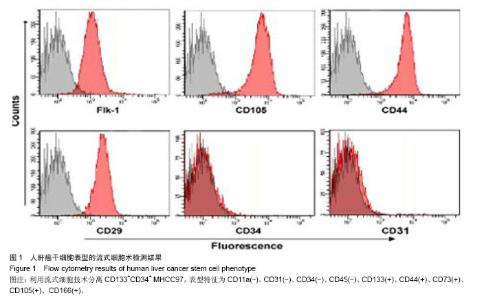
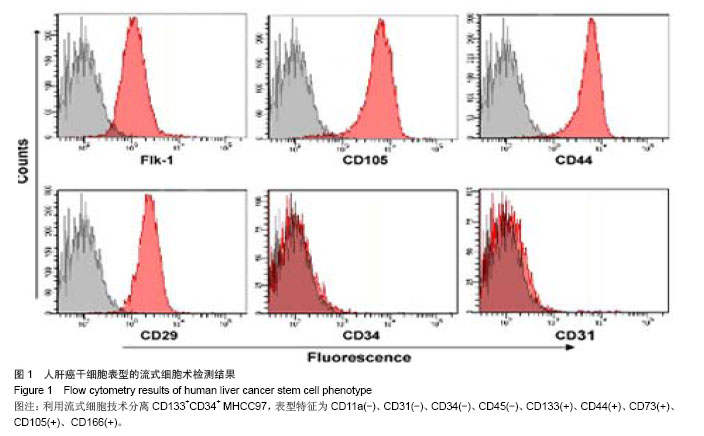
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (28): 4549-4554.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.28.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Liver cancer stem cell isolation and biological characteristics
Liu Yan, Zhou Yue-su, He Jing, Liu Peng
- Department of Emergency, the 302 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100039, China
-
Online:2014-07-02Published:2014-07-02 -
Contact:Zhou Yue-su, Department of Emergency, the 302 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100039, China -
About author:Liu Yan, Master, Physician, Department of Emergency, the 302 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100039, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yan, Zhou Yue-su, He Jing, Liu Peng. Liver cancer stem cell isolation and biological characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(28): 4549-4554.
share this article
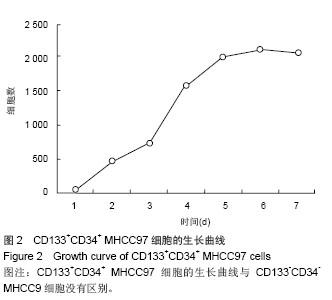
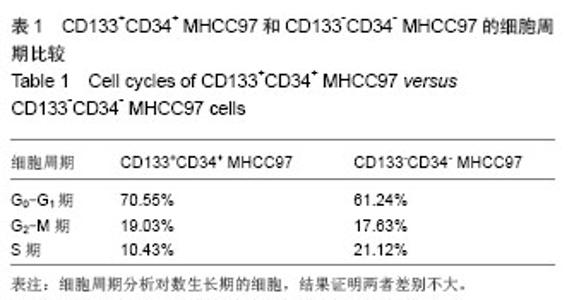
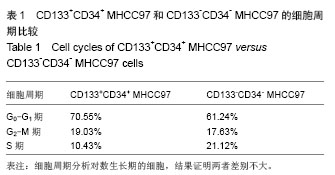
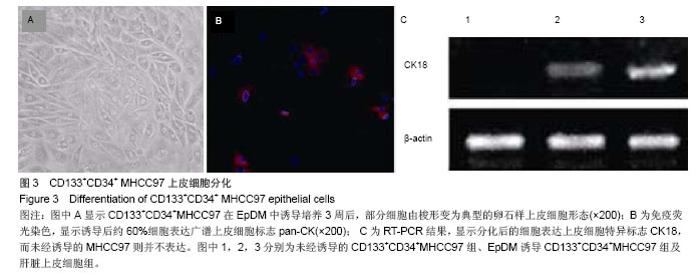
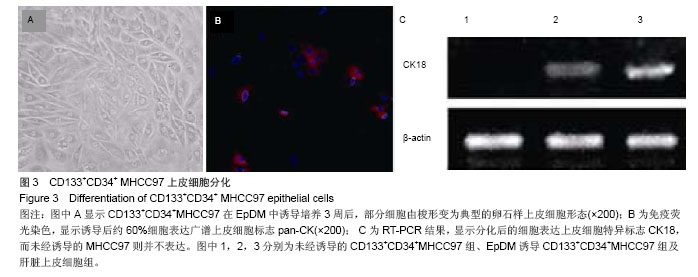
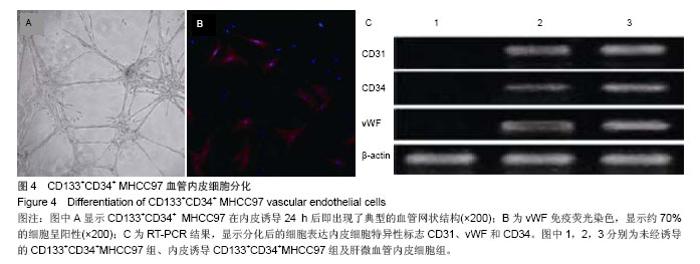
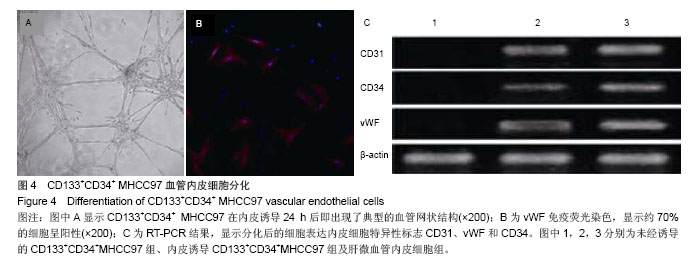
2.2 人肝癌干细胞生长曲线和细胞周期 肿瘤干细胞的特征在于可以逃逸化疗,比较恶性能力的一个指标就是体外扩增和分化能力,本实验证明CD133+CD34+ MHCC97细胞的生长曲线与CD133-CD34-MHCC9细胞没有区别(图2)。 24 h后,去除悬浮细胞,补充培养基,细胞每隔3 d换液1次,待细胞长至70%-80%汇合时,用0.125%胰蛋白 酶+0.01% EDTA消化传代。CD133+CD34+ MHCC97来源的细胞在第6天细胞基本上达到汇合,而CD133-CD34- MHCC97来源的细胞在第9天达到汇合。CD133+CD34+ MHCC97和CD133-CD34- MHCC97的倍增时间分别为 26 h和37 h。细胞周期分析对数生长期的细胞,结果证明两者差别不大,差异无显著性意义(表1)。"
| [1]Gao X, Johnson KD, Chang YI, et al. Gata2 cis-element is required for hematopoietic stem cell generation in the mammalian embryo. J Exp Med. 2013;210(13):2833- 2842.
