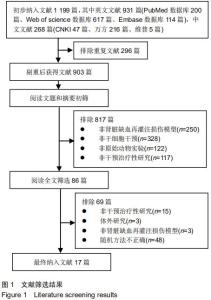
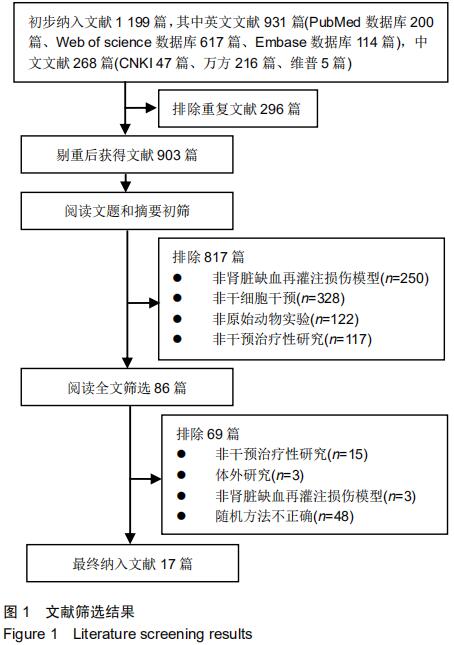
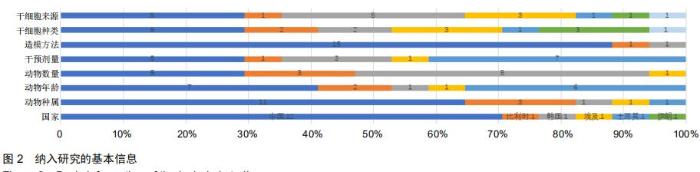
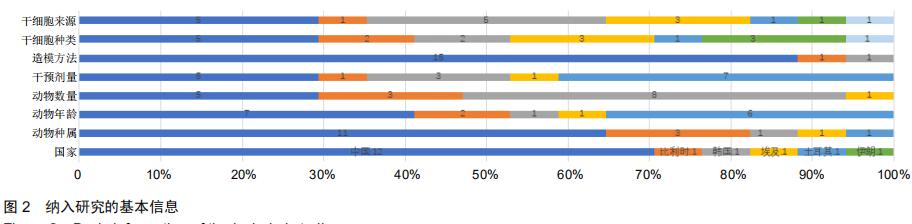
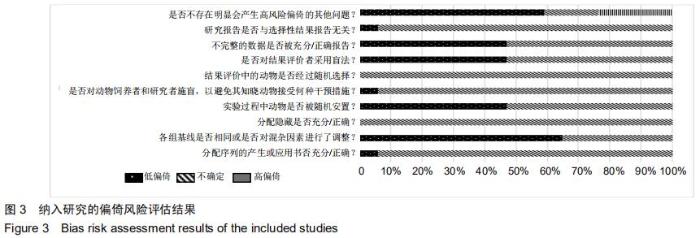
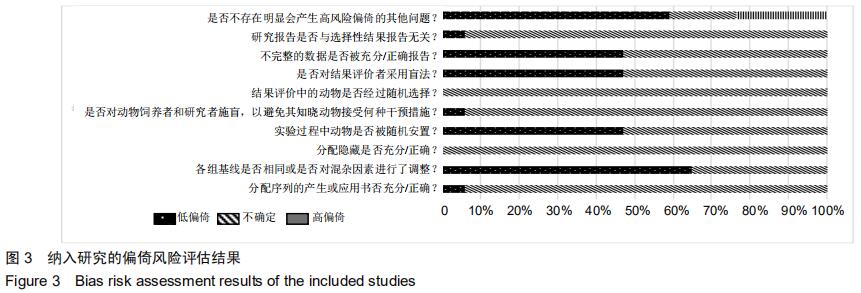
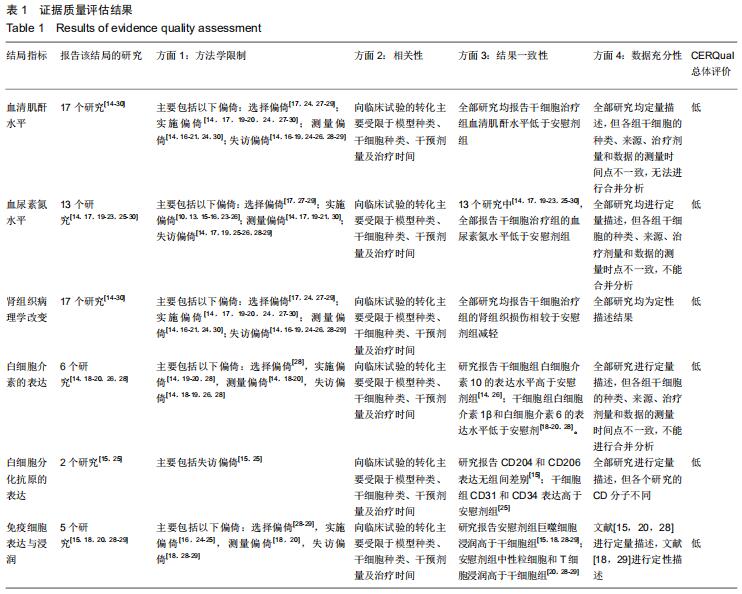
|
[1] WEIGHT SC, BELL PR, NICHOLSON ML. Renal ischaemia--reperfusion injury. Br J Surg. 1996;83(2): 162-170.
[2] ERPICUM P, ROWART P, POMA L, et al. Administration of mesenchymal stromal cells before renal ischemia/reperfusion attenuates kidney injury and may modulate renal lipid metabolism in rats. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):8687.
[3] KIL HK, KIM JY, CHOI YD, et al. Effect of Combined Treatment of Ketorolac and Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Patients Undergoing Partial Nephrectomy: Pilot Study. J Clin Med.2018;7(12): E470.
[4] KAABAK M, BABENKO N, ZOKOYEV A, et al. Eculizumab for Prevention and Treatment of Kidney Graft Reperfusion Injury, Preliminary Results of RCT. Transplantation.2014;98: 257-258.
[5] REINDERS ME, RABELINK TJ. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells: can impure cell preparations give pure results. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(12):3805-3807.
[6] 胡红林,邹丛,习小庆,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的免疫调节机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(37): 5977-5982.
[7] HU C, ZHAO L, WU D, et al. Modulating autophagy in mesenchymal stem cells effectively protects against hypoxia- or ischemia-induced injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1): 120.
[8] BURST VR, GILLIS M, PÜTSCH F, et al. Poor cell survival limits the beneficial impact of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on acute kidney injury. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2010;114(3):e107-116.
