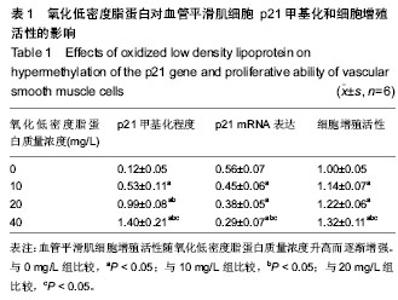
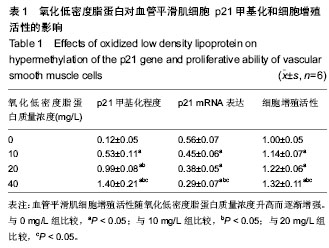
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (38): 6074-6078.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.38.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of methylation of p21 gene in the proliferation of human vascular smooth muscle cells
Hou Xiao-fei1, Sun Xiao-jian2
- 1Clinical Laboratory, 2Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Yuhuangding Hospital, Qingdao University Medical School, Yantai 264000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2014-08-25Online:2014-09-10Published:2014-09-10 -
Contact:Sun Xiao-jian, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Yuhuangding Hospital, Qingdao University Medical School, Yantai 264000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Hou Xiao-fei, Master, Laboratorian in charge, Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Yuhuangding Hospital, Qingdao University Medical School, Yantai 264000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Development Plan of Yantai City, No. 2010148-5
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hou Xiao-fei, Sun Xiao-jian. Role of methylation of p21 gene in the proliferation of human vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(38): 6074-6078.
share this article
| [1] Findeisen HM,Kahles FK,Bruemmer D.Epigenetic regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell function in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep.2013;15(5):319. [2] Alexander MR, Owens GK.Epigenetic control of smooth muscle cell differentiation and phenotypic switching in vascular development and disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 2012; 74:13-40. [3] Wei CY,Chou YH,Ho FM,et al.Signaling pathways of LIGHT induced macrophage migration and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.J Cell Physiol. 2006;209(3):735-743. [4] Beier I,Düsing R,Vetter H,et al.Epidermal growth factor stimulates Rac1 and p21 activated kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells.Atherosclerosis. 2008;196(1):92-97. [5] Sedding DG, Trobs M, Reich F,et al. 3-Deazaadenosine Prevents Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Neointima Formation by Interfering With Ras Signaling. Circ Res. 2009; 104:1192-1200. [6] Kavurma MM, Khachigian LM.Vascular smooth muscle cell-specific regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(WAF1/Cip1) transcription by Sp1 is mediated via distinct cis-acting positive and negative regulatory elements in the proximal p21(WAF1/Cip1) promoter.J Cell Biochem. 2004; 93(5):904-916. [7] Nathe TJ, Deou J, Walsh B,et al.Interleukin-1beta inhibits expression of p21(WAF1/CIP1) and p27(KIP1) and enhances proliferation in response to platelet-derived growth factor-BB in smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002; 22(8):1293-1298. [8] Marra DE, Simoncini T, Liao JK.Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by sodium salicylate mediated by upregulation of p21(Waf1) and p27(Kip1). Circulation. 2000; 102(17):2124-2130. [9] Hsieh JK, Kletsas D, Clunn G, et al.p53, p21(WAF1/CIP1), and MDM2 involvement in the proliferation and apoptosis in an in vitro model of conditionally immortalized human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20(4):973-981. [10] Takahashi A, Taniguchi T, Ishikawa Y,et al.Tranilast inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell growth and intimal hyperplasia by induction of p21(waf1/cip1/sdi1) and p53. Circ Res. 1999; 84(5):543-550. [11] Turunen MP, Aavik E, Herttuala S. Epigenetics and atherosclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1790(9): 886-891. [12] Pons D,de Vries FR,van den Elsen PJ, et al.Epigenetic histone acetylation modifiers in vascular remodelling: new targets for therapy in cardiovascular disease.Eur Heart J. 2009;30(3):266-277. [13] Webster AL, Yan MS, Marsden PA.Epigenetics and cardiovascular disease.Can J Cardiol.2013;29(1):46-57. [14] Xu SS, Alam S, Margariti A.Epigenetics in vascular disease - therapeutic potential of new agents. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2014;12(1):77-86. [15] Napoli C, Crudele V, Soricelli A, et al. Primary prevention of atherosclerosis: a clinical challenge for the reversal of epigenetic mechanisms? Circulation.2012 15;125(19): 2363-2373. [16] Zhang D,Wen X, Wu W, et al.Homocysteine-related hTERT DNA demethylation contributes to shortened leukocyte telomere length in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2013; 231(1):173-179. [17] Zhang K, Zhang R, Li X.Promoter methylation status of p15 and p21 genes in HPP-CFCs of bone marrow of patients with psoriasis. Eur J Dermatol.2009;19(2):141-146. [18] Connelly JJ, Cherepanova OA, Doss JF,et al.Epigenetic regulation of COL15A1 in smooth muscle cell replicative aging and atherosclerosis.Hum Mol Genet.2013;22(25): 5107-5120. [19] Kumar A, Kumar S, Vikram A, et al. Histone and DNA methylation-mediated epigenetic downregulation of endothelial Kruppel-like factor 2 by low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2013;33(8): 1936-1942. [20] Jia L, Zhu L, Wang JZ, et al.Methylation of FOXP3 in regulatory T cells is related to the severity of coronary artery disease.Atherosclerosis.2013;228(2):346-352. [21] Guay SP,Brisson D, Lamarche B,et al.DNA methylation variations at CETP and LPL gene promoter loci: new molecular biomarkers associated with blood lipid profile variability.Atherosclerosis.2013;228(2):413-420. [22] Lund G, Andersson L, Lauria M,et al. DNA methylation polymorphisms precede any histological sign of atherosclerosis in mice lacking apolipoprotein E.J Biol Chem. 2004;279(28):29147-29154. [23] Hiltunen MO, Turunen MP, Häkkinen TP,et al. DNA hypomethylation and methyltransferase expression in atherosclerotic lesions.Vasc Med. 2002;7(1):5-11. [24] Newman PE. Can reduced folic acid and vitamin B12 levels cause deficient DNA methylation producing mutations which initiate atherosclerosis? Med Hypotheses. 