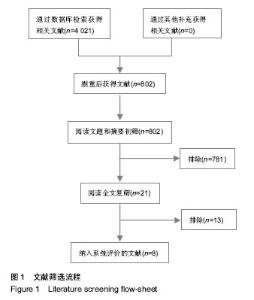
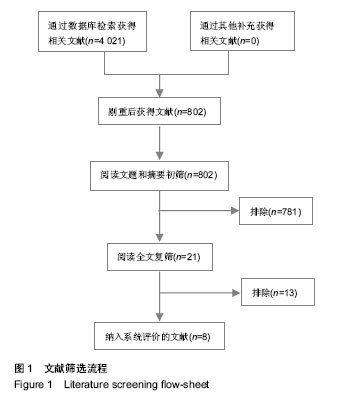
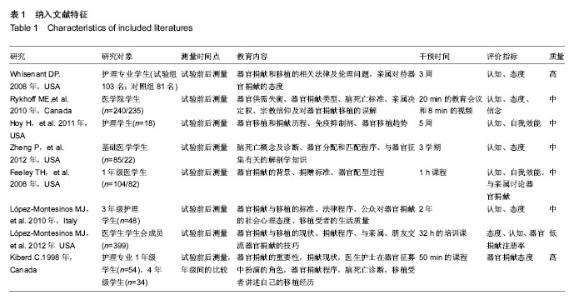
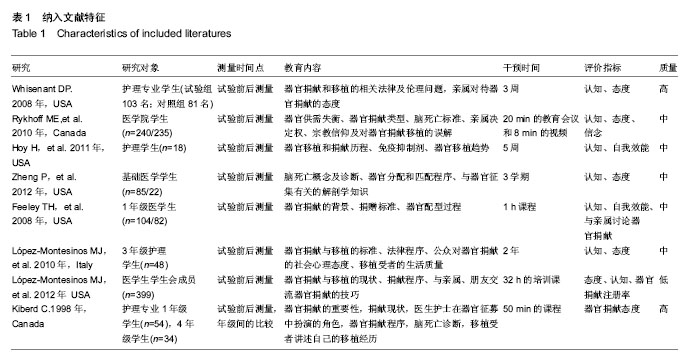
| [1] 韩咏,石炳毅,徐燕杰.国内外器官移植的研究比较[J].医学与哲学:临床决策论坛版,2006,27(11):60-63.
[2] http://www.unos.org/,2014-09-12
[3] 石晶晶. 器官移植立法完善的实证研究[D].沈阳师范大学,2012.
[4] 张雪文,李官彦,李臻,等.在校医学生器官移植与捐献态度及认知的调查[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,53(16):10067-10070.
[5] 唐晓,肖晓,曹冬雷,等. 医学与非医学大学生对遗体捐献认知的比较研究[J].医学与哲学,2012,33(8A):25-27.
[6] Mekahli D,Liutkus A,Fargue S,et al.Survey of first-year medical students to assess their knowledge and attitudes toward organ transplantation and donation.Transplant Proc. 2009;41(2):634-638.
[7] Wale J,Arthur A,Faull C.An analysis of knowledge and attitudes of hospice staff towards organ and tissue donation.BMJ Support Palliat Care.2014;4(1):98-103.
[8] Figueroa CA,Mesfum ET,Acton NT,et al.Medical students' knowledge and attitudes toward organ donation: results of a Dutch survey.Transplant Proc.2013;45(6):2093-2097.
[9] Silva A.Preparation of student nurses to approach the theme of death and organ donation.Revista Enfermagem.2007; 15(4):201-206.
[10] Symvoulakis EK,Rachiotis G,Papagiannis D,et al.Organ donation knowledge and attitudes among health science students in Greece: emerging interprofessional needs.Int J Med Sci.2014;11(6):634-640.
[11] Whisenant DP,Woodring B.Improving attitudes and knowledge toward organ donation among nursing students.Int J Nurs Educ Scholarsh.2012;9:22.
[12] Moher D,Liberati A.Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis : The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med.2009;6:e1000097
[13] Gilbody S, Whitty P, Grimshaw J,et al.Educational and organizational interventions to improve the management of depression in primary care: a systematic review. JAMA. 2003; 289:694-696
[14] Campbell M,Fitzpatrick R,Haines A,et al.Framework for design and evaluation of complex intervention to improve health.BMJ.2000;321(7262):694-696.
[15] 胡雁.循证护理学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.
[16] Atkins D,Briss PA,Eccles M,et al.Systems for grading the quality of evi-dence and the strength of recommendations II: Pilot study of a new system.BMC Health Serv Res.2005; 5(1): 25.
[17] Whisenant DP.Improving Nursing Students Knowledge and Attitudes toward Organ Donation and Transplantation: A Randomized Intervention.Touro University International,2008.
[18] Feeley TH,Tamburlin J,Vincent DE.An educational intervention on organ and tissue donation for first-year medical students.Prog Transplant. 2008;18(2):103-188.
[19] Zheng P,Sammann A,Qiu M,et al.Impact of preclinical exposure to organ donation on knowledge and attitudes of medical students.Prog Transplant. 2012;22(1):79-85,109.
[20] D'Alessandro AM,Peltier JW,Dahl AJ.Use of social media and college student organizations to increase support for organ donation and advocacy: a case report.Prog Transplant. 2012; 22(4):436-441.
[21] Hoy H, Alexander S, Frith KH.Effect of transplant education on nurses' attitudes toward organ donation and plans to work with transplant patients.Prog Transplant. 2011;21(4):317-321.
[22] Rykhoff ME, Coupland C, Dionne J,et al.A clinical group's attempt to raise awareness of organ and tissue donation.Prog Transplant.2010;20(1):33-39.
[23] López-Montesinos MJ,Manzanera Saura JT,Mikla M,et al.Organ donation and transplantation training for future professional nurses as a health and social awareness policy. Transplant Proc.2010;42(1):239-242.
[24] Kiberd C.Curriculum effect on nursing students' attitudes and knowledge towards organ donation and transplantation.ANNA J.1998;25(2):210-216.
[25] Umesh Yamanappa R,Akash G.Impact of an Educational Intervention on Increasing the Knowledge and Changing the Attitude and Beliefs towards Organ Donation among Medical Students.J Clin Diag Res.2014;8(5):JC05-JC07.
[26] 刘畅,刘世庆,刘宝林,等.医学新生对尸体器官捐献的态度及其影响因素分析[J].中国医学伦理学,2013,26(5):559-561.
[27] Mekahli D,Liutkus A,Fargue S,et al.Survey of First-Year Medical Students to Assess Their Knowledge and Attitudes Toward Organ Transplantation and Donation. Transplant Proc.2009;41(2):634-638.
[28] 尹志科.器官捐献动机的质性研究[D].中南大学,2012.
[29] Cantarovich M,Birk P,Ekbeg H,et al.First global forum education on organ donation and transplantation for schools.Pediatr Transplant.2013;17(1):12-18.
[30] Li AH,Rosenblum AM, Nevis IF,et al.Adolescent classroom education on knowledge and attitudes about deceased organ donation: A systematic review.Pediatr Transplant. 2013; 17(2):119-128. |