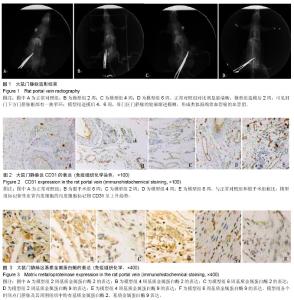
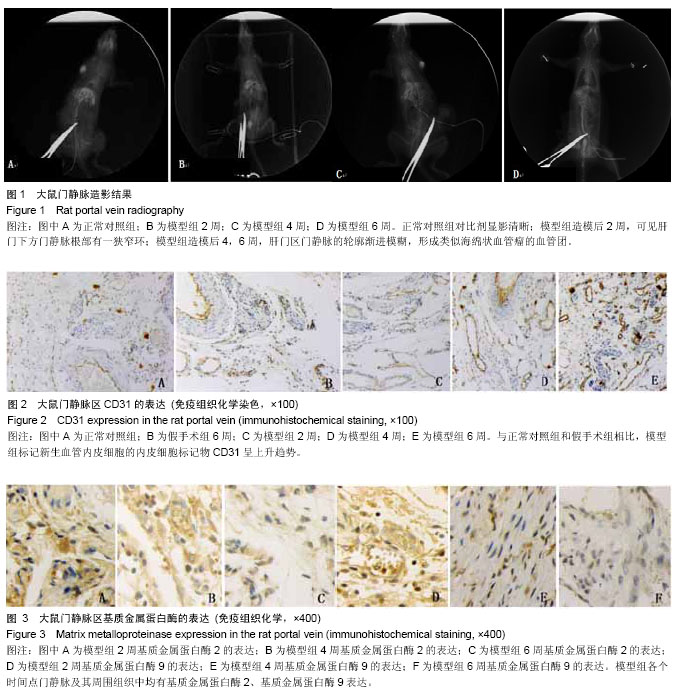
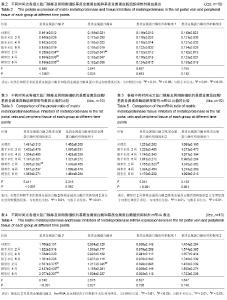
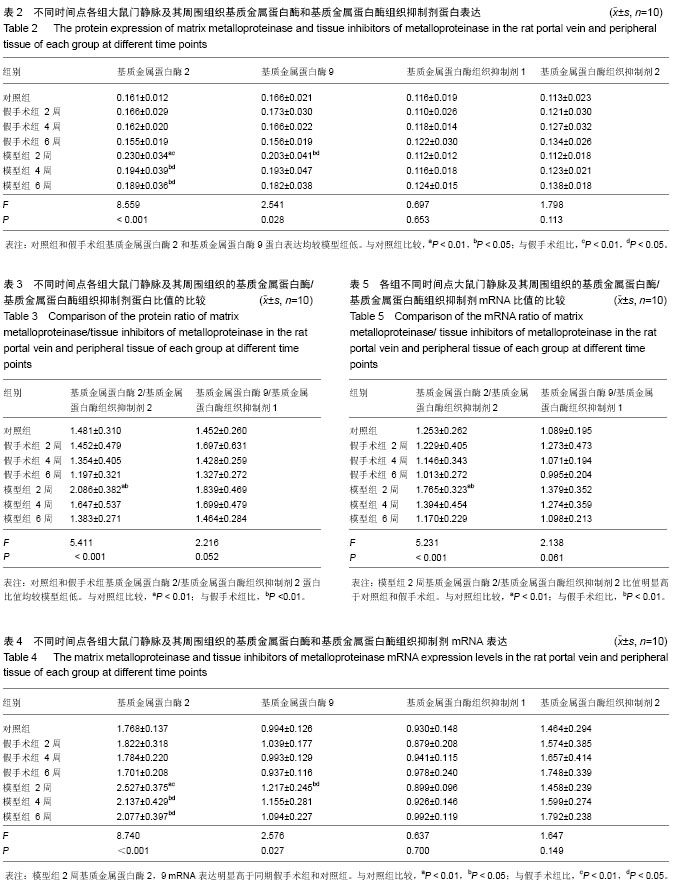
| [1] Gibson JR.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein.J Pathol Bact.1955;70:81-95.
