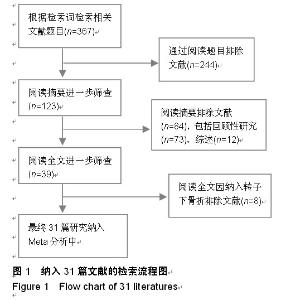
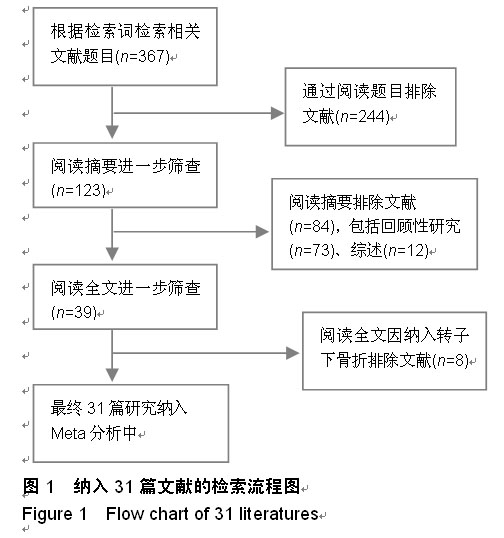
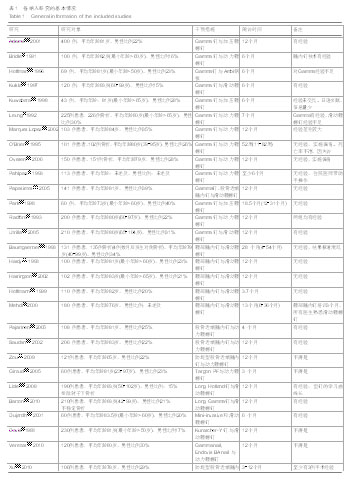
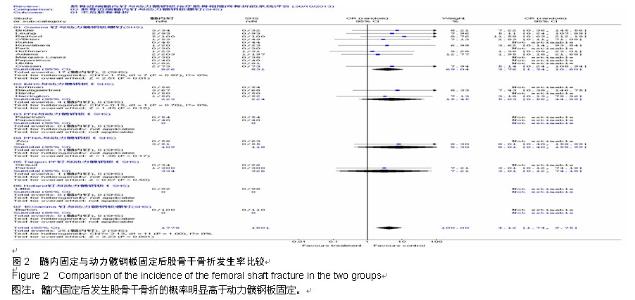
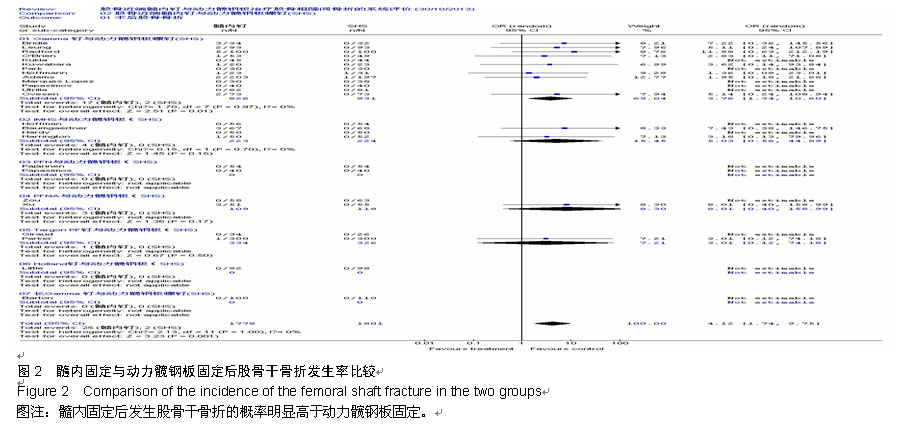
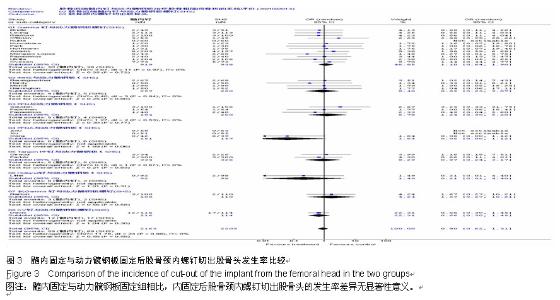
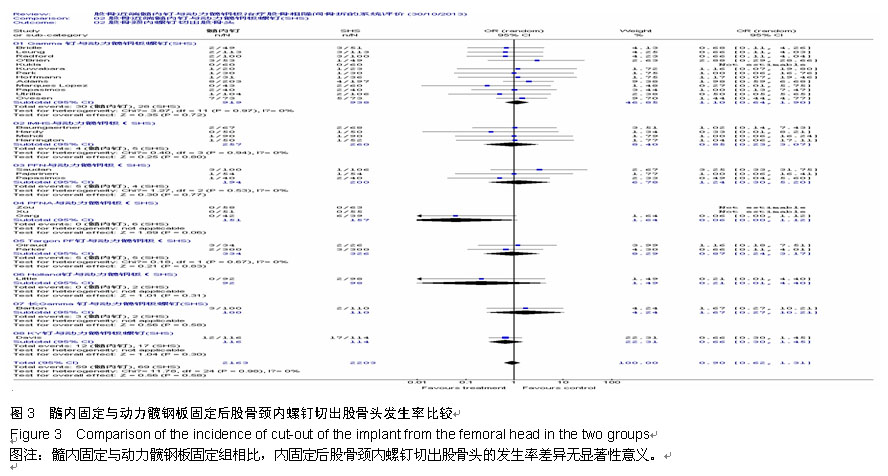
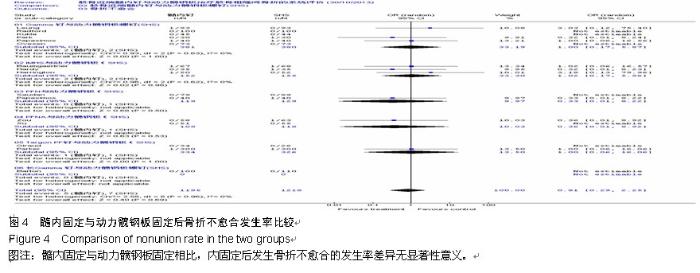
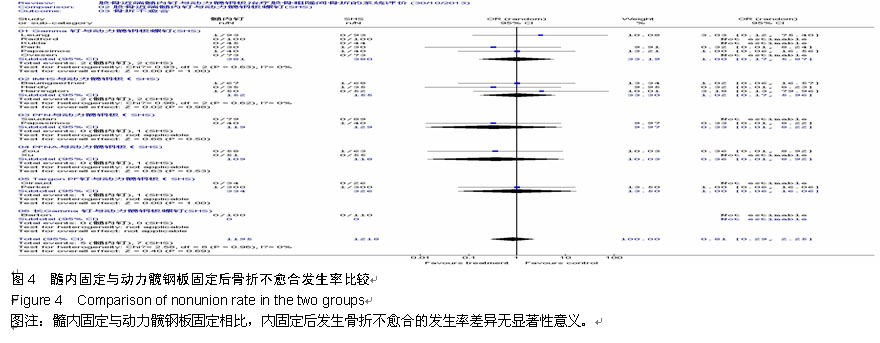
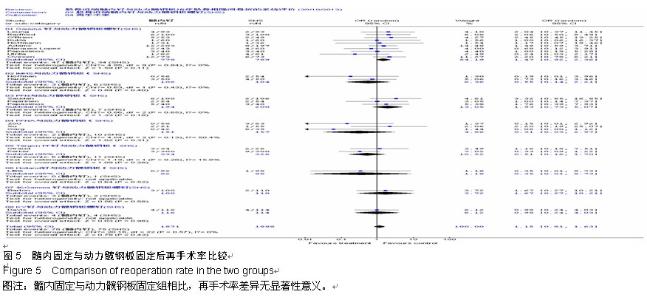
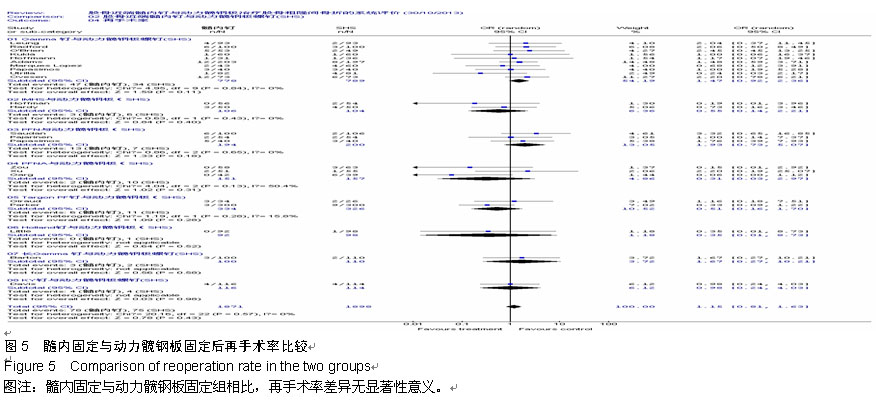
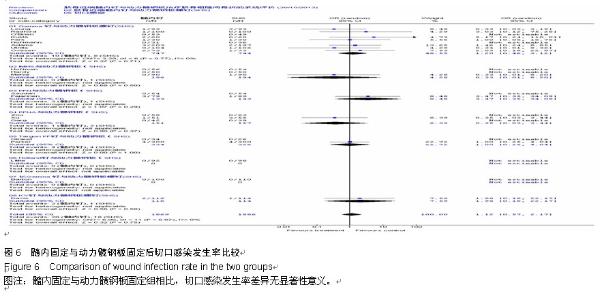
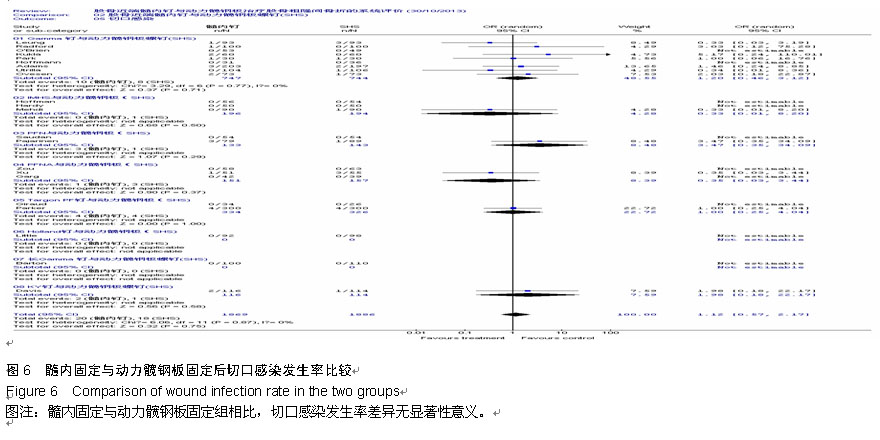
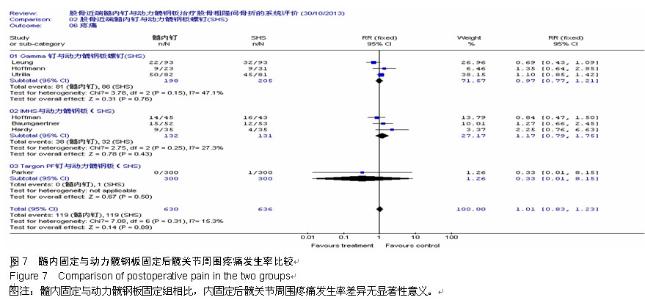
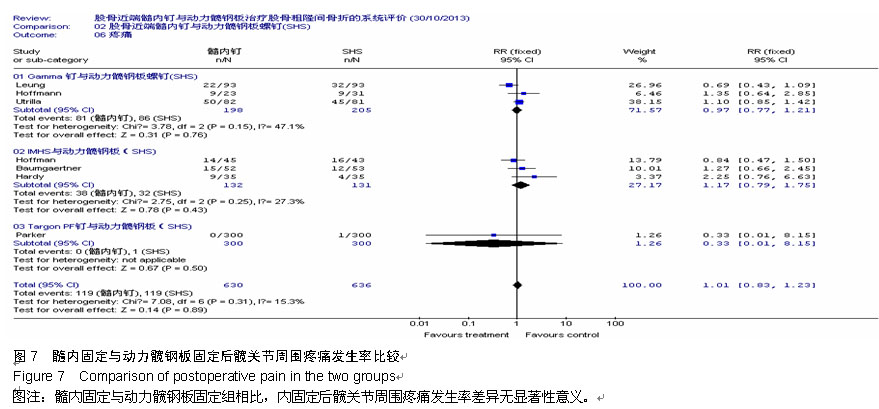
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (22): 3595-3603.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.22.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
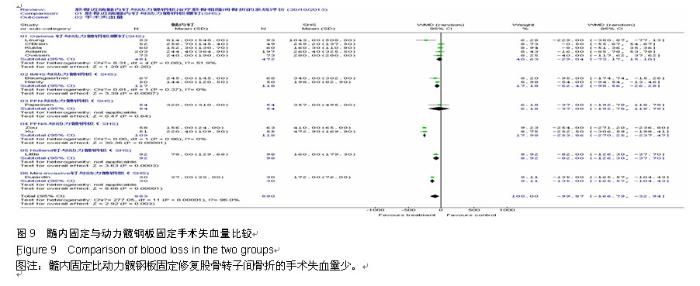
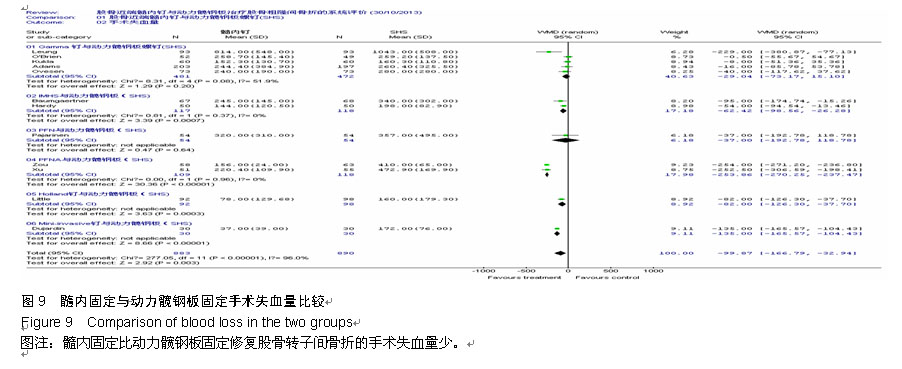
Systematic review of dynamic hip plate and proximal femoral intramedullary nail fixation for intertrochanteric fracture in adults
Zhai Sheng, Lv Qing
- Department of Orthopedics, the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China)
-
Received:2015-03-13Online:2015-05-28Published:2015-05-28
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhai Sheng, Lv Qing. Systematic review of dynamic hip plate and proximal femoral intramedullary nail fixation for intertrochanteric fracture in adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(22): 3595-3603.
share this article
| [1] Kannus P, Oarkkari J, Sievänen H, et al. Epidemiology of hip fractures. Bone. 1996;18 (Suppl 1):57-63. [2] Parker MJ, Handoll HH. Gamma and other cephalocondylic intramedullary nails versus extramedullary implants for extracapsular hip fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;16: CD000093. [3] Bhandari