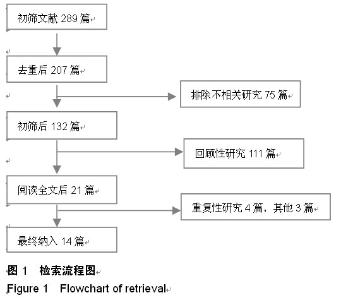
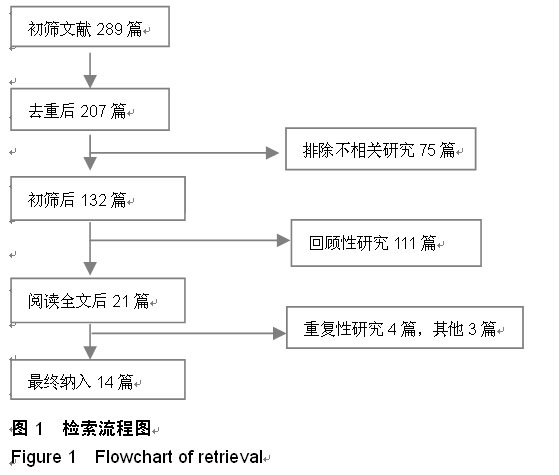
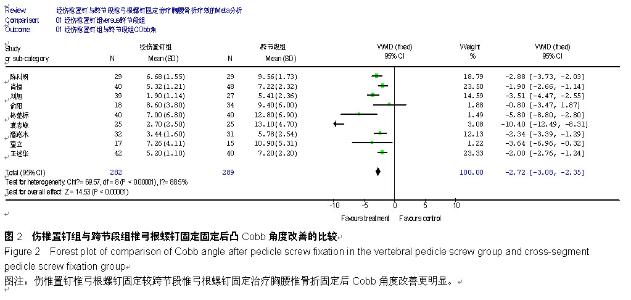
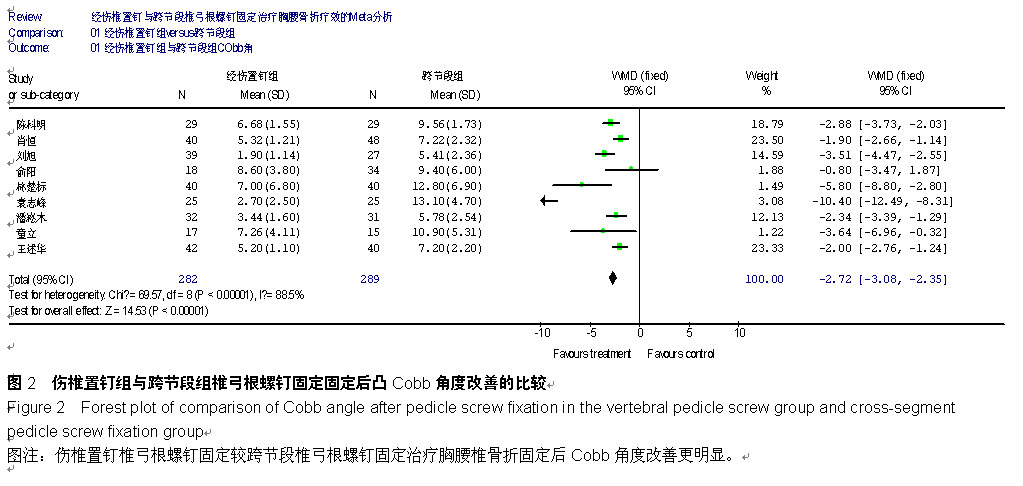
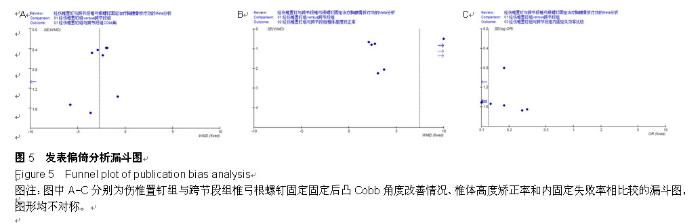
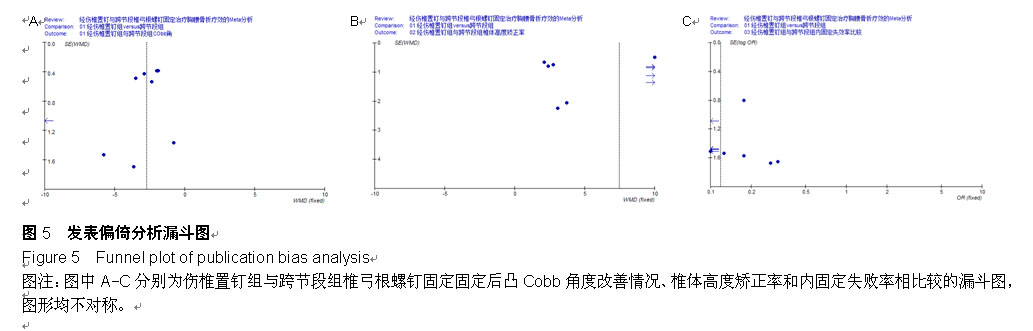
| [1] 何河北,白波,钱东阳,等.保留后交叉与不保留后交叉韧带人工膝关节置换术固定后效果的Meta分析[J/CD].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2013,7(1):33-37.