1999;53(5):421- 424. [25] Thaler R,Agsten M,Spitzer S,et al.Homocysteine suppresses the expression of the collagen cross-linker lysyl oxidase involving IL-6, Fli1, and epigenetic DNA methylation. J Biol Chem.2011 18;286(7):5578-5588. [26] Silvio Z, Marie WL,Gertrud L,et al.Nutrition and Aberrant DNA Methylation Patterns in Atherosclerosis: More than Just Hyperhomocysteinemia? J Nutr. 2005;135(1): 5-8. [27] Huang Y,Zhi Y,Wang S.Hypermethylation of estrogen receptor-α gene in atheromatosis patients and its correlation with homocysteine. Pathophysiology. 2009;16:259-265. [28] Kim J, Kim JY, Song KS,et al. Epigenetic changes in estrogen receptor beta gene in atherosclerotic cardiovascular tissues and in-vitro vascular senescence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007; 1772(1):72-80. [29] Post WS, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, Wilhide CC,et al. Methylation of the estrogen receptor gene is associated with aging and atherosclerosis in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res. 1999;43(4):985-991. [30] Ying AK, Hassanain HH, Roos CM,et al. Methylation of the estrogen receptor-alpha gene promoter is selectively increased in proliferating human aortic smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res.2000;46(1):172-179. [31] Hiltunen MO, Ylä-Herttuala S.DNA methylation, smooth muscle cells, and atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2003 ;23(10):1750-1753. [32] Huang Y, Peng K, Su J,et al. Different effects of homocysteine and oxidized low density lipoprotein on methylation status in the promoter region of the estrogen receptor alpha gene. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2007;39(1):19-26. [33] Yang HP. P53 in atherosclerotic plaques.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1993;73(11):674-676. [34] Mayr U, Mayr M, Li C, et al.Loss of p53 accelerates neointimal lesions of vein bypass grafts in mice . Circ Res. 2002;90(2):197-204. [35] Mercer J,Figg N,Stoneman V,et al.Endogenous p53 protects vascular smooth muscle cells from apoptosis and reduces atherosclerosis in ApoE knockout mice. Circ Res.2005,96(6): 667-674. [36] 智艳芳,黄彦生,李著华,等.动脉粥样硬化病人LDL受体基因启动子序列的高甲基化改变[J].分子细胞生物学报,2007,40(6): 419-427. [37] 宋福津,陈端霞,杨堤,等.抗氧化维生素减轻高脂饮食兔动脉粥样硬化及保护DNA甲基化的作用[J].中华心血管病杂志, 1998, 26(4):302-304. [38] Zaina S, Døssing KB, Lindholm MW, et al. Chromatin modification by lipids and lipoprotein components: an initiating event in atherogenesis? Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005;16(5): 549-553. [39] Mitra S, Khaidakov M, Lu J, et al.Prior exposure to oxidized low-density lipoprotein limits apoptosis in subsequent generations of endothelial cells by altering promoter methylation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301(2): H506-13. [40] Jia L, Zhu L, Wang JZ,et al.Methylation of FOXP3 in regulatory T cells is related to the severity of coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2013;228(2):346-352 |
| [1] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [2] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [3] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [4] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [5] | Ma Zhijie, Li Jingyu, Cao Fang, Liu Rong, Zhao Dewei. Influencing factors and biological property of novel biomedical materials: porous silicon carbide coated with bioactive tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 558-563. |
| [6] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [8] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [9] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [10] | Li Xinping, Cui Qiuju, Zeng Shuguang, Ran Gaoying, Zhang Zhaoqiang, Liu Xianwen, Fang Wei, Xu Shuaimei. Effect of modification of β-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan hydrogel on growth and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| [11] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [12] | Chen Song, He Yuanli, Xie Wenjia, Zhong Linna, Wang Jian. Advantages of calcium phosphate nanoparticles for drug delivery in bone tissue engineering research and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3565-3570. |
| [13] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Sun Changliang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Epigenetic reprogramming and exercise regulation of bone metabolism disorders [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3210-3218. |
| [14] | Liu Kun, Xie Lin, Cao Jun, Ding Ning, Xu Lingbo, Ma Shengchao, Li Guizhong , Jiang Yideng, Lu Guanjun. Increased FoxO1 DNA methylation level in homocysteine-induced podocyte apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 269-273. |
| [15] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||