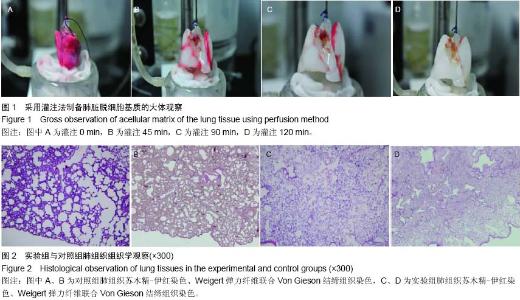
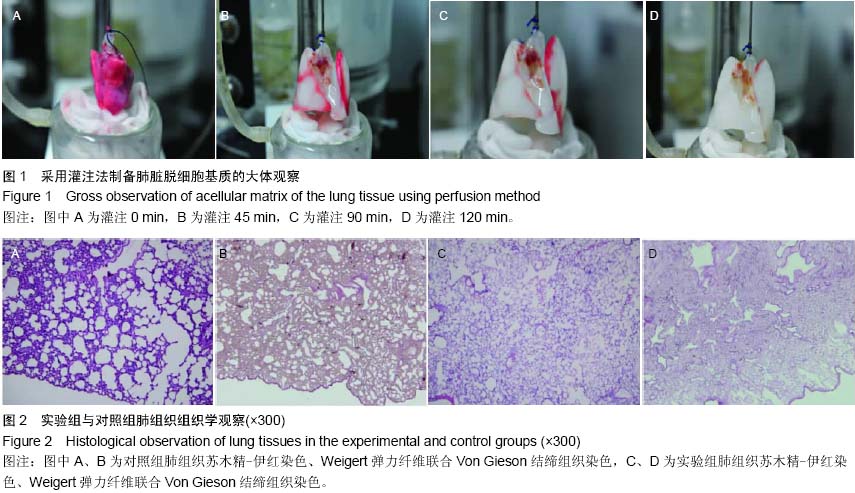
| [1] 黑飞龙,周建业,罗富良,等.灌注法大鼠全肺脏脱细胞基质支架的建立[J].北京生物医学工程,2013,32(1):17-21.
[2] 黄惠民,马良龙,任宏,等.骨髓间质干细胞和脱细胞基质构建组织工程血管的动物实验[J].中华医学杂志,2007,87(48): 3440-3442.
[3] 马良龙,黄惠民,李建华,等.新法制备动脉脱细胞基质的实验研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2009,30(7):468-471.
[4] 徐小雄,段亮,姜格宁,等.激光微孔气管脱细胞基质的制备及对软骨细胞生长的影响[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2012,28(11): 668-669,689.
[5] 张晨,王者生,高景恒,等.软骨脱细胞基质生物性的实验研究[J].实用美容整形外科杂志,2003,14(2):59-61.
[6] Jordan SW,Khavanin N,Fine NA,et al.An Algorithmic Approach for Selective Acellular Dermal Matrix Use in Immediate Two-Stage Breast Reconstruction: Indications and Outcomes.Plast Reconstr Surg.2014;134(2):178-188.
[7] Lopez J,Prifogle E,Nyame TT,et al.The impact of conflicts of interest in plastic surgery: an analysis of acellular dermal matrix, implant-based breast reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg.2014;133(6):1328-1334.
[8] 马良龙,张泽伟,李建华,等.异种血管脱细胞基质的制备[C].//2006年浙江省医学会胸心外科学年会论文汇编.2006.
[9] 董建德,张建,谷涌泉,等.脱细胞基质在血管组织工程中的应用[J].中国肺癌杂志,2009,12(2):152-155.
[10] 王颖楠,赵敏,徐惠成,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与脱细胞基质构建组织工程材料的研究进展[J].现代实用医学,2014,26(8): 1054-1056.
[11] 徐方杰,郑悦,高尚志,等.心脏瓣膜组织工程中理想种植细胞的来源比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(20): 3869-3872.
[12] 宋永周,崔慧先,王振显,等.羊膜脱细胞基质的制备及其生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(1):51-55.
[13] Mestak O,Matouskova E,Spurkova Z,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells seeded on cross-linked and noncross-linked acellular porcine dermal scaffolds for long-term full-thickness hernia repair in a small animal model.Artif Organs. 2014;38(7): 572-579.
