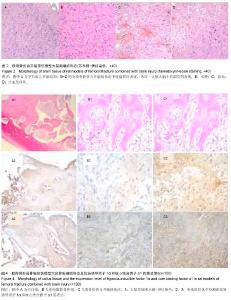
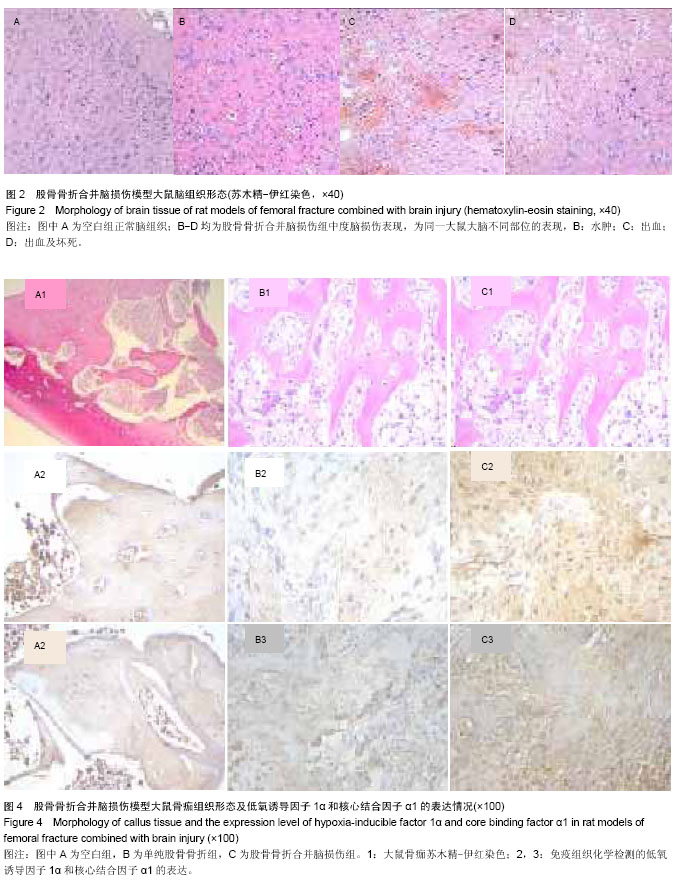
| [1] 罗涛,邓廉夫.低氧诱导因子-1在骨折愈合过程中的调控作用[J].国外医学骨科学分册,2005,26(4):240-242.
[2] 刘志奎,张柳,姜晓华,等.脑损伤对骨折愈合中血管内皮生长因子表达的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2009,15(3):233-235.
[3] 李建华,李建民.HIF-1α 在脑损伤中的作用及其机制的研究进展[J].滨州医学院学报,2009,32(5):367-369, 373.
[4] 刘晓东,邓廉夫,王君,等.低氧诱导因子1α对成骨细胞功能的调控作用[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2007,27(3):298-302.
[5] Li C, Mori S, Li J, et al. Long-term effect of incadronate disodium (YM-175)on fracture healing of femoral shaft in growing rats. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(3):429-436.
[6] Marmarou A, Montasser A, Foda A, et al. A new model of diffuse brain injury in rats. J Neuronal. 1994;296:654-673.
[7] Goldberg VM, Powell A, Shaffer JW, et al. Bone grafting: role of histocompatibility in transplantation. Orthop Res. 1985;3(4): 389-404.
[8] Mavrofrydi O, Papazafiri P. Hypoxia-inducible factor-lα increase is an early and sensitive marker of lung cells responding to benzo[a]pyrene. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2012;31(4):335-347.
[9] Chen YR, Dai AG, Hu RC, et al. The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and its hydroxylases in pulmonary arteries of patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012;28(3):234-238.
[10] Kelley MR, Parsons SH. Redox regulation of the DNA repair function of the human AP endonuclease Ape1/ref-1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2001;3(4):671-683.