[9] BUSSOLATI B, HAUSER PV, CARVALHOSA R, et al. Contribution of stem cells to kidney repair. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009;4(1):2-8.
[10] GHEISARI Y, AZADMANESH K, AHMADBEIGI N, et al. Genetic modification of mesenchymal stem cells to overexpress CXCR4 and CXCR7 does not improve the homing and therapeutic potentials of these cells in experimental acute kidney injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2012; 21(16):2969-2980.
[11] HOOIJMANS CR, ROVERS MM, DE VRIES RB, et al. SYRCLE's risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:43.
[12] GUYATT G, OXMAN AD, AKL EA, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):383-394.
[13] LEWIN S, GLENTON C, MUNTHE-KAAS H, et al. Using qualitative evidence in decision making for health and social interventions: an approach to assess confidence in findings from qualitative evidence syntheses (GRADE-CERQual). PLoS Med. 2015;12(10):e1001895.
[14] CHEN YT, SUN CK, LIN YC, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell protects kidneys against ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction. J Transl Med. 2011;9:51.
[15] MONTEIRO CARVALHO MORI DA CUNHA MG, ZIA S, OLIVEIRA ARCOLINO F, et al. Amniotic Fluid Derived Stem Cells with a Renal Progenitor Phenotype Inhibit Interstitial Fibrosis in Renal Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Rats. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136145.
[16] WANG YL, LI G, ZOU XF, et al. Effect of autologous adipose-derived stem cells in renal cold ischemia and reperfusion injury. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(9):3198-3202.
[17] WANG LJ, YAN CP, CHEN D, et al. Efficacy Evaluation and Tracking of Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells in a Rat Model of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:9105768.