[14] Kajbafzadeh AM,Masoumi A,Hosseini M,et al.Sheep colon acellular matrix: Immunohistologic, biomechanical, scanning electron microscopic evaluation and collagen quantification.J Biosci Bioeng.2014;117(2):236-241.
[15] 张晨,景士兵,杨琨,等.软骨脱细胞基质支架材料的软骨组织工程实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(7):846-850.
[16] 郭铁芳,杨大平,韩雪峰,等.脱细胞基质与血管内皮细胞体外相容性的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2003,17(2):165-168.
[17] Terry MJ,Sue GR,Goldberg C,et al.Hueston revisited: use of acellular dermal matrix following fasciectomy for the treatment of Dupuytren's disease.Ann Plast Surg. 2014;73 Suppl 2: S178-180.
[18] 吕玉明,黄华梅,王秋玲,等.应用猪主动脉脱细胞基质制备新型组织工程血管支架:生物相容性及力学性能评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(47):8921-8926.
[19] 傅强,邓晨亮,殷德明,等.脱细胞基质载体和表皮细胞结合构建尿道的实验研究[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2006,27(z1):128-130.
[20] Urakami S,Shiina H,Enokida H,et al.Functional improvement in spinal cord injury-induced neurogenic bladder by bladder augmentation using bladder acellular matrix graft in the rat. World J Urol.2007;25(2):207-213.
[21] 杨强,彭江,卢世璧,等.软骨脱细胞基质多孔支架与骨髓基质干细胞体外构建组织工程软骨的研究[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(17): 1161-1166.
[22] 马辉,杨大平,郝晨光,等.利用脱细胞基质预构小口径组织工程血管的实验研究[J].中华整形外科杂志,2008,24(4):297-299.
[23] Callanan A,Davis NF,McGloughlinTM,et al.Development of a rotational cell-seeding system for tubularized extracellular matrix (ECM) scaffolds in vascular surgery.J Biomedical Materials Research, Part B. Applied Biomaterials 2014; 102B(4): 781-788.
[24] Baiguera S,Del Gaudio C,Lucatelli E,et al.Electrospun gelatin scaffolds incorporating rat decellularized brain extracellular matrix for neural tissue engineerin.Biomaterials.2014;35(4): 1205-1214.
[25] Levorson EJ,Mountziaris PM,Hu O,et al.Cell-derived polymer/extracellular matrix composite scaffolds for cartilage regeneration, part 1: Investigation of cocultures and seeding densities for improved extracellular matrix deposition.Tissue Eng C Methods.2014;20(4):340-357.
[26] 朱海波,张倩,王秀丽,等.人肺癌H460细胞在脱细胞化鼠肺基质支架中的生长[J].肿瘤研究与临床,2014,26(11):725-728.
[27] 刘春晓,刘思然,徐啊白,等.灌注法制备大鼠全肾脏脱细胞基质的研究[J].南方医科大学学报,2009,29(5):979-982.
[28] Agarwal JP,Mendenhall SD,Anderson LA,et al.The breast reconstruction evaluation of acellular dermal matrix as a sling trial (BREASTrial): design and methods of a prospective randomized trial.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(1):20e-28e.
[29] 刘春晓,陈捷,郑少波,等.灌注法制备大鼠全肾脏脱细胞基质支架的细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(38): 7464-7468.
[30] 戴开宇,伊旭东,赵丽娜,等.脱细胞鼠肾生物支架的制备及其体内相容性[J].温州医科大学学报,2014,44(9):641-645.
[31] 刘思然.灌注法制备大鼠及家兔全肾脏脱细胞基质的研究[D].南方医科大学,2009.
[32] 陈捷.灌注法制备大鼠全肾脏脱细胞基质的细胞相容性研究[D].南方医科大学,2010.
[33] 王磊,许宏,王珏,等.肾脏脱细胞基质结构功能重建的初步研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(6):1038-1044.
[34] 彭蒙蒙,林贤丰,邵培刚,等.灌注法制备离体大鼠心脏脱细胞基质[J].解剖学报,2012,43(4):559-563. |