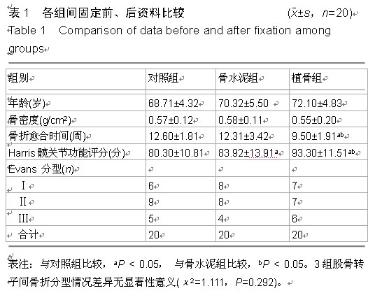
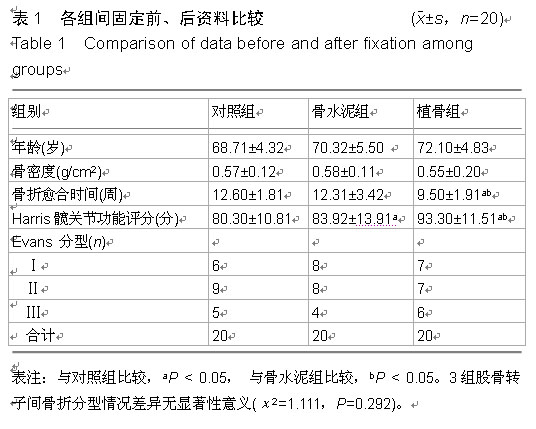
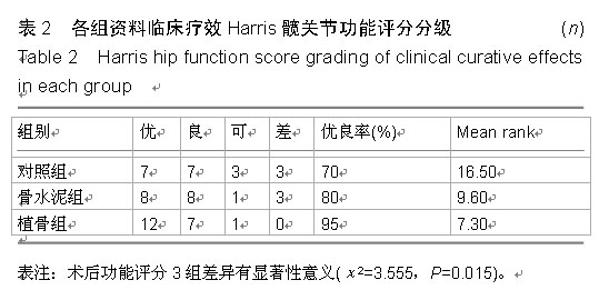
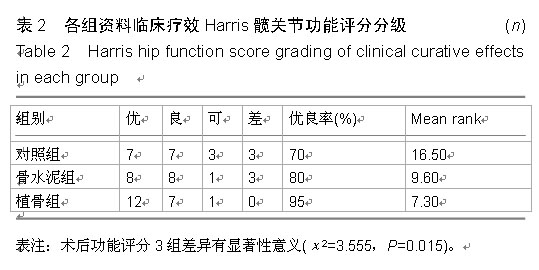
| [1] 刘云,陈爱琴,梁明娟,等.LPFP、DHS与PFNA治疗老年人股骨转子间骨折的研究[J]. 实用医学杂志,2012,28(24):4110-4112.
[2] 胡晒传.动力髋螺钉内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折68例体会[J].广东医学院学报,2011,29(13):57-58.
[3] Nurmi I, Narinen A, Lüthje P, et al. Cost analysis of hip fracture treatment among the elderly for the public health services: a 1-year prospective study in 106 consecutive patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123(10):551-554.
[4] 沈佳祚,练克俭,林达生,等.中空植骨式动力髋螺钉固定并促进股骨颈骨折愈合[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,12:1102-1106.
[5] 吴建伟,效淑莲.一种动力髋螺钉加植骨内固定治疗股骨转子间不稳定型骨折[J].中国临床研究,2013,5:457-458.
[6] 徐剑锋,王光华,胡海.动力髋螺钉内固定加植骨治疗股骨转子间骨折[J].中国现代医生,2008,16:142-143.
[7] Bahl S, Coates PS, Greenspan SL. The management of osteoporosis following hip fracture: have we improved our care? Osteoporosis Int. 2003;14(11):884-888.
[8] Eriksson F, Mattsson P, Larsson S.The effect of augmentation with resorbable or conventional bone cement on the holding strength for femoral neck fracture devices. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(5):302-310.
[9] Mattsson P, Alberts A, Dahlberg G, et al. Resorbable cement for the augmentation of internally-fixed unstable trochanteric fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(9):1203-1209.
[10] 章暐,邹剑,罗从风,等.股骨近端髓内钉与动力髋螺钉治疗老年股骨转子间及转子下骨折的比较研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,11: 12-15.
[11] 徐雍剑.抗旋转型股骨近端髓内钉与动力髋螺钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的比较研究[J].中医正骨,2013,6:20-23.
[12] 姚汉刚,余占洪,苏厂尧,等.髋动力螺钉与锁定钢板治疗不同年龄组股骨转子间骨折疗效比较[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012,603:420-423.