M, Schemitsch E. Gamma Nails Revisited: Gamma Nails Versus Compression Hip Screws in the Management of Intertrochanteric Fractures of the Hip: A Meta-Analysis.J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6):460-464. [4] Davis TR, Sher JL, Checketts RG, et al. Intertrochanteric fractures of the femur: a prospective study comparing the use of the Kuntscher-Y nail and a sliding hip screw. Injury. 1988; 19(6):421-426. [5] Bridle SH, Patel AD, Bircher M, et al. Fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur: a randomised prospective comparison of the gamma nail and the dynamic hip screw. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 1991;73:330-334. [6] Leung KS, So WS, Shen WY, et al. Gamma nails and dynamic hip screws for peritrochanteric fractures. A randomised prospective study in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 1992;74(3):345-351. [7] Pahlplatz PVM, Langius FB. Comparing the Gamma nail and the Dynamic Hip Screw in the treatment of pertrochanteric fractures. Preliminary results of a prospective randomised study. Oper Tech Compl. 1993;2:475-480. [8] Radford PJ, Needoff M, Webb JK. A prospective randomised comparison of the dynamic hip screw and the gamma locking nail. J Bone Joint Surg(Br).1993;75(5):789-793. [9] O'Brien PJ, Meek RN, Blachut PA, et al. Fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures: Gamma nail versus dynamic hip screw. A randomised, prospective study. Can J Surg. 1995; 38(6):516-520. [10] Hoffman CW, Lynskey TG. Intertrochanteric fractures of the femur: a randomized prospective comparision of the Gamma nail and the Ambi hip screw. New Zealand J Surg. 1996;66(3): 151-155. [11] Kukla C, Heinz T, Berger G, et al. Gamma nail vs. Dynamic Hip Screw in 120 patients over 60 years - a randomized trial. Acta Chirurgica Austriaca. 