面证实了铁死亡在脊髓损伤中的发生并进一步揭示其机制。MENG等[18]通过建立脊髓损伤大鼠模型,在透射电镜下观察到组织中出现线粒体的皱缩、外膜破裂和嵴的消失,为铁死亡特征性线粒体形态;YAO等[8]通过检测铁死亡通路关键因子,发现GPx4和谷氨酸/半胱氨酸转运体表达下调,谷胱甘肽耗竭,确定铁死亡参与了脊髓损伤的病理过程;在细胞方面,ZHANG等[19]在脊髓神经细胞培养皿中加入亚铁离子,观察到脂质过氧化代谢产物的量与铁水平成正比,与神经元失活呈正相关。 通过抑制铁死亡可以减少脊髓损伤继发性损伤,促进脊髓修复,同时也进一步了解铁死亡在脊髓损伤中的具体机制。铁抑制素1(Ferrostatin-1,Fer-1)是第一代铁死亡抑制剂,通过小分子文库高通量筛选后发现,铁抑制素1可以特异性地抑制RAS选择性致死小分子3(RAS-selective lethal small molecule-3,RSL-3)诱导的铁死亡[3],这种活性可能源自其作为自由基捕获抗氧化剂的反应性[20],在坐骨神经慢性收缩损伤(CCI)诱导的大鼠模型中应用铁抑制素1治疗后,发现可上调GPx4、下调酰基辅酶A合成酶长链家族成员4( acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4,ACSL4)的表达,降低脊髓中铁离子含量[21],但在体内极其不稳定,容易代谢而失效。在铁抑制素1的基础上,SKOUTA等[22]发现了更为有效的第二代Ferrostatin类化合物,具有更强的活性,其中SRS11-92的活性是铁抑制素1的15倍,主要是通过抑制脂氧合酶,减缓了脂质氢过氧化物的积累[23]。 LINKERMANN等[24]在Erastin处理的HT-1080和NIH3T3细胞过程中发现了较铁抑制素1相比有更高的代谢和血浆稳定性的第三代铁死亡抑制剂Ferrostatin类化合物SRS16-86,具有强大的细胞保护作用;在脊髓损伤动物模型中其作用机制得到了进一步验证,通过上调铁死亡负向调节因子GPx4、谷胱甘肽和谷氨酸/半胱氨酸转运体,下调脂质过氧化标志物4-羟基壬烯醛,最终促进脊髓损伤后功能恢复[19]。最新研究发现在两大铁死亡保护系统的基础上提出了线粒体内膜中二氢乳清酸脱氢酶(DHODH)介导的铁死亡防御机制[25],同时确定了二氢乳清酸脱氢酶作为新型铁死亡抑制剂,这对于寻找更多铁死亡治疗策略和开发新的药物具有积极意义。 2.2 GPx4在铁死亡机制中的作用 2.2.1 GPx4的结构功能 GPx4是一种细胞内硒蛋白抗氧化酶[26],在铁死亡被正式命名的2年后,2014年YANG等[27]通过化学蛋白质组学策略筛选出GPx4这一铁死亡关键调控因子,靶向代谢组学分析发现谷胱甘肽的缺失会导致谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的失活,敲降或者过表达GPx4可以调节铁死亡诱导剂的致死率。 GPx4是以谷胱甘肽为电子供体[28],并以特定的氨基酸序列和空间结构存在,具有清除膜脂过氧化氢产物、预防氧化应激的能力[29]。GPx4能够通过将激活的磷脂氢过氧化物转化为失活的磷脂酰胆碱来消除多聚不饱和脂肪酸的磷脂氢过氧化物,从而干扰自由基的连锁反应,抑制脂质过氧化过程,减少铁死亡的发生。谷胱甘肽在GPx4催化下可以在还原状态和氧化状态之间循环,还原性谷胱甘肽是人机体内重要的抗氧化剂,可将H2O2还原成H2O,清除自由基,维持胞内自由基含量的平衡状态[30]。谷胱甘肽是GPx4发挥生物活性的关键因素,由γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸与甘氨酸结合形成,胞外的胱氨酸通过细胞膜上的谷氨酸/胱氨酸反向转运蛋白系统进行等比交换,胱氨酸进入细胞后诱导产生半胱氨酸,半胱氨酸依赖于ATP的半胱氨酸-谷氨酸连接酶形成γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸,再与甘氨酸经谷胱甘肽合成酶催化生成谷胱甘肽[27]。 2.2.2 GPx4在铁死亡中的作用机制 由谷胱甘肽介导的GPx4调控途径是铁死亡重要调节途径之一,GPx4在其中起着关键作用。GPx4降低脂质活性氧和阻断铁死亡有两条重要的途径,包括抗脂质氧化和拮抗活性Fe2+。 GPx4抗脂质过氧化:低水平脂质活性氧是重要的信号分子,但过量的脂质活性氧具有毒性[31]。早期研究认识到GPx4是通过控制细胞过氧化物张力来抵消某些脂氧合酶的活性[32],将脂质氢过氧化物转化为脂质醇,这一过程阻断了Fe2+依赖的毒性脂质活性氧的形成,而脂氧合酶正是经过酶促脂质过氧化途径导致铁死亡的发生。GPx4独特之处在于它能够减少较大的有机过氧化物,包括将活性位点硒醇(Se-H)氧化成硒酸(Se-OH)和使用谷胱甘肽将硒酸还原回活性硒醇[33]。有研究指出多聚不饱和脂肪酸的酶促过氧化主要由脂氧合酶催化,脂氧合酶从双烯丙基位置提取质子之后加入分子氧。只有当游离的二价铁被过氧化物氧化成三价铁时,脂氧合酶才能结合分子氧[34]。但在另外一项研究中对于脂氧合酶的催化作用提出了质疑,虽然在许多研究中经常使用的所谓异构体选择性的脂氧合酶抑制剂,但其是通过作为非特异性的自由基捕获剂来抑制脂质过氧化累积,而不是通过抑制各自的脂氧合酶异构体来抑制细胞铁死亡过程。对几种人类脂氧合酶异构体(5-LOX、p12-LOX和15-LOX-1)的过表达研究清楚地证明了脂质过氧化是铁死亡的关键驱动因素。事实上,在以前的许多研究的动物模型中是使用这些特异性抑制剂进行的,这让人怀疑这些效应实际上是由脂氧合酶的抑制作用还是由一般的抗氧化剂作用。 越来越多GPx4相关激活剂和抑制剂的发现及其作用方式的揭示都在很大程度上帮助阐明了GPx4在铁死亡中的分子机制和治疗潜力。基于结构和计算的方法确定了GPx4中的变构位点,从而发现了第一个GPx4变构激活剂[35],其通过增加GPx4的酶活性,抑制了由Erastin和胆固醇氢过氧化物引发的铁死亡。细胞诱导实验发现,GPx4是小分子化合物RSL-3的靶蛋白[36],由于RSL3含有亲电的氯乙酰胺,它与GPX4的亲核活性位点Sec共价相互作用,导致酶的不可逆失活[12],RSL-3正是通过直接作用于GPx4从而造成脂质活性氧的累积诱发铁死亡。 GPx4拮抗活性Fe2+:Fe2+稳态失衡后载量过大,涉及多种神经系统疾病的发病机制[37-39],是铁死亡形成的重要因素。铁死亡过程中的脂质过氧化是以铁依赖的方式发生,铁通过转铁蛋白或转铁蛋白受体系统输入细胞,并在溶酶体中从转铁蛋白中释放出来,转铁蛋白的免疫耗竭或转铁蛋白受体的基因沉默可抑制细胞铁死亡。线粒体是脂质活性氧的一个重要来源,Fe2+在参与氧化磷酸化过程中,细胞除了获得ATP,也会有一定量的脂质活性氧产生。Fe2+是脂氧合酶活性所必需的,细胞内Fe2+的存在,还可加速饱和脂肪酸的脂质过氧化过程[40]。一些新的证据表明,铁可以直接与游离脂肪酸和磷脂结合[41]。推测来看,位于质膜的铁池以高度局部化的方式促进该部位的脂质过氧化,另外局部发生在质膜上的脂质过氧化是铁死亡所必需的。一方面GPx4可以通过拮抗活性Fe2+,使H2O2转化为H2O[42],以此减弱氧化系统,维持平衡;另一方面GPx4通过限制脂质活性氧的产生和减少细胞铁的摄取而作为铁死亡的负调节因子。 GPx4在铁死亡中研究成果时间脉络图,见图4。"