[13] 沈海敏,梁承伟,范永前,等.DHS、Gamma钉和PFN治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的临床研究[J].中国临床医学,2007,2:226-228.
[14] 黄笑鹏,龚龑,张洪涛,等.改良DHS手术治疗股骨转子间骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(30):1445-1448.
[15] Sadowski C, Lubbeke A, Saudan M. Treatment of reverse oblique and transverse interochanteric fractures with use of an intramedullary nail or 95 screw-plate. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:372.
[16] 杨傲飞,何承建,徐超敏.LCP与DHS内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的疗效对比[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂,2012,(27):680-682.
[17] 张小林,陈永华,陈小勇,等.锁定钢板和动力髋螺钉治疗股骨转子骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,6:684-686.
[18] 王华,管国平,杨业林,等.含锶羟基磷灰石骨水泥强化动力髋螺钉的极限载荷性能测试[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2011,1:5-7.
[19] Buciuto R, Hammer R. AB-plate versus sliding hip screws for unstable trochanteric hip fractures: stability of the fixation and modes of failure-radiographic analysis of 218 fractures. J Trauma. 2001;50:545.
[20] Verettas DA, Ifantidis P, Chatzipapas CN, et al. Systematic effects of surgical treatment of hip fractures: gliding screw-plating vs intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2010;41(3): 279-284.
[21] 黎宁,彭阿钦,柴仪,等.骨水泥强化正常骨质动力髋螺钉固定的生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,12:1299-1301.
[22] 曾秋涛,张普国,黄明光,等.DHS与骨水泥并用治疗伴有严重骨质疏松的股骨转子间骨折[J].广东医学,2001,5:415-416.
[23] 郑海,李祎,郭艳龙.骨水泥填塞动力髋螺钉主钉孔:抗弯曲和抗扭转强度[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,4:698-701.
[24] 佘远时,陈广祥,陈广东,等.可灌注骨水泥动力髋螺钉内固定修复骨质疏松股骨转子间骨折的优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(26):4158-4162.
[25] 张英泽,王庆贤,潘进社,等.微创动力髋螺钉(DHS)治疗老年股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,4:318-321.
[26] 赵海波,蔡翔宇,张峰.加压空心螺钉与动力髋螺钉治疗老年性股骨转子间骨折的疗效对比[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,16: 1221-1223.
[27] 田伟明,柴仪,彭阿钦,等.两孔与四孔动力髋螺钉固定股骨转子间骨折生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2006,5:571-576.
[28] 陈述伟,杨述华,杨超.老年人股骨转子骨折的特点及手术方法探讨[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(4):291
[29] 刘东,孙远新,李刚,等.骨水泥强化动力髋螺钉治疗高龄骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折[J].中国伤残医学,2014,7:39-40.
[30] Elder S. Biomechanical evaluation of calcium phosphate cement-augmented fixation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14(6):386-393.
[31] Yetkinler DN. Mechanical evaluation of a carbonated apatite cement in the fixation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 2002;73(2):157-164.
[32] Chandavarkar SM, Ram SM. A comparative evaluation of the effect of dentin desensitizers on the retention of complete cast metal crowns. Contemp Clin Dent. 2015;6(Suppl 1):S45-S50. [33] Nishizuka T, Kurahashi T, Hara T, et al. Novel intramedullary-fixation technique for long bone fragility fractures using bioresorbable materials. PLoS One. 2014; 9(8):e104603.
[34] Zou H, Ma X, Tang C, et al. Biomechanical study on a novel injectable calcium phosphate cement containing poly (latic-co-glycolic acid) in repairing tibial plateau fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(7): 855-859.
[35] Kainz H, Dall'Ara E, Antoni A, et al. Calcium phosphate cement augmentation after volar locking plating of distal radius fracture significantly increases stability. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(6):869-875.
[36] Thormann U, Ray S, Sommer U, et al. Bone formation induced by strontium modified calcium phosphate cement in critical-size metaphyseal fracture defects in ovariectomized rats. Biomaterials. 2013;34(34):8589-8598.
[37] Gupta N, Reddy UN, Vasundhar PL, et al. Effectiveness of desensitizing agents in relieving the pre- and postcementation sensitivity for full coverage restorations: a clinical evaluation. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2013;14(5):858-865. |