1997;29(5):290-293. [12] Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM. Intramedullary versus extramedullary fixation for the treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 348:87-94. [13] Hardy DC, Descamps P, Krallis P, et al. Use of an intramedullary hip-screw compared with a compression hip-screw with a plate for intertrochanteric femoral fractures. A prospective, randomized study of one hundred patients. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1998;80(5):618-630. [14] Kuwabara H, Wada T, Minagi Y, et al. Compression hip screw and gamma nail for intertrochanteric fractures - Randomized prospective study. Hokkaido J Orthop Traumatol. 1998;40(2): 29-33. [15] Park SR, Kang JS, Kim HS, et al. Treatment of intertrochanteric fracture with the Gamma AP locking nail or by a compression hip screw - a randomised prospective trial. Int Orthop. 1998; 22(3): 157-160. [16] Hoffmann R, Schmidmaier G, Schulz R, et al. Classic nail versus DHS. A prospective randomised study of fixation of trochanteric femur fractures. Unfallchirurg. 1999;102: 182-190. [17] Mehdi SA, Kinninmonth AWG, MacLeod C, et al. Extracapsular hip fracture fixation: a prospective randomised comparison of the intramedullary hip screw with the sliding hip screw [Abstract]. Injury. 2000;31:287. [18] Adams CI, Robinson CM, Court-Brown C, et al. Prospective randomised controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus dynamic hip screw and plate for intertrochanteric fractured femur. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(6):394-400. [19] Dujardin FH, Benez C, Polle G, et al. Prospective randomized comparison between a dynamic hip screw and a mini-invasive statis nail in fractures of the trochanateric area: preliminary results. