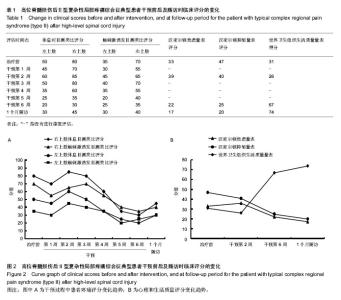
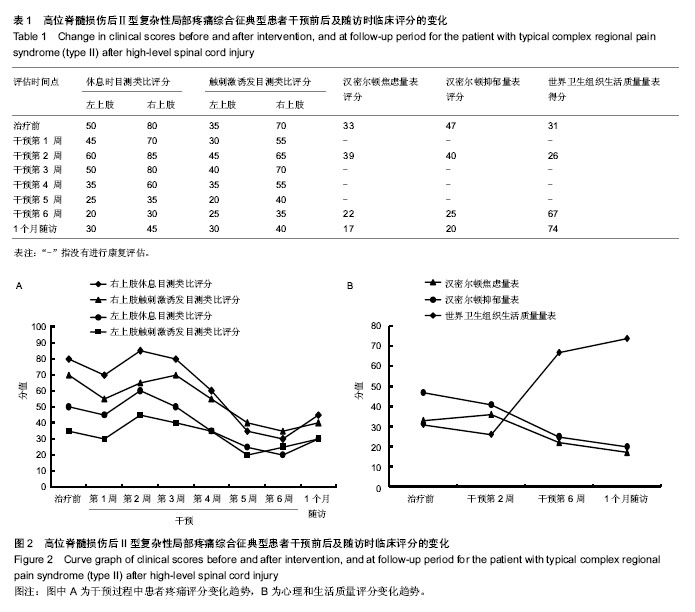
| [1] Watson CP, Mackinnon SE, Dostrovsky JO, et al. Nerve resection, crush and re-location relieve complex regional pain syndrome type II: a case report. Pain. 2014;155(6):1168- 1173.
[2] Borchers AT, Gershwin ME. Complex regional pain syndrome: a comprehensive and critical review. Autoimmun Rev. 2014; 13(3):242-265.
[3] Bultitude JH, Rafal RD. Derangement of body representation in complex regional pain syndrome: report of a case treated with mirror and prisms. Exp Brain Res. 2010;204(3):409-418.
[4] Carroll I, Curtin CM. Management of chronic pain following nerve injuries/CRPS type II. Hand Clin. 2013;29(3):401-408.
[5] McCabe CS, Haigh RC, Blake DR. Mirror visual feedback for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome (type 1). Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2008;12(2):103-107.
[6] Moseley GL. Graded motor imagery is effective for long-standing complex regional pain syndrome: a randomised controlled trial. Pain. 2004;108(1-2):192-198.
[7] Karmarkar A, Lieberman I. Mirror box therapy for complex regional pain syndrome. Anaesthesia. 2006;61(4):412-413.
[8] Foell J, Bekrater-Bodmann R, Diers M, et al. Mirror therapy for phantom limb pain: brain changes and the role of body representation. Eur J Pain. 2014;18(5):729-739.
[9] Hasanzadeh Kiabi F, Habibi MR, Soleimani A, et al. Mirror therapy as an alternative treatment for phantom limb pain: a short literature review. Korean J Pain. 2013;26(3):309-311.
[10] Cacchio A, De Blasis E, De Blasis V, et al. Mirror therapy in complex regional pain syndrome type 1 of the upper limb in stroke patients. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009;23(8): 792-799.
[11] Selles RW, Schreuders TA, Stam HJ. Mirror therapy in patients with causalgia (complex regional pain syndrome type II) following peripheral nerve injury: two cases. J Rehabil Med. 2008;40(4):312-314.
[12] Sato K, Fukumori S, Matsusaki T, et al. Nonimmersive virtual reality mirror visual feedback therapy and its application for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: an open-label pilot study. Pain Med. 2010;11(4):622-629.
[13] 郝又国,陆伟伟,施海燕,等.心理康复介入时机对脊柱骨折所致脊髓损伤患者的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2013,19(8): 768-770.
[14] Ekim A, Arma?an O, Oner C. Efficiency of TENS treatment in hemiplegic shoulder pain: a placebo controlled study. Agri. 2008;20(1):41-46.
[15] Moniruzzaman M, Salek KM, Shakoor MA, et al. Effects of therapeutic modalities on patients with post stroke shoulder pain. Mymensingh Med J. 2010;19(1):48-53.
[16] 唐朝正,贾杰. 经皮电神经刺激在脑卒中后上肢功能障碍中的应用[J].中国康复理论与实践,2014,20(4):306-310.
[17] Price CI, Pandyan AD. Electrical stimulation for preventing and treating post-stroke shoulder pain: a systematic Cochrane review. Clin Rehabil. 2001;15(1):5-19.
[18] Anandkumar S, Manivasagam M. Multimodal physical therapy management of a 48-year-old female with post-stroke complex regional pain syndrome. Physiother Theory Pract. 2014;30(1):38-48.
[19] Vladimir Tichelaar YI, Geertzen JH, Keizer D, et al. Mirror box therapy added to cognitive behavioural therapy in three chronic complex regional pain syndrome type I patients: a pilot study. Int J Rehabil Res. 2007;30(2):181-188.
[20] 陆慧红,李桂凤,白浪.全膝关节置换后局部浸润的持续镇痛效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(4):529-534.
[21] Cossins L, Okell RW, Cameron H, et al. Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome in adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials published from June 2000 to February 2012. Eur J Pain. 2013;17(2):158-173.
[22] Ramachandran VS, Altschuler EL. The use of visual feedback, in particular mirror visual feedback, in restoring brain function. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 7):1693-1710.
[23] Ramachandran VS, Brang D, McGeoch PD. Size reduction using Mirror Visual Feedback (MVF) reduces phantom pain. Neurocase. 2009;15(5):357-360.
[24] Harris AJ. Cortical origin of pathological pain. Lancet. 1999; 354(9188):1464-1466.
[25] Maihöfner C, Baron R, DeCol R, et al. The motor system shows adaptive changes in complex regional pain syndrome. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 10):2671-2687.
[26] Maihöfner C, Handwerker HO, Neundörfer B, et al. Cortical reorganization during recovery from complex regional pain syndrome. Neurology. 2004;63(4):693-701.
[27] Pleger B, Ragert P, Schwenkreis P, et al. Patterns of cortical reorganization parallel impaired tactile discrimination and pain intensity in complex regional pain syndrome. Neuroimage. 2006;32(2):503-510.
[28] Maihöfner C, Handwerker HO, Neundörfer B, et al. Patterns of cortical reorganization in complex regional pain syndrome. Neurology. 2003;61(12):1707-1715.
[29] Giraux P, Sirigu A. Illusory movements of the paralyzed limb restore motor cortex activity. Neuroimage. 2003;20 Suppl 1:S107-111.
[30] Breuer AJ, Mainka T, Hansel N, et al. Short-term treatment with parecoxib for complex regional pain syndrome: a randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind trial. Pain Physician. 2014;17(2):127-137. |