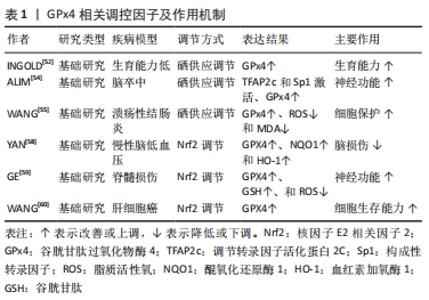
2.3 GPx4相关表达的调控 2.3.1 硒供应调节 GPx4是谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶家族中含有硒元素的第4个成员[49],GPx4 mRNA在翻译过程中,因硒代半胱氨酸插入序列(SECIS)元件的存在[50],需要一组不同的蛋白质系统来引导硒代半胱氨酸插入到GPx4中,将UGA密码子编码为一个活性位点硒代半胱氨酸(U46),使得GPx4的表达具备硒调节的能力[51]。硒酶GPx4对早期胚胎发生和细胞存活至关重要,且GPx4的存活功能是由其通过Sec介导的过氧化物酶活性所赋予[52]。GPx4对硒的利用不仅使细胞和组织变得高度抵抗促铁代谢的病理条件,而且可能利用过氧化氢作为细胞信号分子[53]。ALIM等[54]在动物实验中发现人体细胞可通过硒的摄入抑制细胞损伤,并进一步研究得出Sec是利用激活转录协同因子SP1来上调GPx4抑制铁死亡。WANG等[55]通过药物提高IEC-6细胞对硒的敏感性,发现GPx4转录水平的升高,进而减少丙二醛和脂质活性氧的生成。Sec对于GPx4的表达和活性来说必不可少,在缺乏Sec的情况下,GPx4活性降低,增加了细胞对氧化应激的敏感性和诱发铁死亡的可能性[56]。 2.3.2 核因子E2相关因子2 (nuclear factor erythroid derived 2-like 2,Nrf2)基因调节 Nrf2是调节细胞内抗氧化应激反应的关键转录因子,能够激活内源性抗氧化应答反应[57]。同时Nrf2与铁死亡氧化应激通路密切相关。Nrf2/ARE信号通路的激活可上调GPx4表达来改善神经损伤症状,其机制是通过减轻神经炎症、氧化应激损伤和抑制神经元的铁死亡实现的[58]。GE等[59]通过建立脊髓损伤动物模型发现锌对Nrf2/血红素加氧酶1(heme oxygenase 1,HO-1)有很强的调节作用,锌可以促进超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽的合成来加速脂质活性氧的去除,从而在局部微环境中达到平衡状态,并推断锌对GPx4的激活会抑制炎症反应,从而保护周围受损的神经元。WANG等[60]发现谷胱甘肽硫转移酶(GSTZ1)耗竭能增强Nrf2途径的激活,并可增加GPx4水平,从而抑制Erastin诱导的细胞损伤及其伴随铁过量积累、脂质过氧化和随后发生的铁死亡。铁死亡的明星调节因子GPx4是转录因子Nrf2的下游靶基因,也是唯一报道的能够直接还原复合磷脂氢过氧化物的酶[61]。因此,靶向GPx4目前被认为是触发铁死亡的关键策略[41],体外和体内的激活Nrf2/GPx4轴均能抑制铁死亡。 GPx4相关调控因子及作用机制总结,见表1。"

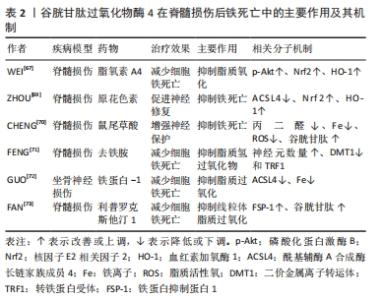
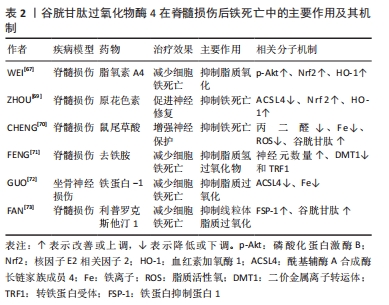
2.4 GPx4调控脊髓损伤铁死亡 铁死亡是脊髓损伤继发性损伤神经细胞死亡的主要机制之一,GPx4通过抑制脂质过氧化来调控脊髓损伤后神经元铁死亡,其调节途径涉及Akt/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路和多个分子。 2.4.1 Akt/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路 Akt/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路与抗氧化应激相关,通路的激活可促进细胞的内源性抗氧化作用[62]。多项研究表明,AKT和Nrf2/HO-1信号通路参与铁死亡的调节[62-63],同时,激活AKT和Nrf2信号通路减弱了Erastin诱导的铁死亡[65]。脂氧素A4(Lipoxin A4,LXA4)是一种重要的抗炎递质,在脊髓损伤中发挥神经保护作用[66],WEI等[67]使用Erastin处理初级脊髓神经元来诱导铁死亡,观察到细胞中GPx4的水平受到抑制而活性氧水平得到增加,经过脂氧素A4处理可有效消除铁死亡带来的影响,评估了脂氧素A4对铁死亡相关蛋白表达的影响,证实脂氧素A4通过激活Akt/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路在Erastin诱导的脊髓神经元的铁死亡中发挥神经保护作用;并进一步确定该通路激活是增加GPx4的表达来限制PTGS2和ACSL4水平,作为花生四烯酸代谢的限制性酶,PTGS2与铁死亡密切相关[68],而ACSL4作为铁死亡执行的一个重要组成部分发挥作用,通过塑造细胞脂质成分决定细胞铁死亡的敏感性。同样,在原花色素治疗后脊髓损伤处Nrf2和ACSL4的基因水平显著提升,并确认Nrf2是调节GPX4和HO-1等氧化还原相关蛋白的关键分子[69]。在另一项研究中也发现Nrf2信号通路的激活可增加GPx4的表达,鼠尾草酸对铁死亡的抑制作用可能部分受激活Nrf2信号通路以调节谷胱甘肽合成和代谢以及细胞铁稳态[70]。 2.4.2 其他调控途径 FENG等[71]在动物实验中也观察到脊髓损伤后GPx4的表达降低,并认为调节GPx4可能是治疗包括脊髓损伤在内的铁死亡相关神经疾病一个有效的选择。有研究在坐骨神经慢性收缩损伤模型(CCI)中评估了与脊髓神经元铁死亡相关包括铁含量、GPx4等生化和形态学变化,并用透射电子显微镜证实了线粒体存在异常形态变化,在对CCI大鼠施用Liproxstatin-1(利普罗克斯他汀1)后发现可减轻超敏反应,降低铁水平,减少脊髓脂质过氧化,恢复GPx4水平的失调[72]。上述GPx4是小分子化合物RSL-3的靶蛋白,通过RSL-3建立铁死亡模型(OLN-93细胞系)显著增加细胞内活性氧和丙二醛的浓度,同样在体外实验中使用Liproxstatin-1不仅抑制线粒体脂质过氧化,还可恢复谷胱甘肽、GPx4的表达,表明GPx4抑制剂可诱导少突胶质细胞的铁死亡,并且可证实liproxstatin-1是铁死亡的有效抑制剂[73]。铁死亡后GPx4活性下降,引发毒性脂质过氧化的连锁反应。动力蛋白抑制剂(dynasore)已被证明可保护脊髓免受缺血/再灌注损伤以及脊髓损伤后的神经元细胞死亡,在最新的研究中可能被用作一种新的有效的活性氧阻滞剂和脂质活性氧诱导细胞死亡的抑制剂[74],但其介导的体内外效应的研究尚不清楚。GPx4既是抗氧化脂质损伤的保护者,也是生理上重要的脂质信号调节者,二者需要对立统一才能维持体内平衡。 GPx4在脊髓损伤后铁死亡中的主要作用及其机制研究总结,见表2。"