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(6):401-406. [20] Harrington P, Nihal A, Singhania AK, et al. Intramedullary hip screw versus sliding hip screw for unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures in the elderly. Injury. 2002;33(1):23-28. [21] Marques Lopez F, Pelfort Lopez X, Garcia Casas O, et al. Prospective, comparative, randomized study of the sliding screw and Gamma nail in the treatment of pertrochanteric fractures. Revista Ortoped Traumatol. 2002;46(6):505-509. [22] Saudan M, Lubbeke A, Sadowski C, et al. Pertrochanteric fractures: is there an advantage to an intramedullary nail? A randomized, prospective study of 206 patients comparing the dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(6):386-393. [23] Giraud B, Dehoux E, Jovenin N, et al. Pertrochanteric fractures: a randomized prospective study comparing dynamic screw plate and intramedullary fixation. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2005;91 (8):732-736. [24] Papasimos S, Koutsojannis CM, Panagopoulos A, et al. A randomised comparison of AMBI, TGN and PFN for treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(7):462-468. [25] Pajarinen J, Lindahl J, Michelsson O, et al. Pertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with a dynamic hip screw or a proximal femoral nail; a randomised study comparing postoperative rehabilitation. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2005;87(1):76–81. [26] Utrilla AL, Reig JS, Munoz FM, et al. Trochanteric gamma nailand compression hip screw for trochanteric fractures: a randomized,prospective, comparative study in 210 elderly patients with a new design of the gamma nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19:229-233. [27] Ovesen O, Andersen M, Poulsen T, et al. The trochanteric