[2]Wang H, Qiu X, Ni P, et al. Immunological characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and the therapeutic effects of their transplantion on hyperglycemia in diabetic rats. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33(2):263-270.
[3]Parchur AK, Ansari AA, Singh BP, et al. Enhanced luminescence of CaMoO4:Eu by core@shell formation and its hyperthermia study after hybrid formation with Fe3O4: cytotoxicity assessment on human liver cancer cells and mesenchymal stem cells. Integr Biol (Camb). 2013;6(1): 53-64.
[4]Elhefnawi M, Soliman B, Abu-Shahba N, et al. An Integrative Meta-analysis of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2013. pii: S1672-0229 (13)00117-4.
[5]Barone M, Scavo MP, Maiorano E, et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cells and hepatocarcinogenesis in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Dig Liver Dis. 2013. pii: S1590-8658(13)00622-1.
[6]Ng R, Song G, Roll GR, et al. A microRNA-21 surge facilitates rapid cyclin D1 translation and cell cycle progression in mouse liver regeneration. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3): 1097-1108.
[7]Trivedi S, Wiber SC, El-Zimaity HM, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-2 increases dysplasia in rodent models of colon cancer. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;302(8): G840-849.
[8]Du J, Chen Y, Li Q, et al. HIF-1α deletion partially rescues defects of hematopoietic stem cell quiescence caused by Cited2 deficiency. Blood. 2012;119(12):2789-2798.
[9]Newman RG, Ross DB, Barreras H, et al. The allure and peril of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: overcoming immune challenges to improve success. Immunol Res. 2013; 57(1-3):125-139.
[10]Hsu HW, Wall NR, Hsueh CT, et al. Combination antiangiogenic therapy and radiation in head and neck cancers. Oral Oncol. 2014;50(1):19-26.
[11]Saran S, Tran DD, Klebba-Färber S, et al. THOC5, a member of the mRNA export complex, contributes to processing of a subset of wingless/integrated (Wnt) target mRNAs and integrity of the gut epithelial barrier. BMC Cell Biol. 2013; 14(1):51.
[12]Ali N, Allam H, Bader T, et al. Fluvastatin Interferes with Hepatitis C Virus Replication via Microtubule Bundling and a Doublecortin-like Kinase-Mediated Mechanism. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e80304.
[13]Govaert KM, Emmink BL, Nijkamp MW, et al. Hypoxia After Liver Surgery Imposes an Aggressive Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype on Residual Tumor Cells. Ann Surg. 2013. [Epub ahead of print]
[14]Zubeldia IG, Bleau AM, Redrado M, et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotypes leading to liver metastasis are abrogated by the novel TGFβ1-targeting peptides P17 and P144. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(3):12-22.
[15]Malfitano A, Barbaro G, Perretti A, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated malignancies: a therapeutic update. Curr HIV Res. 2012;10(2):123-132.
[16]曹莹.脂肪来源的间充质干细胞的生物学特性以及间充质干细胞在急性肝损伤中治疗机制的研究[D].中国协和医科大学, 2006.
[17]朱希山,施薇,台卫平,等.脂肪与骨髓来源间充质干细胞生物学特性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(32): 5936-5940.
[18]Neumann J, Reu S, Kirchner T. Prognostic marker profiles for risk of distant metastases in colorectal cancer. Pathologe. 2012;33(1):39-44.
[19]Okazaki I, Inagaki Y. Novel strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma based on MMPs science. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012;12(7):753-763.
[20]Nakagawa M, Matsuda M, Masaji H, et al. Successful preoperative diagnosis of biliary cystadenoma with mesenchymal stroma and its characteristic imaging features: report of two cases. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2011;22(6): 631-635.
[21]Nautiyal J, Du J, Yu Y, et al. EGFR regulation of colon cancer stem-like cells during aging and in response to the colonic carcinogen dimethylhydrazine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;302(7):G655-663.
[22]Belton A, Gabrovsky A, Bae YK, et al. HMGA1 induces intestinal polyposis in transgenic mice and drives tumor progression and stem cell properties in colon cancer cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30034. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||