| [1] HUTSON TH, DI GIOVANNI S. The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(12):732-745. [2] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17018. [3] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072. [4] DO VB, GOUEL F, JONNEAUX A, et al. Ferroptosis, a newly characterized form of cell death in Parkinson’s disease that is regulated by PKC. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;94:169-178. [5] XIE BS, WANG YQ, LIN Y, et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis attenuates tissue damage and improves long-term outcomes after traumatic brain injury in mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25(4):465-475. [6] ASHRAF A, JEANDRIENS J, PARKES HG, et al. Iron dyshomeostasis, lipid peroxidation and perturbed expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2020;32:101494. [7] YAN N, ZHANG JJ. The Emerging Roles of Ferroptosis in Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:811. [8] YAO X, ZHANG Y, HAO J, et al. Deferoxamine promotes recovery of traumatic spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(3):532-541. [9] YUAN H, LI X, ZHANG X, et al. CISD1 inhibits ferroptosis by protection against mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478(2):838-844. [10] CONRAD M, ANGELI JP, VANDENABEELE P, et al. Regulated necrosis: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15(5):348-366. [11] HASSANNIA B, VANDENABEELE P, VANDEN BT. Targeting Ferroptosis to Iron Out Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2019;35(6):830-849. [12] YANG WS, KIM KJ, GASCHLER MM, et al. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(34):E4966-E4975. [13] CONRAD M, PRONETH B. Selenium: Tracing Another Essential Element of Ferroptotic Cell Death. Cell Chem Biol. 2020;27(4):409-419. [14] DI DOMENICO F, TRAMUTOLA A, BUTTERFIELD DA. Role of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) in the pathogenesis of alzheimer disease and other selected age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;111:253-261. [15] GALEIRAS VR, FERREIRO VM, MOURELO FM, et al. Update on traumatic acute spinal cord injury. Part 1. Med Intensiva. 2017;41(4):237-247. [16] XIAO W, YU A, LIU D, et al. Ligustilide treatment promotes functional recovery in a rat model of spinal cord injury via preventing ROS production. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10):12005-12013. [17] HAO J, LI B, DUAN HQ, et al. Mechanisms underlying the promotion of functional recovery by deferoxamine after spinal cord injury in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(6):959-968. [18] MENG FX, HOU JM, SUN TS. Effect of oxidative stress induced by intracranial iron overload on central pain after spinal cord injury. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):24. [19] ZHANG Y, SUN C, ZHAO C, et al. Ferroptosis inhibitor SRS 16-86 attenuates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in contusion spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2019;1706:48-57. [20] ZILKA O, SHAH R, LI B, et al. On the Mechanism of Cytoprotection by Ferrostatin-1 and Liproxstatin-1 and the Role of Lipid Peroxidation in Ferroptotic Cell Death. ACS Cent Sci. 2017;3(3):232-243. [21] WANG H, HUO X, HAN C, et al. Ferroptosis is involved in the development of neuropathic pain and allodynia. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(8):3149-3161. [22] SKOUTA R, DIXON SJ, WANG J, et al. Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136(12):4551-4556. [23] COTTICELLI MG, XIA S, LIN D, et al. Ferroptosis as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Friedreich’s Ataxia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;369(1):47-54. [24] LINKERMANN A, SKOUTA R, HIMMERKUS N, et al. Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(47):16836-16841. [25] MAO C, LIU X, ZHANG Y, et al. DHODH-mediated ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nature. 2021;593(7860):586-590. [26] ANANDHAN A, DODSON M, SCHMIDLIN CJ, et al. Breakdown of an Ironclad Defense System: The Critical Role of NRF2 in Mediating Ferroptosis. Cell Chem Biol. 2020;27(4):436-447. [27] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1-2):317-331. [28] CHEN L, NA R, DANAE MK, et al. Overexpression of ferroptosis defense enzyme Gpx4 retards motor neuron disease of SOD1G93A mice. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):12890. [29] FLOHE L, TOPPO S, COZZA G, et al. A comparison of thiol peroxidase mechanisms. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(3):763-780. [30] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125. [31] RECZEK CR, CHANDEL NS. ROS-dependent signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015;33:8-13. [32] CONRAD M, SCHNEIDER M, SEILER A, et al. Physiological role of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase in mammals. Biol Chem. 2007;388(10):1019-1025. [33] KOEBERLE SC, GOLLOWITZER A, LAOUKILI J, et al. Distinct and overlapping functions of glutathione peroxidases 1 and 2 in limiting NF-kappaB-driven inflammation through redox-active mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2020;28:101388. [34] WOOD I, TROSTCHANSKY A, RUBBO H. Structural considerations on lipoxygenase function, inhibition and crosstalk with nitric oxide pathways. Biochimie. 2020;178:170-180. [35] GRIESSER M, SHAH R, VAN KESSEl AT, et al. The Catalytic Reaction of Nitroxides with Peroxyl Radicals and Its Relevance to Their Cytoprotective Properties. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(10):3798-3808. [36] CHEN L, HAMBRIGHT WS, NA R, et al. Ablation of the Ferroptosis Inhibitor Glutathione Peroxidase 4 in Neurons Results in Rapid Motor Neuron Degeneration and Paralysis. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(47): 28097-28106. [37] DRECOURT A, BABDOR J, DUSSIOT M, et al. Impaired Transferrin Receptor Palmitoylation and Recycling in Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;102(2):266-277. [38] CAO S, HUA Y, KEEP RF, et al. Minocycline Effects on Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Induced Iron Overload in Aged Rats: Brain Iron Quantification With Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Stroke. 