gamma nail versus the dynamic hip screw: a prospective randomised study. One-year follow-up of 146 intertrochanteric fractures. Hip Int. 2006;16(4):293-298. [28] Little NJ, Verma V, Fernando C, et al. A prospective trial comparing the Holland nail with the dynamic hip screw in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2008;90(8):1073-1078. [29] Zou J, Xu Y, Yang H. A comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw devices in trochanteric fractures. J Int Med Res. 2009;37(4): 1057-1064. [30] Barton TM, Gleeson R, Topliss C, et al. A comparison of the long Gamma nail with the sliding hip screw for the treatment of AO/OTA 31-A2 fractures of the proximal part of the femur; a prospective randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 2010; 92(4):792-798. [31] Xu YZ, Geng DC, Mao HQ, et al. A comparison of the proximal femoral nail antirotation device and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fracture. J Int Med Res. 2010;38: 1266-1275. [32] Verettas DA, Ifantidis P, Chatzipapas CN, et al. Systematic effects of surgical treatment on hip fractures: Gliding screw-plating vs intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2010;41(3): 279-284. [33] Garg B, Marimuthu K, Kumar V, et al. Outcome of short proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw for fixation of unstable trochanteric fractures. A randomized prospective comparative trial. Hip Int. 2011;21:531-536. [34] Parker MJ, Bowers TR, Pryor GA. Sliding hip screw versus the Targon PF nail in the treatment of trochanteric fractures of the hip: a randomised trial of 600 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2012;94(3):391-397. 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
|
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||