[11] 刘振东,高敏伟,钟杰林,等.2型糖尿病大鼠骨髓腔内过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ和核心结合因子α1 mRNA表达与骨折的愈合[J].中国组织工程研究与临床,2009,13(15):2891-2895.
[12] Dai Z, Guo F, Wu F, et al. Integrin αvβ3 mediates the synergetic regulation of core-binding factor α1 transcriptional activity by gravity and insulin-like growth factor-1 through phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Bone. 2014;69(12):126-132.
[13] Hong YY, Yu FY, Qu JF, et al. Fibroblasts regulate variable aggressiveness of syndromic keratocystic and non-syndromic odontogenic tumors. J Dent Res. 2014;93(9):904-910.
[14] Duan X, Xu H, Wang Y, et al. Expression of core-binding factor α1 and osteocalcin in fluoride-treated fibroblasts and osteoblasts. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2014;28(3):278-283.
[15] Houser J, Komarek J, Kostlanova N, et al. A soluble fucose-specific lectin from Aspergillus fumigatus conidia-- structure, specificity and possible role in fungal pathogenicity. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e83077.
[16] Pei Z,Zhang F, Niu Z, et al. Effect of icariin on cell proliferation and the expression of bone resorption/formation-related markers in human periodontal ligament cells. Mol Med Rep. 2013;8(5):1499-1504.
[17] Takarada T, Hinoi E, Nakazato R, et al. An analysis of skeletal development in osteoblast-specific and chondrocyte-specific runt-related transcriptionfactor-2 (Runx2) knockout mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(10):2064-2069.
[18] Boes M, Kain M, Kakar S, et al. Osteogenic effects of traumatic braininjury on experiment fracture-healing. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88(4):738-743.
[19] Ostrowski RP, Colohan AR, Zhang JH. Mechanisms of hyperbaric oxygen induced neuroprotect ion in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005; 25(5):554.
[20] Gerber HP, Condoreeli F, Park J, et al. Differential transcriptional regulation of the two vascular endothelial growthfactor receptor genes. Fit-J.butnot T FIk-1/KDR, is upregulated by hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(38):23659-23667.
[21] Bergeron M, Gidday JM, Yu AY, et al. Role of hypoxia inducible factor in hypoxia-induced ischemic tolerance in neonatal rat brain. Ann Neurol. 2000;48(3):285.
[22] Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, et al. Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by directlyst imulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biolchem. 2005;280(39): 33132-33140.
[23] Jones NM, Lee EM, Brown TCS, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning produces differential expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-lalpha (HTF-lalpha) and its regulatory enzyme HTF poly 1 hydroxylase 2 in neonatal rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 2006;404 (1-2): 72-77.
[24] 邓廉夫,冯伟,张玥,等.诱导成纤维细胞表达核结合因子的研究[J].中华外科杂志,2002,40(8):35-38.
[25] 张劲娥,王淑红,张忻,等.低氧诱导因子1α慢病毒载体转染骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨基因表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(1):57-62.
[26] 戚金威,程景林,周姝,等.低氧诱导因子1α高表达对急性心肌梗死大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的动员[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(10):1579-1584.
[27] 惠春影,肖洪艳,何欣玲,等.低氧诱导因子1α基因三点突变体体外转染骨髓间充质干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(19): 2953-2960.
[28] Chen Y, Zhu HB, Liao J, et al. Regulation of naotai recipe on the expression of HIF-lα/VEGF signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi. 2014; 34(10):1225-1230.
[29] Huang H, Yu J, Yu D, et al. Effects of chemically induced hypoxia on in vitro expression of hypoxia inducible factor-lα, vascular endothelial growth factor, aggrecanase-1, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 in rat mandibular condylar chondrocytes. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2014;28(3):269-276.
[30] Chai DM, Bao ZQ, Hu JG, et al. Vasculogenic mimicry and aberrant expression of HIF-lα/E-cad are associated with worse prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013;33(3):385-391. |