2018;49(4): 995-1002. [39] DAGLAS M, ADLARD PA. The Involvement of Iron in Traumatic Brain Injury and Neurodegenerative Disease. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:981. [40] SAINT-GERMAIN E, MIGNACCA L, VERNIER M, et al. SOCS1 regulates senescence and ferroptosis by modulating the expression of p53 target genes. Aging (Albany NY). 2017;9(10):2137-2162. [41] GIOVANNI CF, SCOTT JD. GPX4 at the Crossroads of Lipid Homeostasis and Ferroptosis. Proteomics. 2019;19(18):e1800311. [42] IMAI H, NAKAGAWA Y. Biological significance of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (PHGPx, GPx4) in mammalian cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;34(2):145-169. [43] URSINI F, MAIORINO M, VALENTE M, et al. Purification from pig liver of a protein which protects liposomes and biomembranes from peroxidative degradation and exhibits glutathione peroxidase activity on phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982; 710(2):197-211. [44] GEIGER PG, THOMAS JP, GIROTTI AW. Lethal damage to murine L1210 cells by exogenous lipid hydroperoxides: protective role of glutathione-dependent selenoperoxidases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991;288(2):671-680. [45] SEILER A, SCHNEIDER M, FORSTER H, et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4 senses and translates oxidative stress into 12/15-lipoxygenase dependent- and AIF-mediated cell death. Cell Metab. 2008;8(3):237-248. [46] DOLL S, PRONETH B, TYURINA YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017; 13(1):91-98. [47] INGOLD I, BERNDT C, SCHMITT S, et al. Selenium Utilization by GPX4 Is Required to Prevent Hydroperoxide-Induced Ferroptosis. Cell. 2018; 172(3):409-422. [48] BERSUKER K, HENDRICKS JM, LI Z, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575(7784): 688-692. [49] ADENIRAN SO, ZHENG P, FENG R, et al. The Antioxidant Role of Selenium via GPx1 and GPx4 in LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bovine Endometrial Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02731-0. [50] WANG Y, HUANG J, SUN Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 suppresses mRNA expression of selenoproteins associated with ferroptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and DNA synthesis. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021;153: 112286. [51] MIN Z, GUO Y, SUN M, et al. Selenium-sensitive miRNA-181a-5p targeting SBP2 regulates selenoproteins expression in cartilage. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(12):5888-5898. [52] INGOLD I, AICHLER M, YEFREMOVA E, et al. Expression of a Catalytically Inactive Mutant Form of Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (Gpx4) Confers a Dominant-negative Effect in Male Fertility. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(23): 14668-14678. [53] INGOLD I, CONRAD M. Selenium and iron, two elemental rivals in the ferroptotic death process. Oncotarget. 2018;9(32):22241-22242. [54] ALIM I, CAULFIELD JT, CHEN Y, et al. Selenium Drives a Transcriptional Adaptive Program to Block Ferroptosis and Treat Stroke. Cell. 2019; 177(5):1262-1279. [55] WANG S, LIU W, WANG J, et al. Curculigoside inhibits ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis through the induction of GPX4. Life Sci. 2020;259: 118356. [56] CARDOSO BR, HARE DJ, BUSH AI, et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4: a new player in neurodegeneration? Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(3):328-335. [57] SHAW P, CHATTOPADHYAY A. Nrf2-ARE signaling in cellular protection: Mechanism of action and the regulatory mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3119-3130. [58] YAN N, XU Z, QU C, et al. Dimethyl fumarate improves cognitive deficits in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis via NRF2/ARE/NF-kappaB signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;98:107844. [59] GE MH, TIAN H, MAO L, et al. Zinc attenuates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in contusion spinal cord injury by activating Nrf2/GPX4 defense pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021;27(9):1023-1040 [60] WANG Q, BIN C, XUE Q, et al. GSTZ1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib-induced ferroptosis via inhibition of NRF2/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):426. [61] JOSÉ PFA, DMITRI VK, MARCUS C. Ferroptosis at the crossroads of cancer-acquired drug resistance and immune evasion. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2019;19(7):97-111. [62] WU X, WANG J, SONG L, et al. Catalpol weakens depressive-like behavior in mice with streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia via PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 2021; S0306-4522(21)00383-3. [63] JIANG B, ZHAO Y, SHI M, et al. DNAJB6 Promotes Ferroptosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65(7):1999-2008. [64] LI X, ZOU Y, XING J, et al. Pretreatment with Roxadustat (FG-4592) Attenuates Folic Acid-Induced Kidney Injury through Antiferroptosis via Akt/GSK-3beta/Nrf2 Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020: 6286984. [65] FUJIKI K, INAMURA H, SUGAYA T, et al. Blockade of ALK4/5 signaling suppresses cadmium- and erastin-induced cell death in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells via distinct signaling mechanisms. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(11):2371-2385. [66] LU T, WU X, WEI N, et al. Lipoxin A4 protects against spinal cord injury via regulating Akt/nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:905-910. [67] WEI N, LU T, YANG L, et al. Lipoxin A4 protects primary spinal cord neurons from Erastin-induced ferroptosis by activating the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(8):2118-2126 [68] XIAO X, JIANG Y, LIANG W, et al. miR-212-5p attenuates ferroptotic neuronal death after traumatic brain injury by targeting Ptgs2. Mol Brain. 