[2] De Gaetano AM,Lafortune M,Patriquin H,et al.Cavernous transformation of the portal vein: patterns of intrahepatic and splanchnic collateral circulation of intrahepatic and splanchnic collateral circulation detected with Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol.1995;165:1151-1155.
[3] Fernandez M, Mejias M, Angermayr B,et al. Inhibition of VEGF receptor-2 decreases the development of hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation and portal-systemic collateral vessels in portal hypertensive rats.Hepatol.2005;43 (1):98-103.
[4] 梁颖,蒋涛,王亚杰,等. 螺旋CT评价门静脉海绵样变性及其侧支循环的特点[J].中国医学影像技术,2008,24(7):1076-1079.
[5] Hijova E. Matrix metalloproteinases:their biological funcations and clinical implications.Bratisl Lek Listy.2005;106(3): 127-132.
[6] Chistiakov DA,Sobenin IA,Orekhov AN.Vascular extracellular matrix in atherosclerosis. Cardiol Rev.2013;21(6):270-288.
[7] 王建尧,刘磊,王斌,等.门静脉海绵样变性大鼠模型制作方法的探讨及体会[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2010,17(1):46-51.
[8] 毛建雄,刘磊,王斌,等.门静脉部分缩窄制作SD大鼠门静脉海绵样变性动物模型[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2012,20(6):89-91.
[9] Fernandez M, Mejias M, Garcia-Pras E,et al. Reversal of portal hypertension and hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation by combined vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor blockade in rats. Hepatology. 2007;46(4):1208-1217.
[10] Mejias M, Garcia-Pras E, Tiani C,et al. The somatostatin analogue octreotide inhibits angiogenesis in the earliest, but not in advanced, stages of portal hypertension in rats. Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(5A):1690-1699.
[11] Fang J, Shing Y, Wiederschain D, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 is required for the switch to the angiogemc phenotype in anlulor model.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(8):3884-3889.
[12] 王兆京,张丹丹,陈志伟,等.MMP-9与VEGF在成人肝血管瘤中的表达及其意义[J].东南大学学报,2014,33(1):66-70.
[13] Murphy G. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Genome Biol.2011;12(11):233.
[14] Rosenberg GA , Estrada EY, Dencoff JE. Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs are associated with blood-brain barrier opening after reperfusion in rat brain. Stroke.1998;29(10):2189-2195.
[15] van Hinsbergh VW, Engelse MA, Quax PH. Pericellular protcases in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(4):716-728.
[16] 刘海龙,吴黎明,许圆圆. 在体大鼠心肌缺血再灌注中MMP-2/9、TIMP-1 /2mRNA和蛋白表达及MMP-2/9酶活性的同步动态变化[J]. 中国分子心脏病学杂志,2009.9(6):332-337.
[17] Lu H, Cao X, Zhang H,et al. Imbalance between MMP-2, 9 and TIMP-1 promote the invasion and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via SKP2 signaling pathways. Tumour Biol, 2014.2. [Epub ahead of print].
[18] Mohamed MM, EI-Ghonaimy EA, Nouh MA, et al. Cytokines secreted by macrophages isolated from tumor microenvironment of inflammatory breast cancer patients possess chemotactic properties. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014; 46:138-147.
[19] Marzano AV, Cugno M, Trevisan V, et al. Inflammatory cells, cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in amicrobial pustulosis of the folds and other neutrophilic dermatoses. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2011;24(2):451-460.
[20] Nagase H1, Woessner JF Jr. Matrix Metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(31):21491-21494..
[21] Dimas G, Iliadis F, Grekas D. Matrix metalloproteinases, atherosclerosis, proteinuria and kidney disease: Linkage-based approaches. Hippokratia. 2013;17(4):292-297 |