[18] FENG Z, TING J, ALFONSO Z, et al. Fresh and cryopreserved, uncultured adipose tissue-derived stem and regenerative cells ameliorate ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(12): 3874-3884.
[19] CHEN Y, QIAN H, ZHU W, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor modification promotes the amelioration effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on rat acute kidney injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(1):103-113.
[20] SUN P, LIU J, LI W, et al. Human endometrial regenerative cells attenuate renal ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. J Transl Med. 2016;14:28.
[21] HAVAKHAH S, SANKIAN M, KAZEMZADEH GH, et al. In vivo effects of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of acute ischemic kidney injury. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018;21(8): 824-831.
[22] LIU H, WU R, JIA RP, et al. Ischemic preconditioning increases endothelial progenitor cell number to attenuate partial nephrectomy-induced ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55389.
[23] LEE SJ, RYU MO, SEO MS, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Contribute to Improvement of Renal Function in a Canine Kidney Injury Model. In Vivo. 2017;31(6):1115-1124.
[24] SHEASHAA H, LOTFY A, ELHUSSEINI F, et al. Protective effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells against acute kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in Sprague-Dawley rats. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(5):1573-1580.
[25] XUE J, QIN Z, LI X, et al. Protective Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning-Mediated Homing of Endothelial Progenitor Cells on Renal Acute Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Male Rats. Ann Transplant. 2017;22:66-74.
[26] DU T, CHENG J, ZHONG L, et al. The alleviation of acute and chronic kidney injury by human Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells triggered by ischemia-reperfusion injury via an endocrine mechanism. Cytotherapy. 2012;14(10): 1215-1227.
[27] CHEN B, BO CJ, JIA RP, et al. The renoprotective effect of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell transplantation on acute ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(5):2034-2039.
[28] TSUDA H, YAMAHARA K, OTANI K, et al. Transplantation of allogenic fetal membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(7):889-899.
[29] ALTUN B, YILMAZ R, AKI T, et al. Use of mesenchymal stem cells and darbepoetin improve ischemia-induced acute kidney injury outcomes. Am J Nephrol. 2012;35(6):531-539.
[30] 刘荣福,高加胜,付国.可分化为肾小管上皮细胞的脂肪间充质干细胞对大鼠急性肾损伤的修复作用研究[J].中华泌尿外科杂志, 2014,35(10): 778-781.
[31] TONG A, PALMER S, CRAIG JC, et al. A guide to reading and using systematic reviews of qualitative research. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(6):897-903.
[32] EDWARDS J, KAIMAL G. Using meta-synthesis to support application of qualitative methods findings in practice: A discussion of meta-ethnography, narrative synthesis, and critical interpretive synthesis. The Arts in Psychotherapy. 2016; 51: 30-35.
[33] IOANNIDIS JP, PATSOPOULOS NA, ROTHSTEIN HR. Reasons or excuses for avoiding meta-analysis in forest plots. BMJ. 2008;336(7658):1413-1415.
[34] 陈匡阳,马彬,王亚楠,等. SYRCLE 动物实验偏倚风险评估工具简介[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2014,14(10):1281-1285.
[35] FULBROOK P, MBUZI V, MILES S. Effectiveness of prophylactic sacral protective dressings to prevent pressure injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019;100:103400.
[36] 曾宪涛,熊期,沈可. Meta 分析系列之十三:盲法的评价[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2013,5(4):331-333.
[37] 陶功财,张楠,尚志忠,等.评估动物实验偏倚风险的SYRCLE工具实例解读[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2019,11(3):42-45,50.
[38] SIDI Y, HAREL O. The treatment of incomplete data: Reporting, analysis, reproducibility, and replicability. Soc Sci Med. 2018;209:169-173.
[39] LIU Y, HE L, LIU J, et al. Establishing the acupuncture- moxibustion clinical trial registry and improving the transparence of clinical trials of acupuncture and moxibustion. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2017;37(7):685-689.
[40] HOOIJMANS CR, INTHOUT J, RITSKES-HOITINGA M, et al. Meta-analyses of animal studies: an introduction of a valuable instrument to further improve healthcare. ILAR J. 2014;55(3): 418-426.
|