2019;12(1):78. [69] ZHOU H, YIN C, ZHANG Z, et al. Proanthocyanidin promotes functional recovery of spinal cord injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. J Chem Neuroanat. 2020;107:101807. [70] CHENG J, XU T, XUN C, et al. Carnosic acid protects against ferroptosis in PC12 cells exposed to erastin through activation of Nrf2 pathway. Life Sci. 2021;266:118905. [71] FENG Z, MIN L, CHEN H, et al. Iron overload in the motor cortex induces neuronal ferroptosis following spinal cord injury. Redox Biol. 2021;43:101984. [72] GUO Y, DU J, XIAO C, et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis-like cell death attenuates neuropathic pain reactions induced by peripheral nerve injury in rats. Eur J Pain. 2021;25(6):1227-1240. [73] FAN BY, PANG YL, LI WX, et al. Liproxstatin-1 is an effective inhibitor of oligodendrocyte ferroptosis induced by inhibition of glutathione peroxidase 4. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(3):561-566. [74] CLEMENTE LP, RABENAU M, TANG S, et al. Dynasore Blocks Ferroptosis through Combined Modulation of Iron Uptake and Inhibition of Mitochondrial Respiration. Cells. 2020;9(10):2259. |
| [1] | Li Zhiyi, He Pengcheng, Bian Tianyue, Xiao Yuxia, Gao Lu, Liu Huasheng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1202-1209. |
| [2] | Kan Houming, Fan Lijun, Chen Xuetai, Shen Wen. Application of platelet-rich plasma in neuropathic pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1286-1292. |
| [3] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [4] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [5] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [6] | Jiang Shengyuan, Deng Bowen, Xu Lin, Liu Gang, He Feng, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Mu Xiaohong. Role and mechanism of tetramethylpyrazine in spinal cord injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1799-1804. |
| [7] | Mei Yunyun, Zhang Jianjun, Wang Dong. Hyperbaric oxygen combined with NgR gene silencing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation for spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 12-19. |
| [8] | Xie Xingqi, Hu Wei, Tu Guanjun. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes combined with chondroitinase ABC for treating spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 20-26. |
| [9] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [10] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [11] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [12] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [13] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [14] | Tan Rongbang, Wei Bo, Li Guangsheng. Nrf2-ARE regulated neurovascular interaction is involved in neural repair after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5694-5701. |
| [15] | Min Youjiang, , Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4600-4607. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