[2] 陈科明,白龙,陈亮清,等.应用伤椎置钉复位固定技术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(16):46-47.
[3] 肖恒伤椎置钉与跨节段椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的对比研究[J].现代医药卫生,2011,27(12):1819-1821.
[4] 刘旭.经伤椎置钉与跨伤椎内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效分析[J].新疆医科大学,2012.
[5] 俞阳,范海泉,陈铭,等.经伤椎和跨伤椎椎弓根钉棒系统内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(4):288-231.
[6] 林楚标,黄海安,叶育强,等.伤椎置钉与跨节段椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的比较研究[J].医学综述,2013,19(11):确良2077-2079.
[7] 袁志峰,邵斌,曾景平,等.经伤椎置钉治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床运用及疗效分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(1):32-35.
[8] 潘崧木.经伤椎置钉治疗胸腰椎骨折的应用研究[J].南宁:广西医科大学,2014.
[9] 童立,王弘,王辉,等.胸腰椎骨折经伤椎置钉与跨伤椎内固定的临床研究[J].临床医学工程,2014,21(3):300-302.
[10] 王述华,邓经德,刘立斌,等.胸腰椎骨折伤椎置钉固定的疗效观察[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(6):652-654.
[11] 王军,王乾坤,周宪华,等.后路AF内固定系统同时经伤椎置钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].河南大学学报(医学版),2009,29(3):200-202.
[12] 彭放兵.经伤椎置钉技术治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效分析[J].中外医学研究,2013,11(2):139-140.
[13] 李占良,马兴科.经伤推置钉与跨节段推弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰推骨折的疗效比较[C].第三届全国脊损伤治疗与康复研讨会,2012, 185-187.
[14] 谭家昌,徐鸿育,杨有猛,等.伤椎置钉与跨节段椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(14): 1094-1096.
[15] 刘丹.胸腰椎骨折经伤椎置钉椎弓根钉系统内固定术[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(19):20-21.
[16] Singh K, Vaccaro AR, Eichenbaum MD, et al. The surgical management of thoracolumbar injuries. J Spinal Cord Med. 2004;27(2):95-101.
[17] Carl AL, Tranmer BI, Sachs BL. Anterolateral dynamized instrumentation and fusion for unstable thoracolunmbar and lumbar burst fractures. Spine. 1997;22(6):686-690.
[18] Yue JJ, Sossan A, Selgrath C, et al. The treatment of unstablethoracic spine fractures with transpedicuar screw instrumentation: a 3-year consecutive series. Spine (Phila Pa 1976),2002,27(24):2782-2787.
[19] Anekstein Y, Brosh T, Mirovsky Y. Intermediate screws in short segment pedicular fixation for thoracic and lumbar fractures: a biomechanical study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(1):72.
[20] 程坚,陶波,孙成群,等.后路经伤椎置钉短节段固定联合后外侧植骨融合治疗胸腰段骨折的临床观察[J].现代实用医学,2012,24(11): 1222-1223.
[21] 何少奇,林立兴,戴鸣海,等.后路经伤椎置钉短节段复位固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(1):40-43.
[22] 丁源.后路经伤椎置钉内固定融合治疗胸腰椎骨折脱位15例[J].广西医学,2011,33(1):384-385.
[23] Meng H, Gao Y, Li M, et al. Posterior atlantoaxial dislocation complicating odontoid fracture without neurologic deficit: a case report and review of the literature. Skeletal Radiol. 2014; 43: 1001-1006.
[24] Shen WJ, Liu TJ, Shen YS. Nonoperative treatment versus posteriorfixation for thoracolumbar junction burst fractureswithout neurologic deficit. Spine. 2001;26(9):1038.
[25] 陈德纯,来津,谭俊铭,等.伤椎椎弓根长螺钉在治疗胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013,34(1):46-49.
[26] 杨文彬,韦国平,黄锐,等.伤椎置钉椎弓根钉棒系统治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国医药导刊,2013,15(4):640-641.
[27] 向乾彬,范海泉,黄海讯,等.伤椎置钉治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2012,33(2):111-113.
[28] 昌耘冰,范志丹,夏虹,等.应用伤椎置钉技术治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学研究与临床应用[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(3): 347-350.
[29] 潘兵,张志敬,宋舟锋,等.胸腰椎骨折伤椎短椎弓根钉固定的生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(4):368-372.
[30] 冯鹏,马虎升.伤椎椎体置椎弓根螺钉单节段固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2014,22(5):36-38.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
|